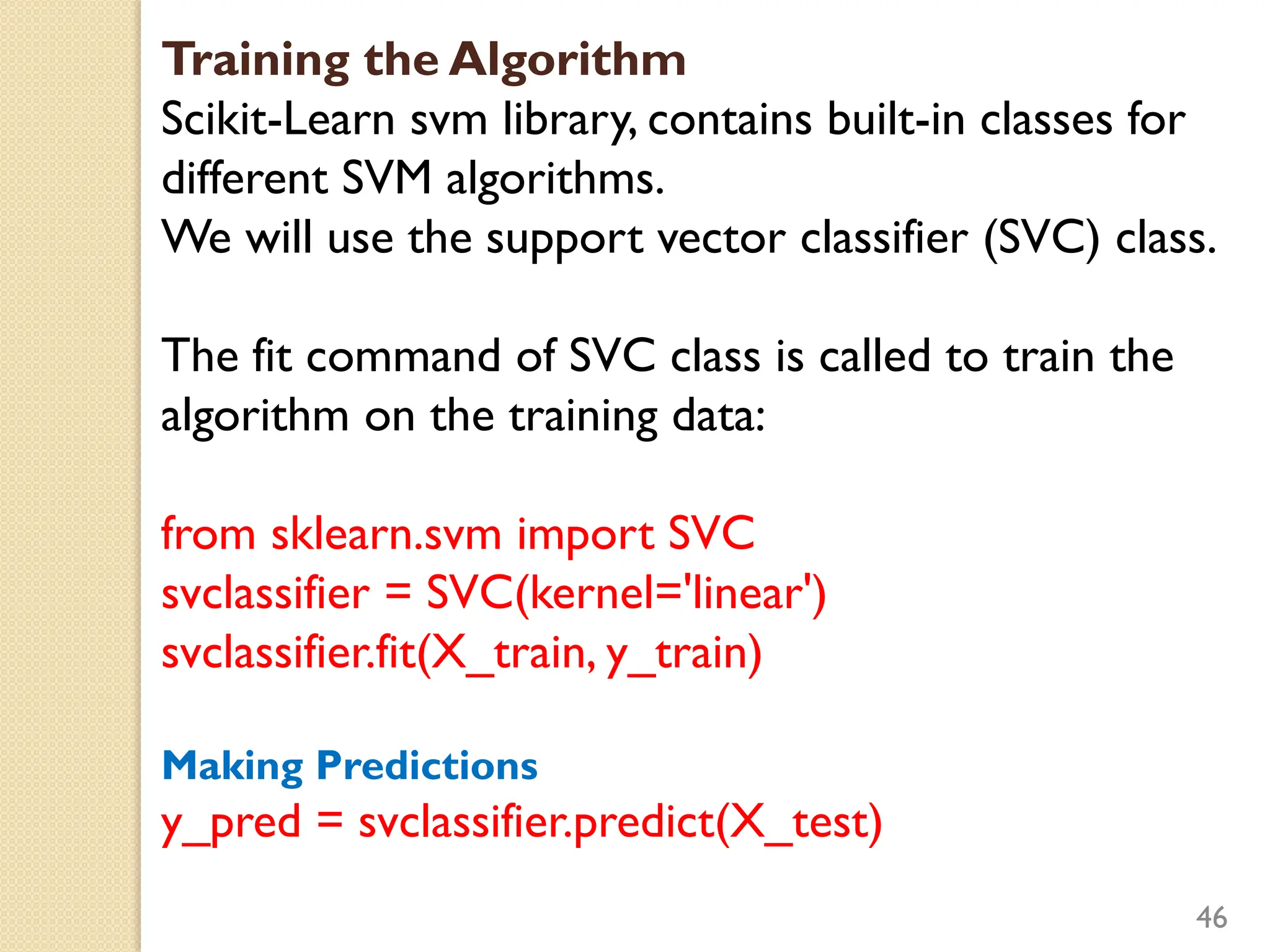
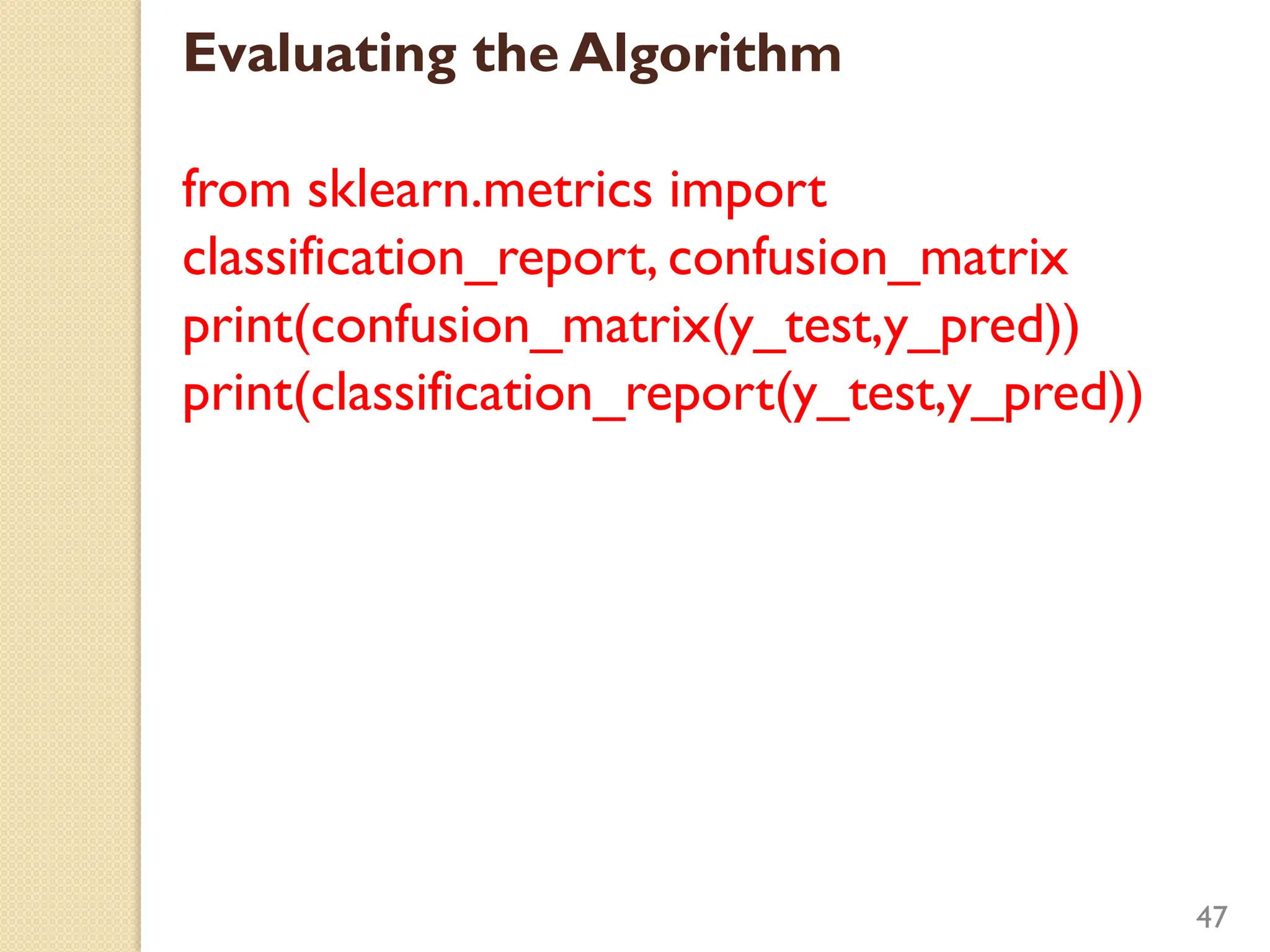
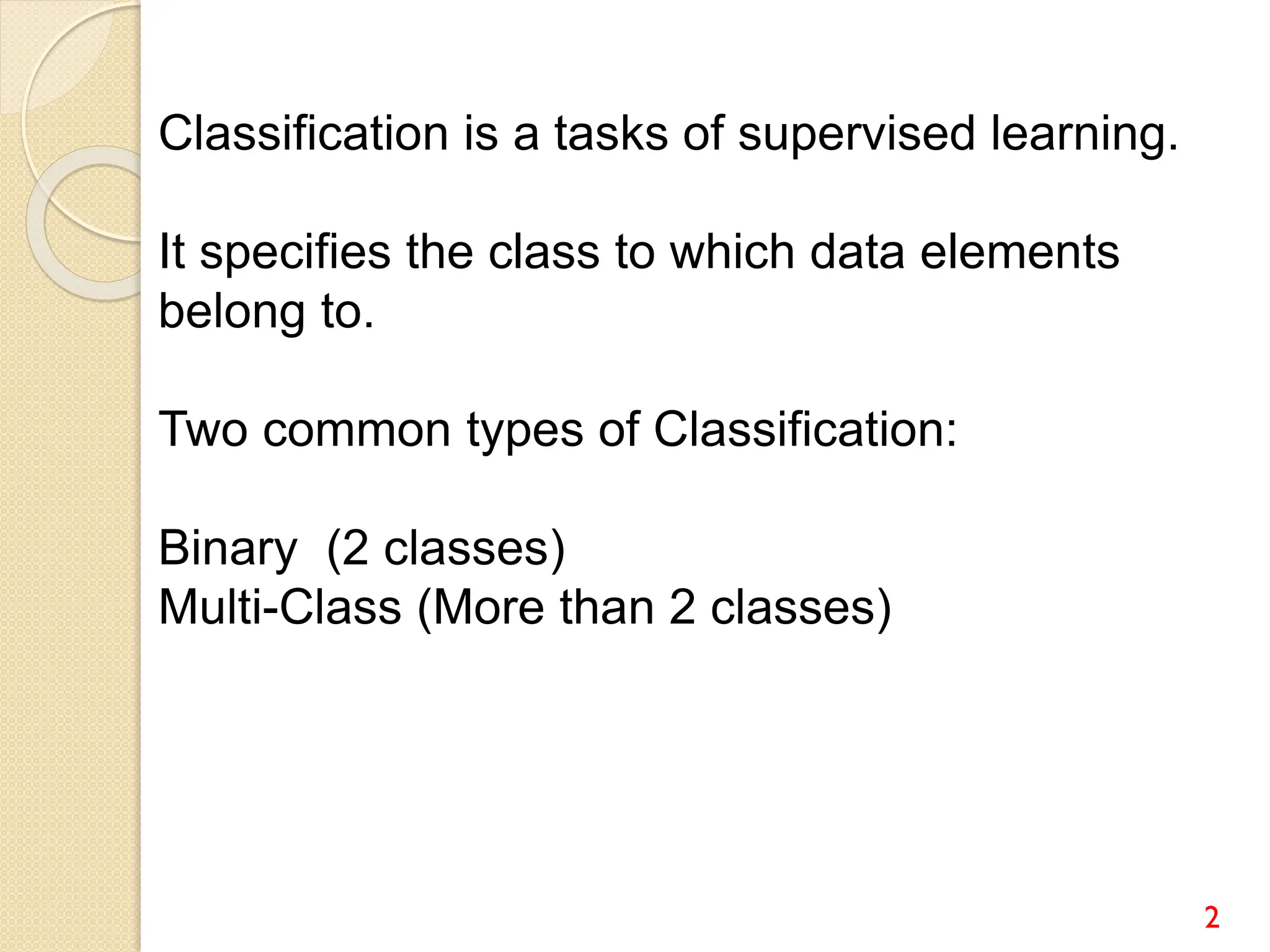
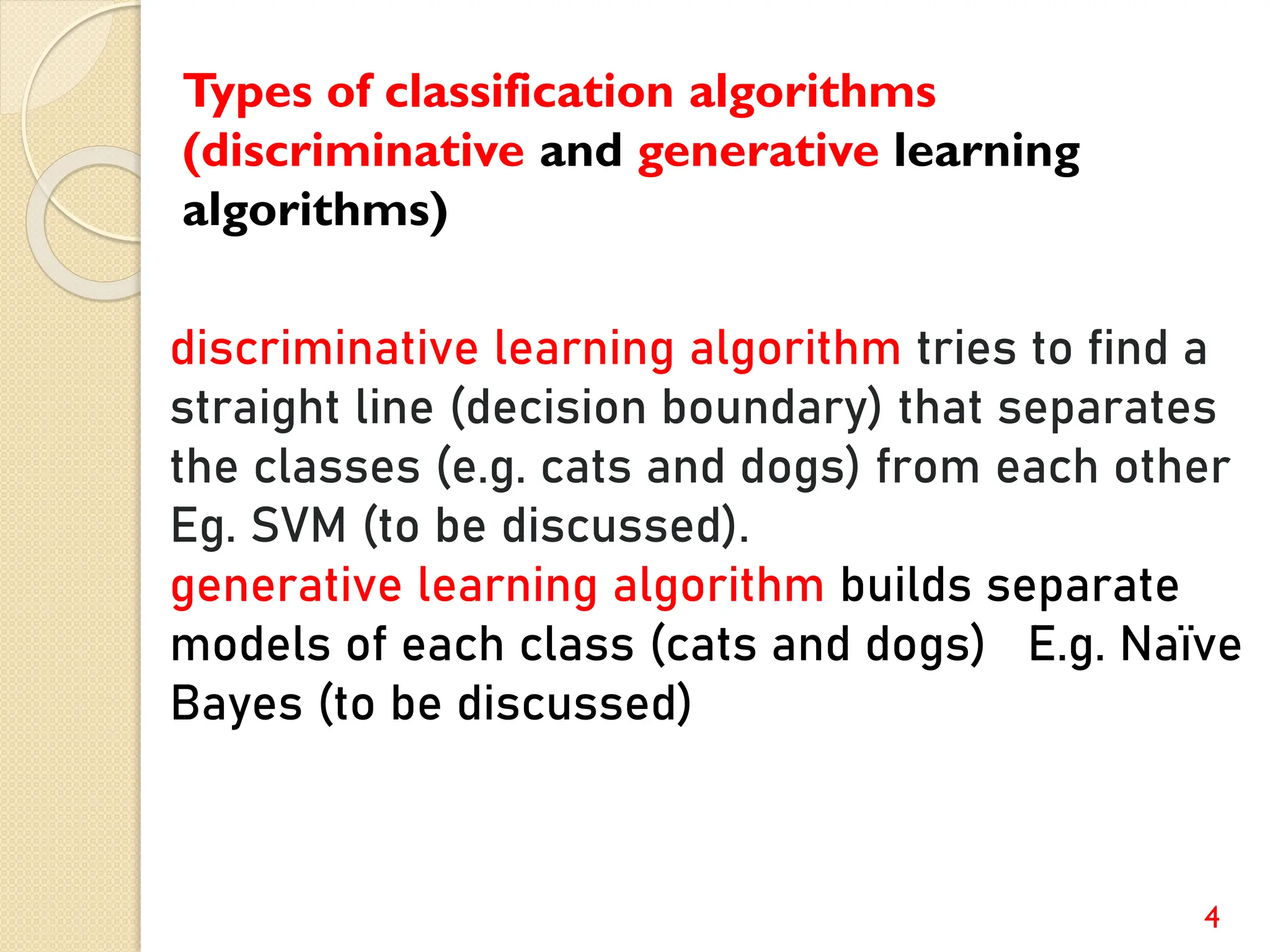
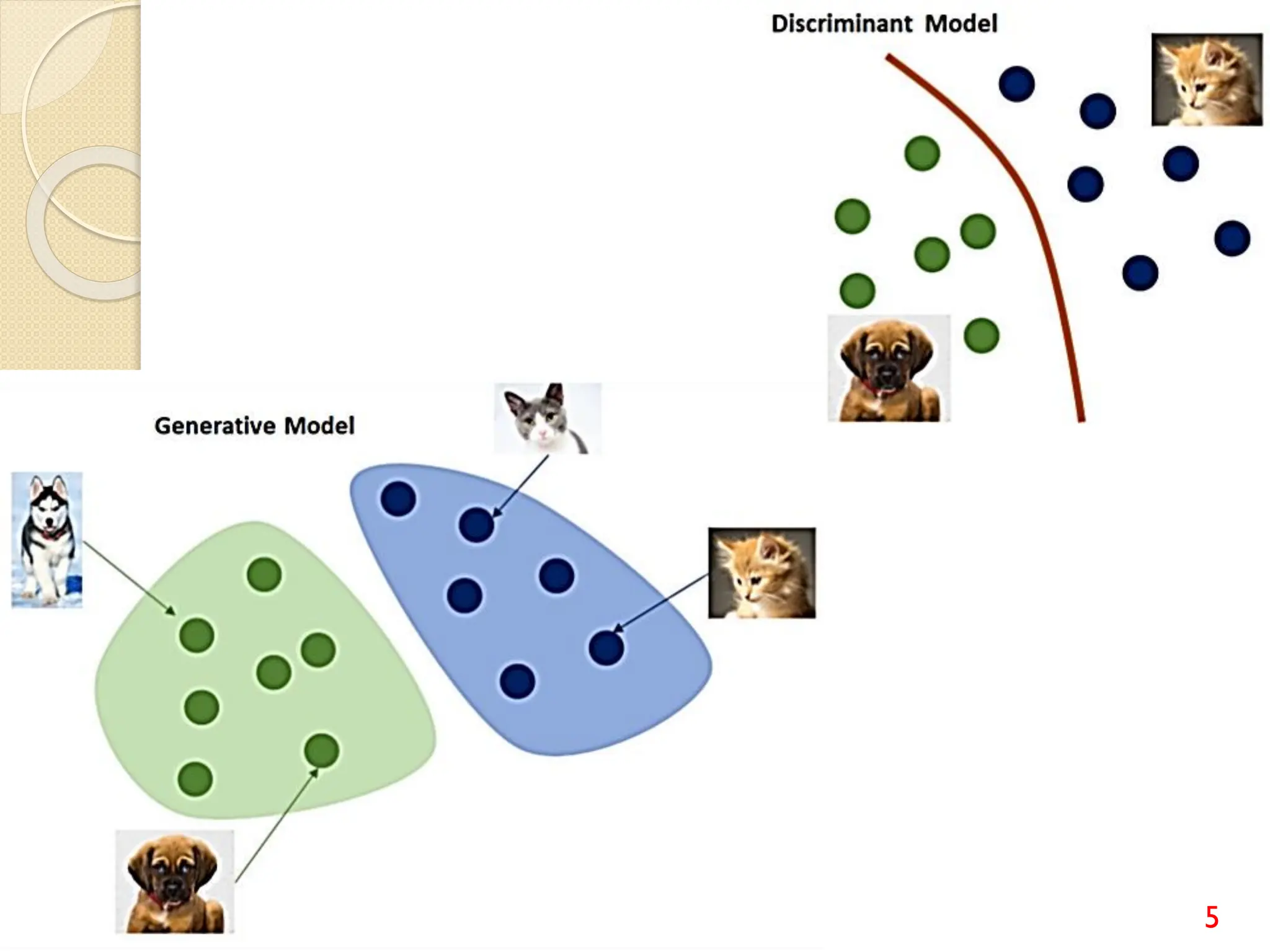
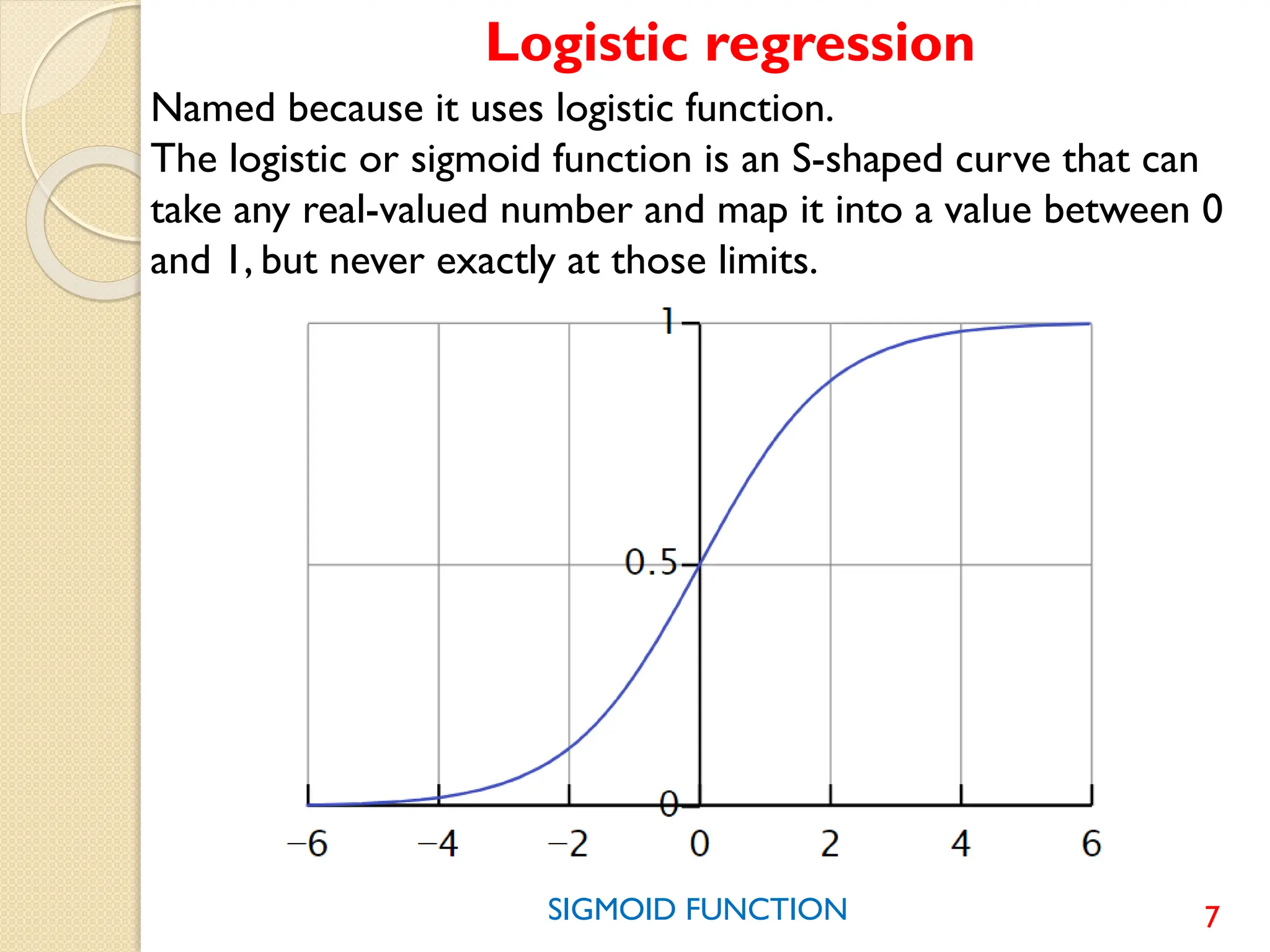
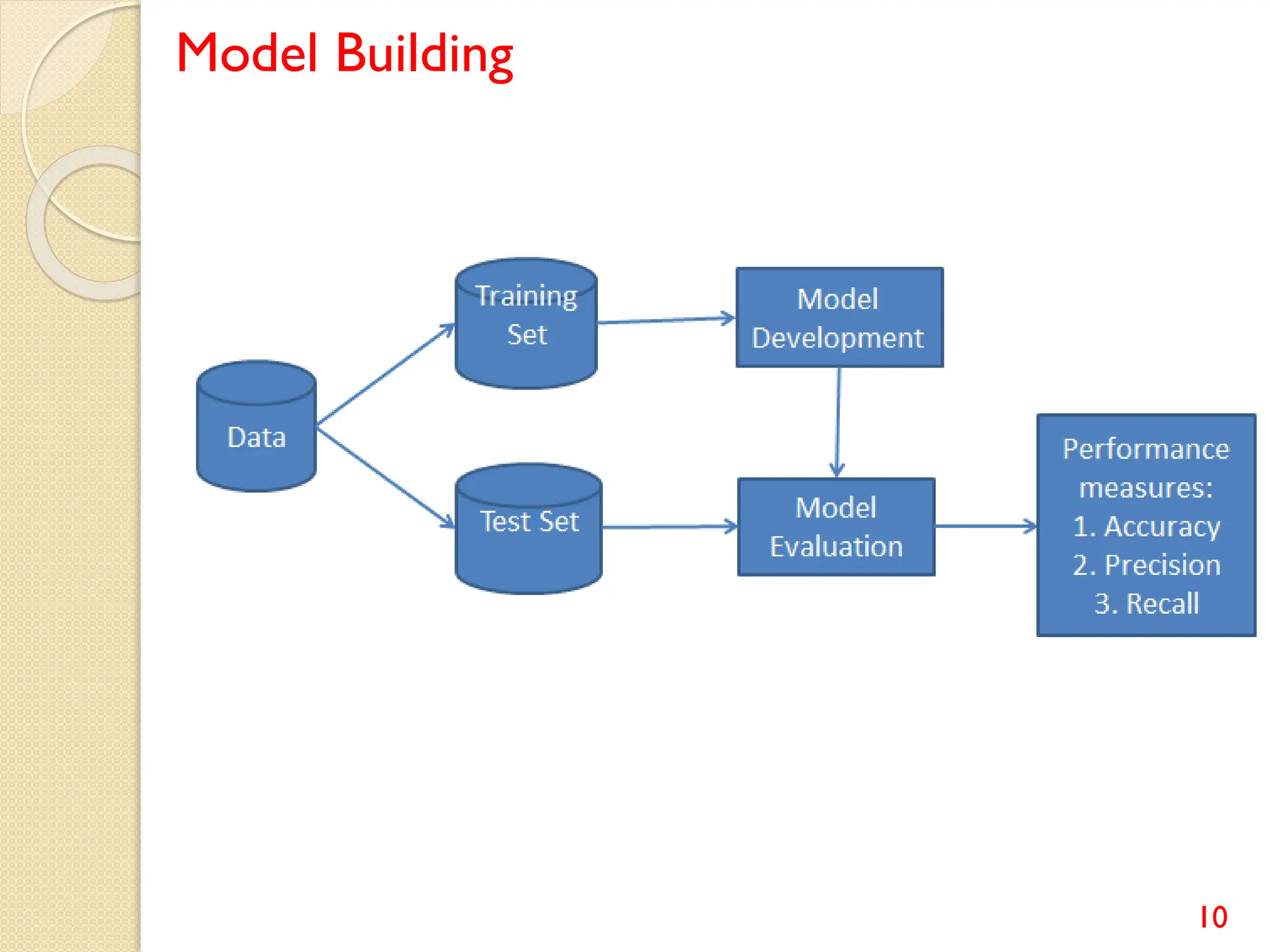
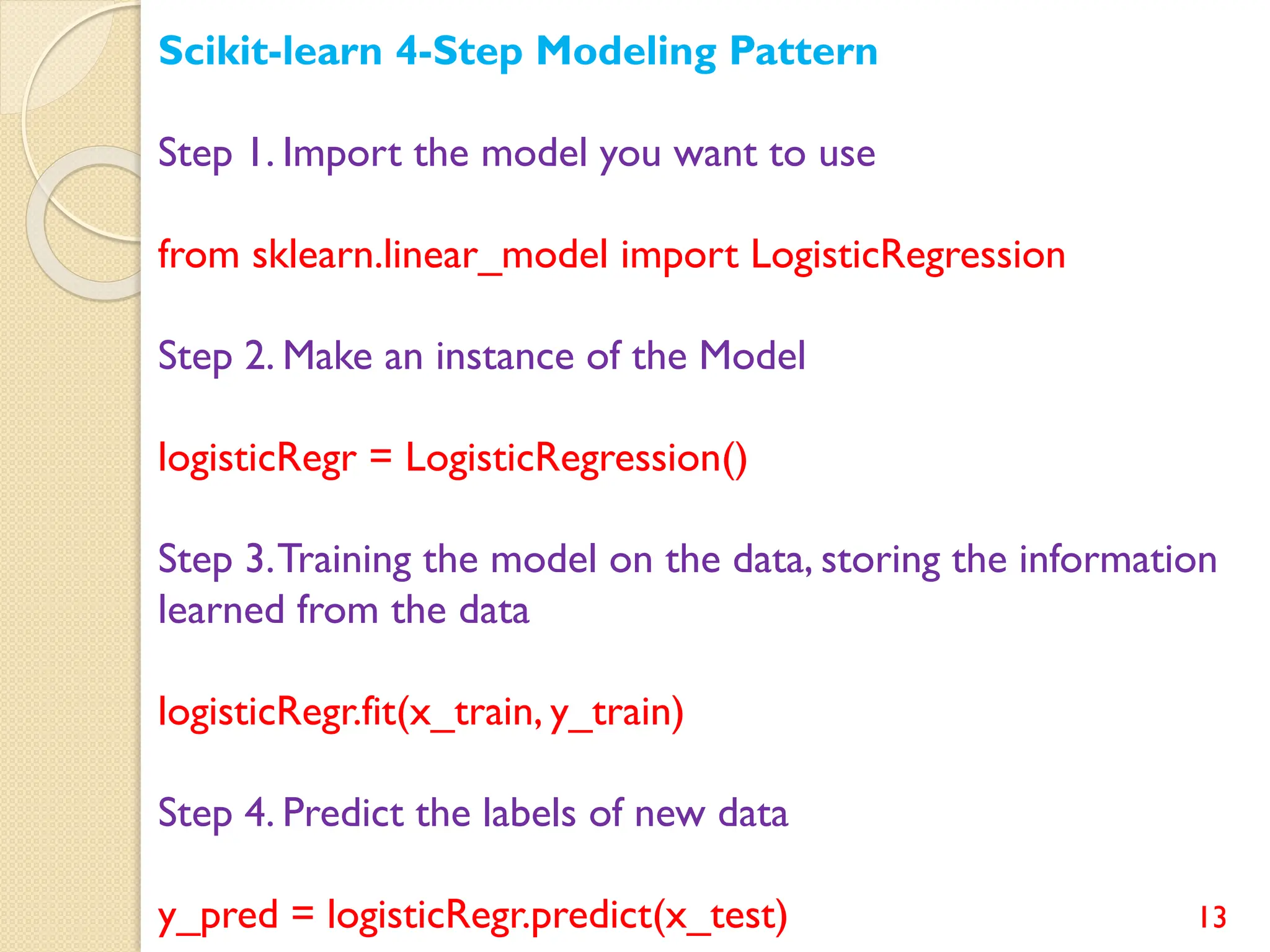
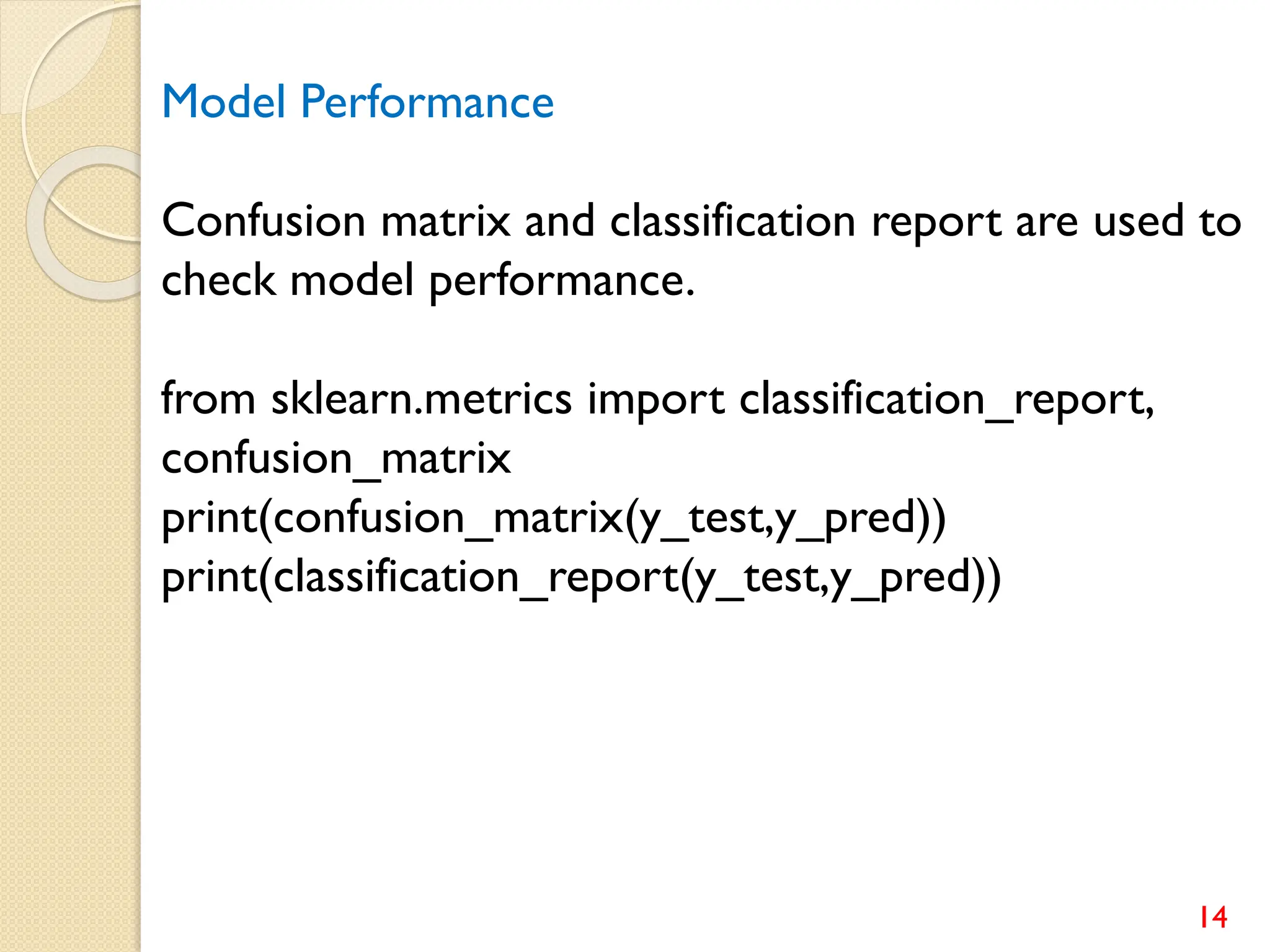
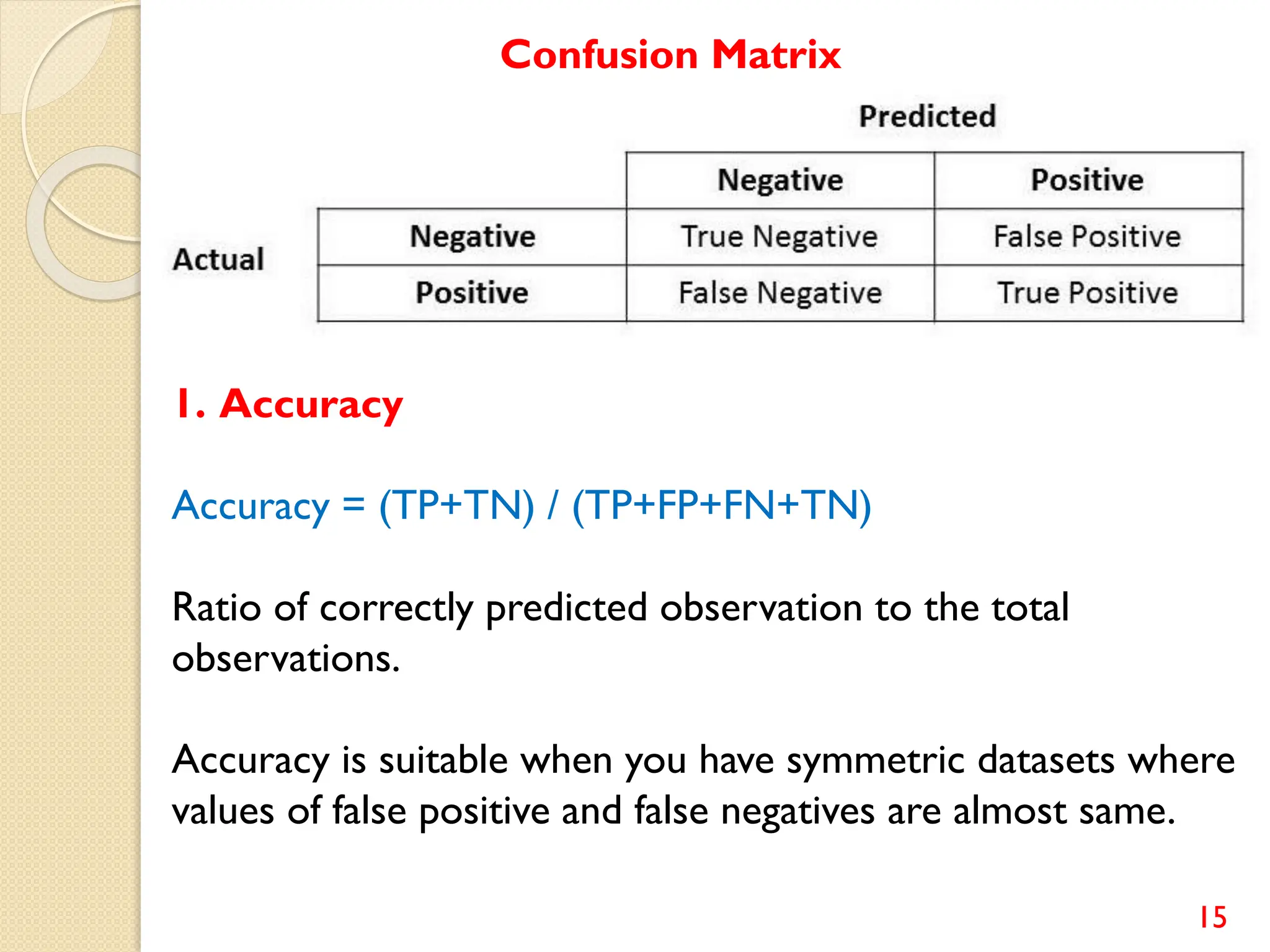
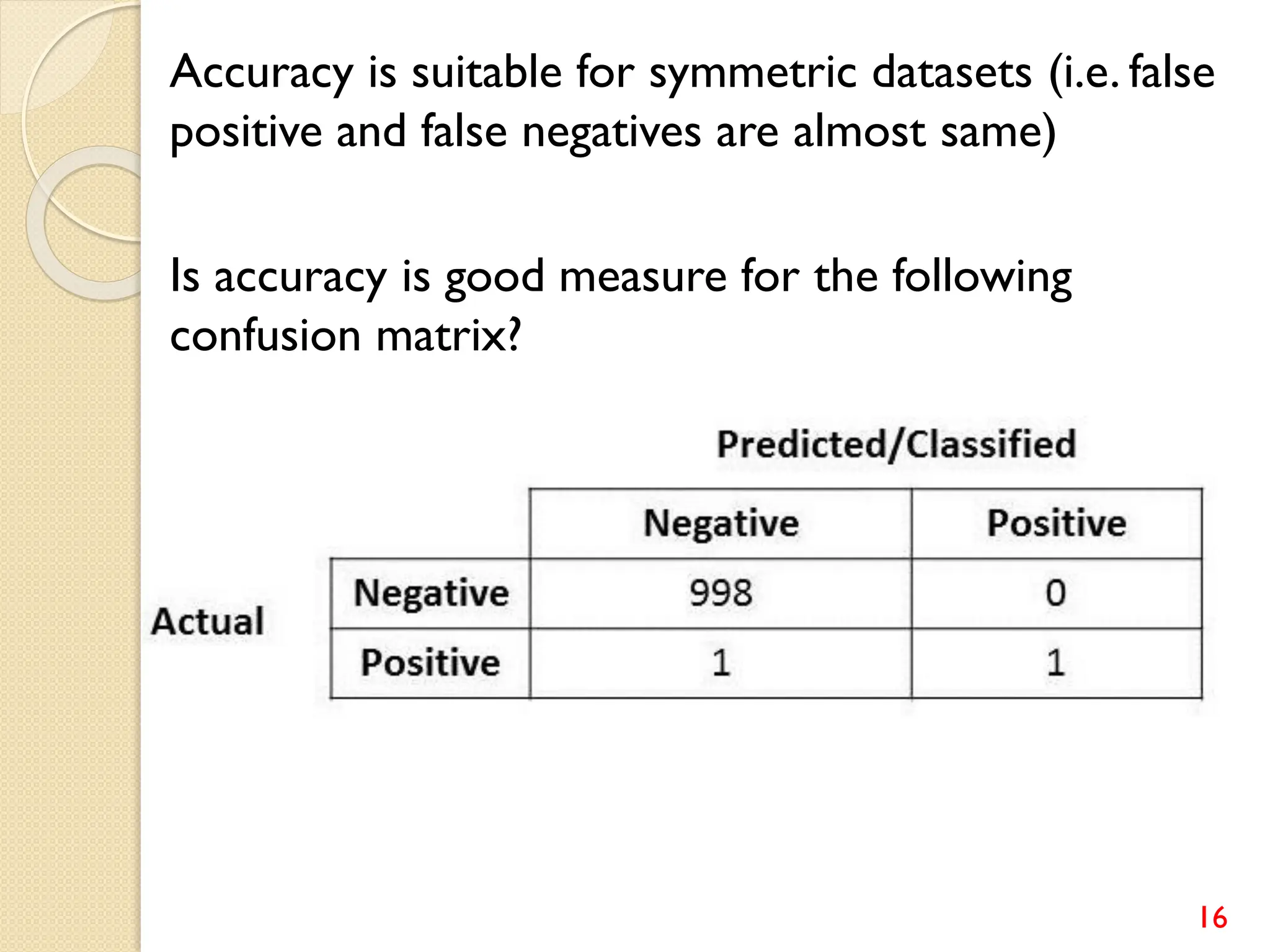
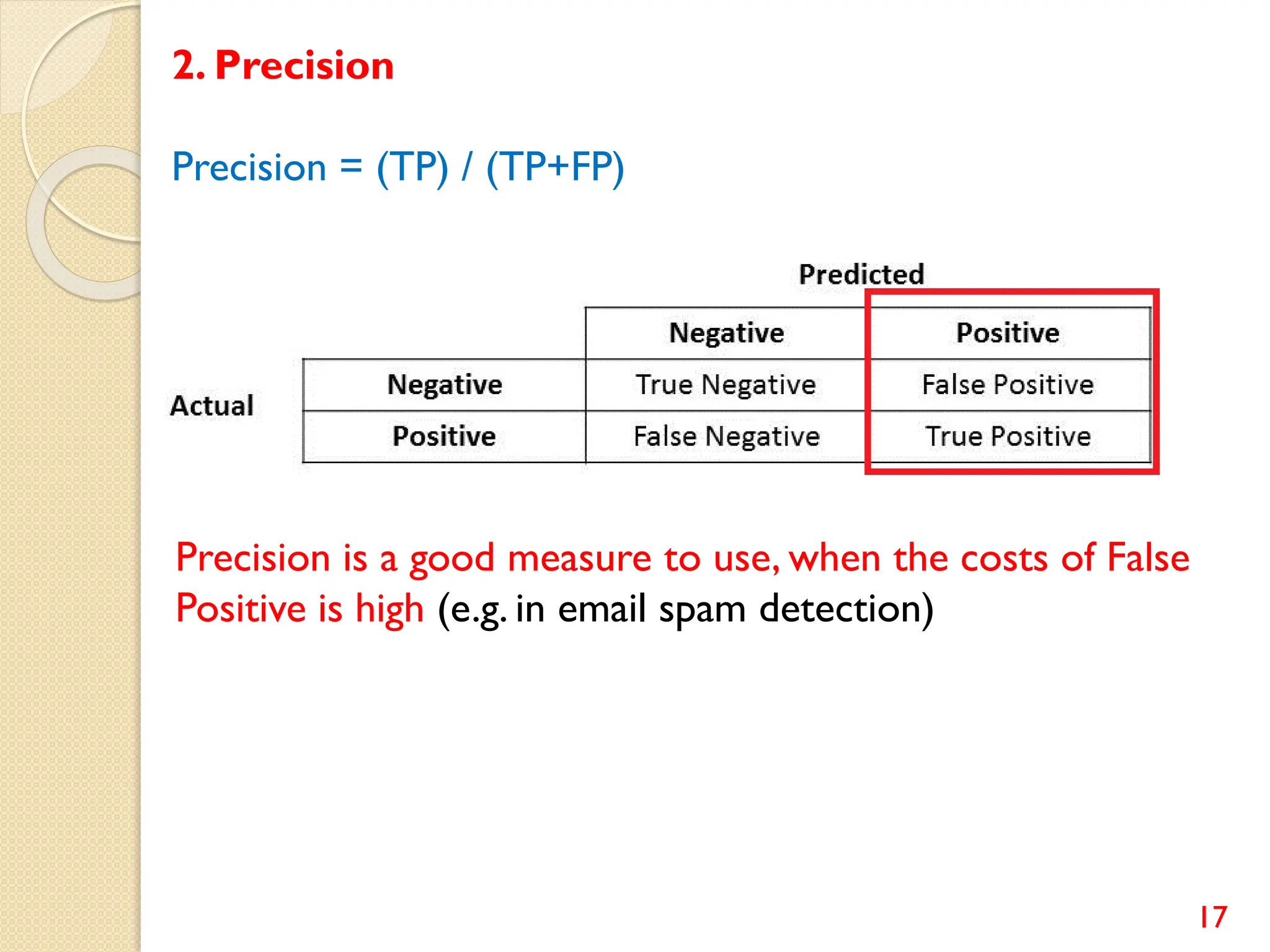
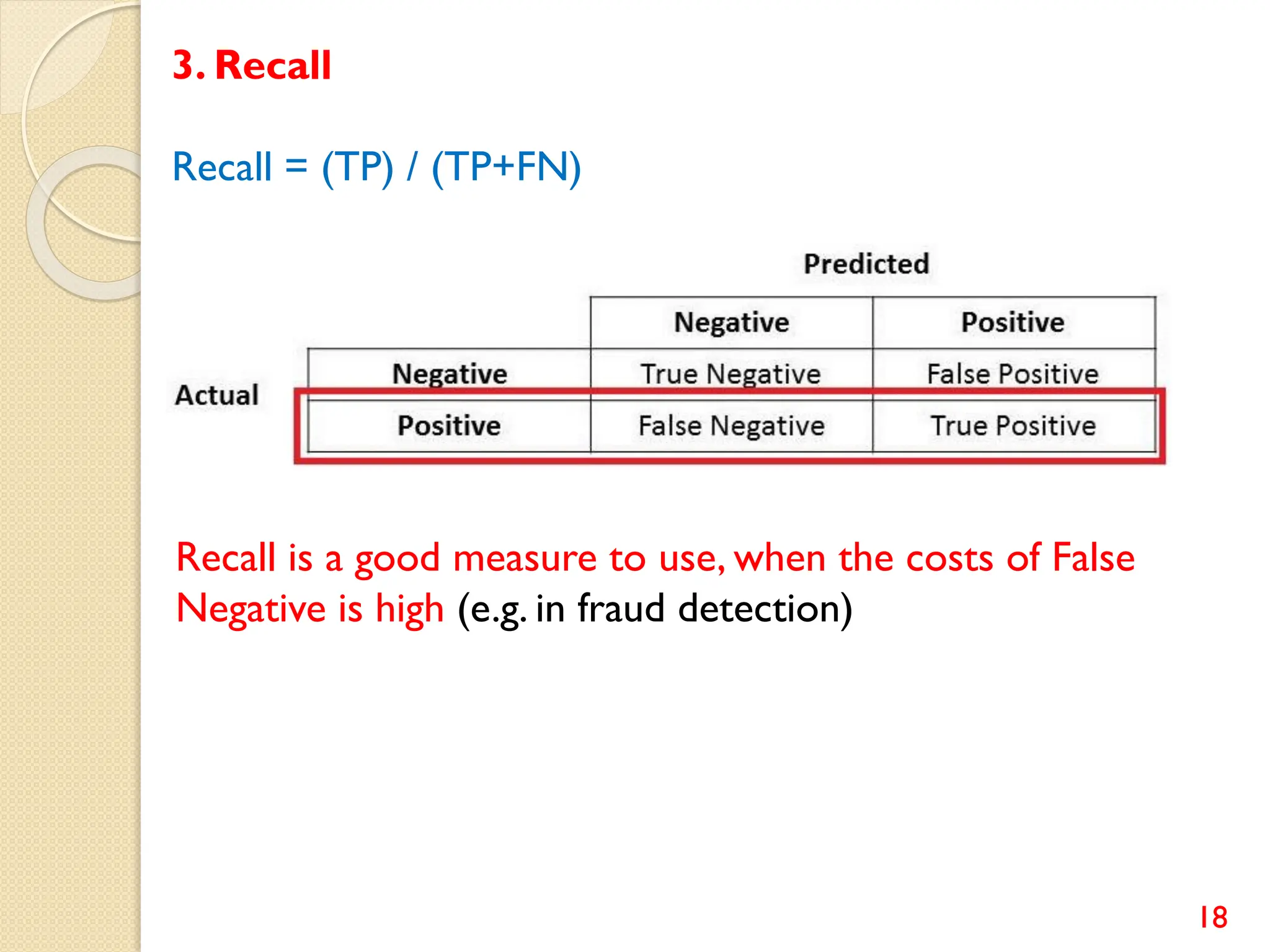
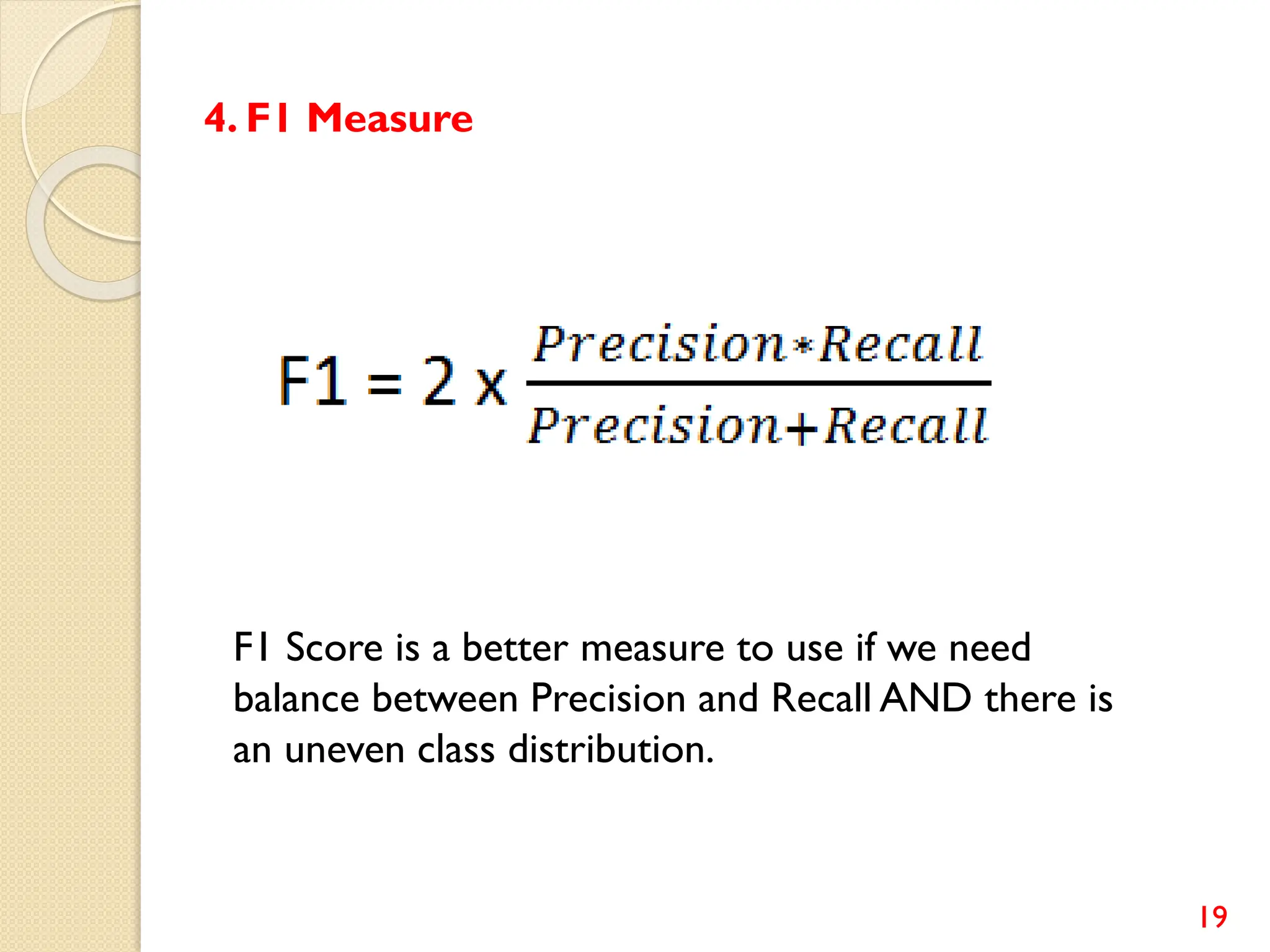
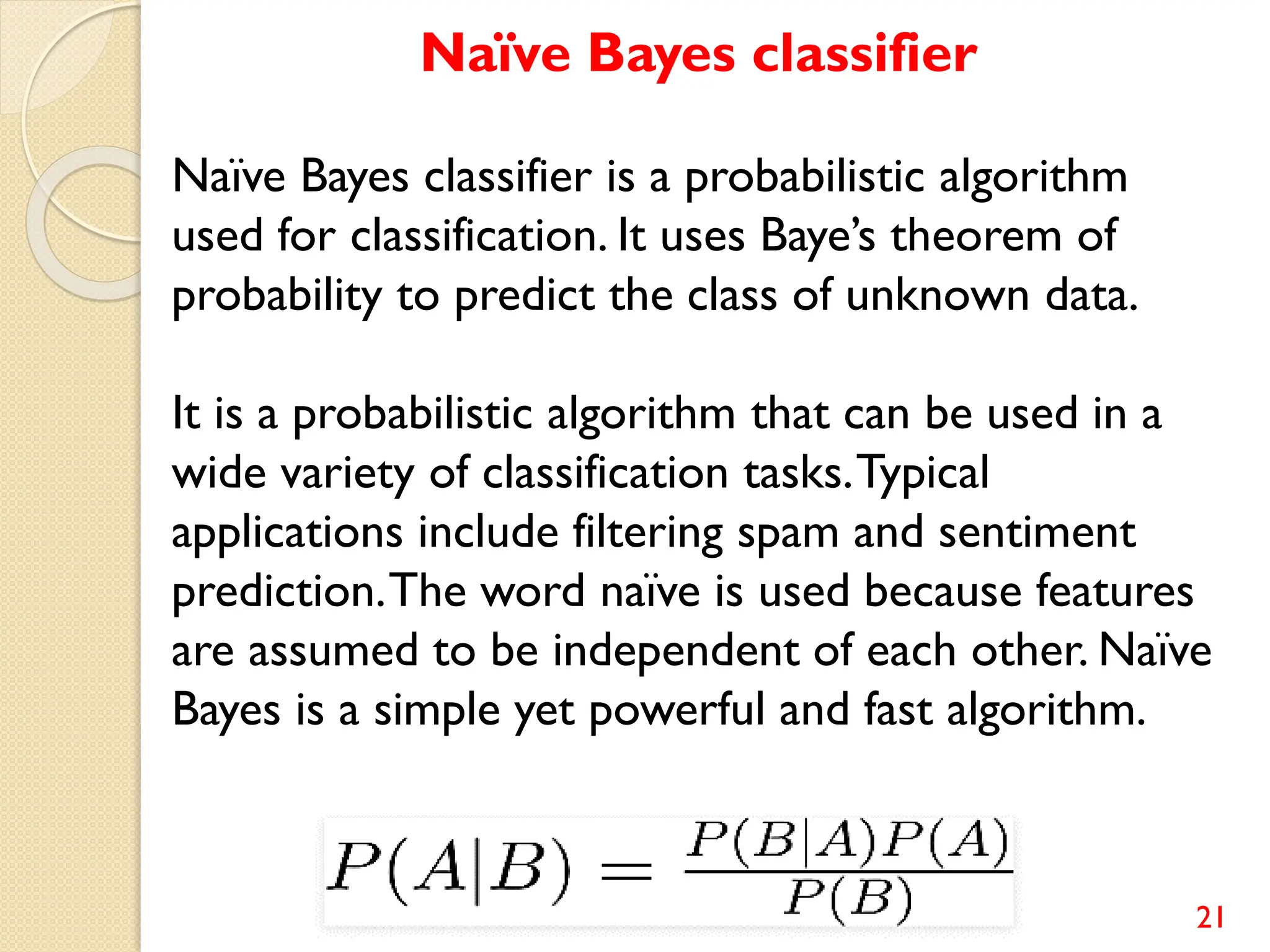
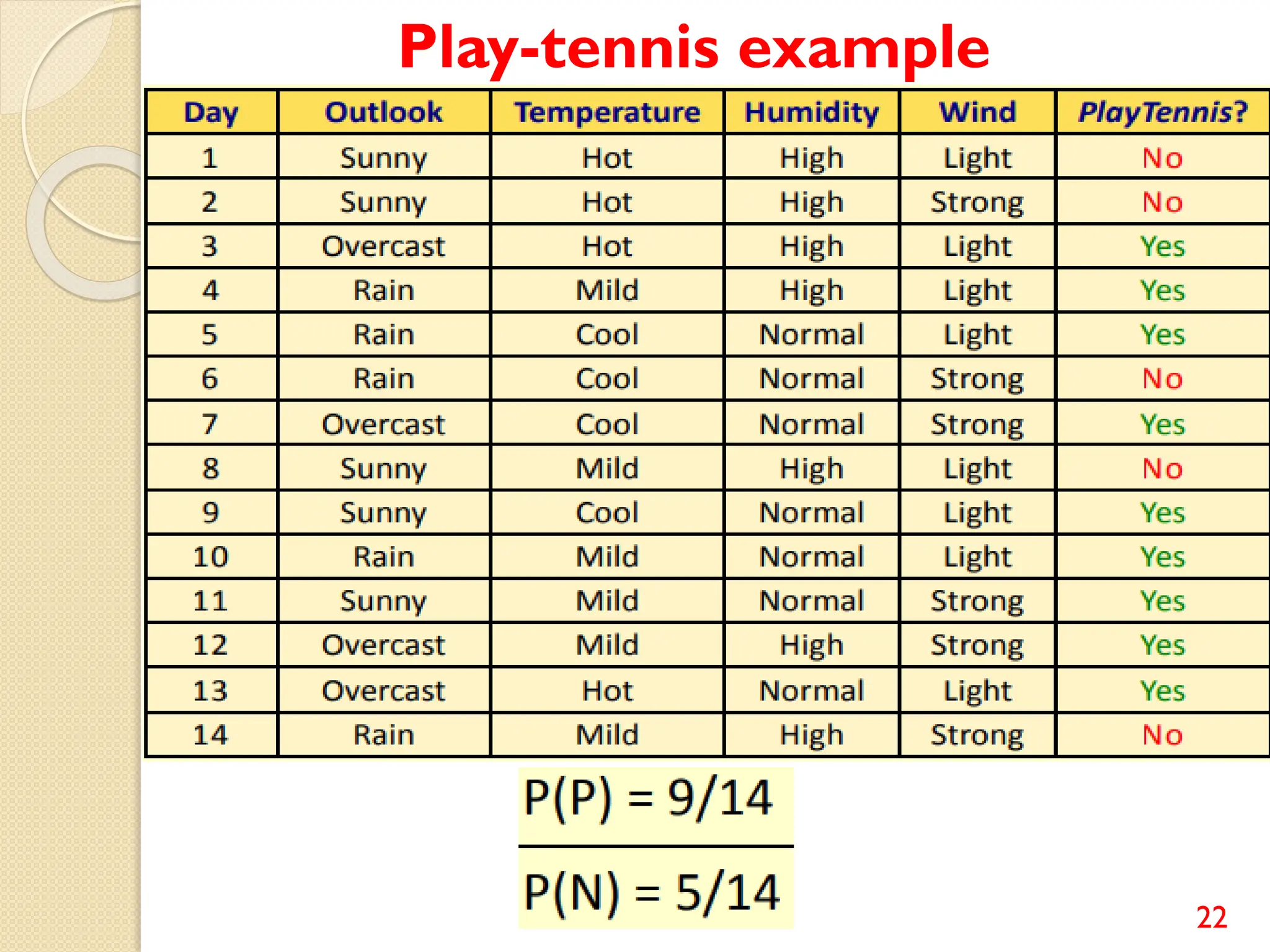
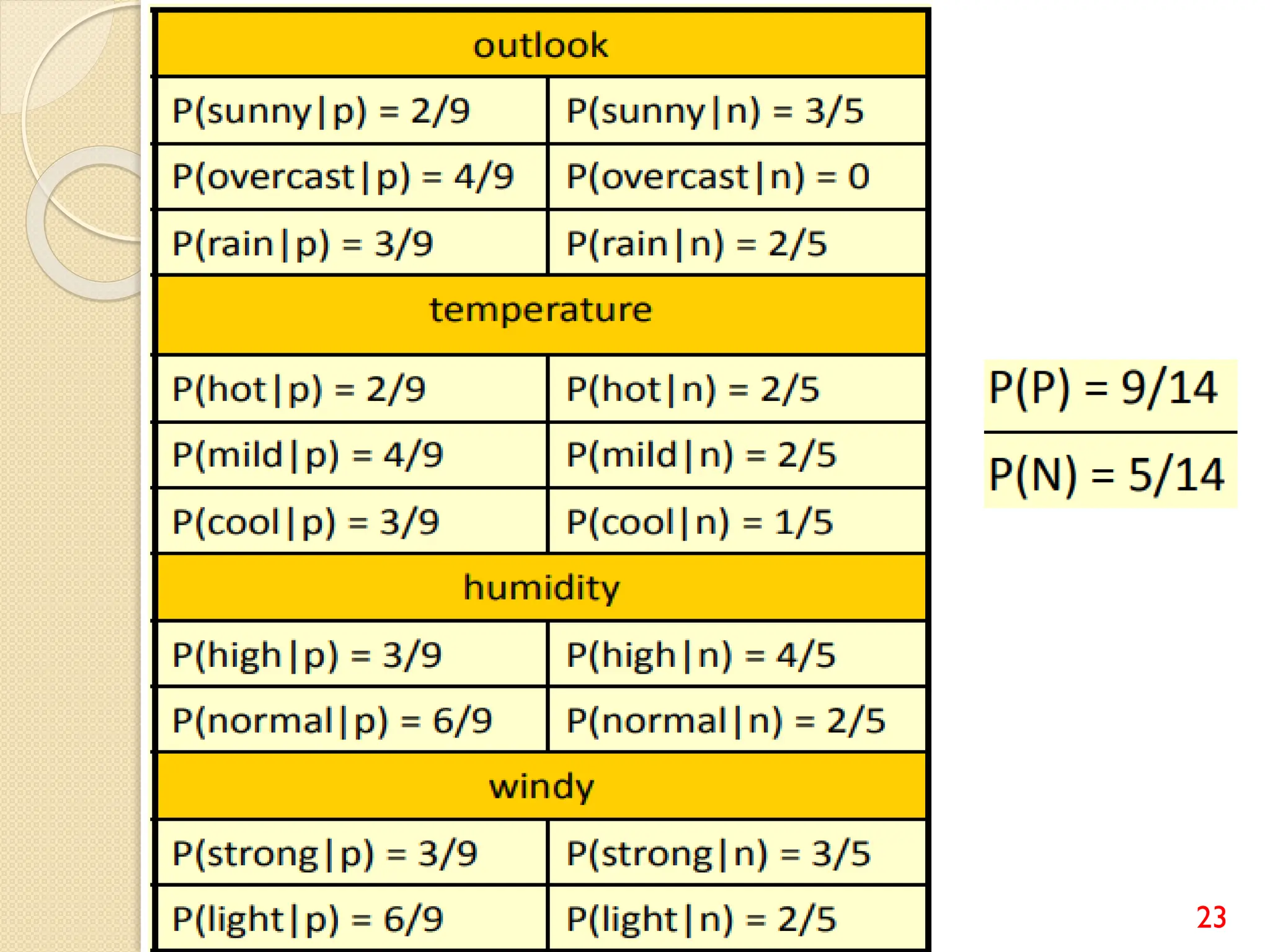
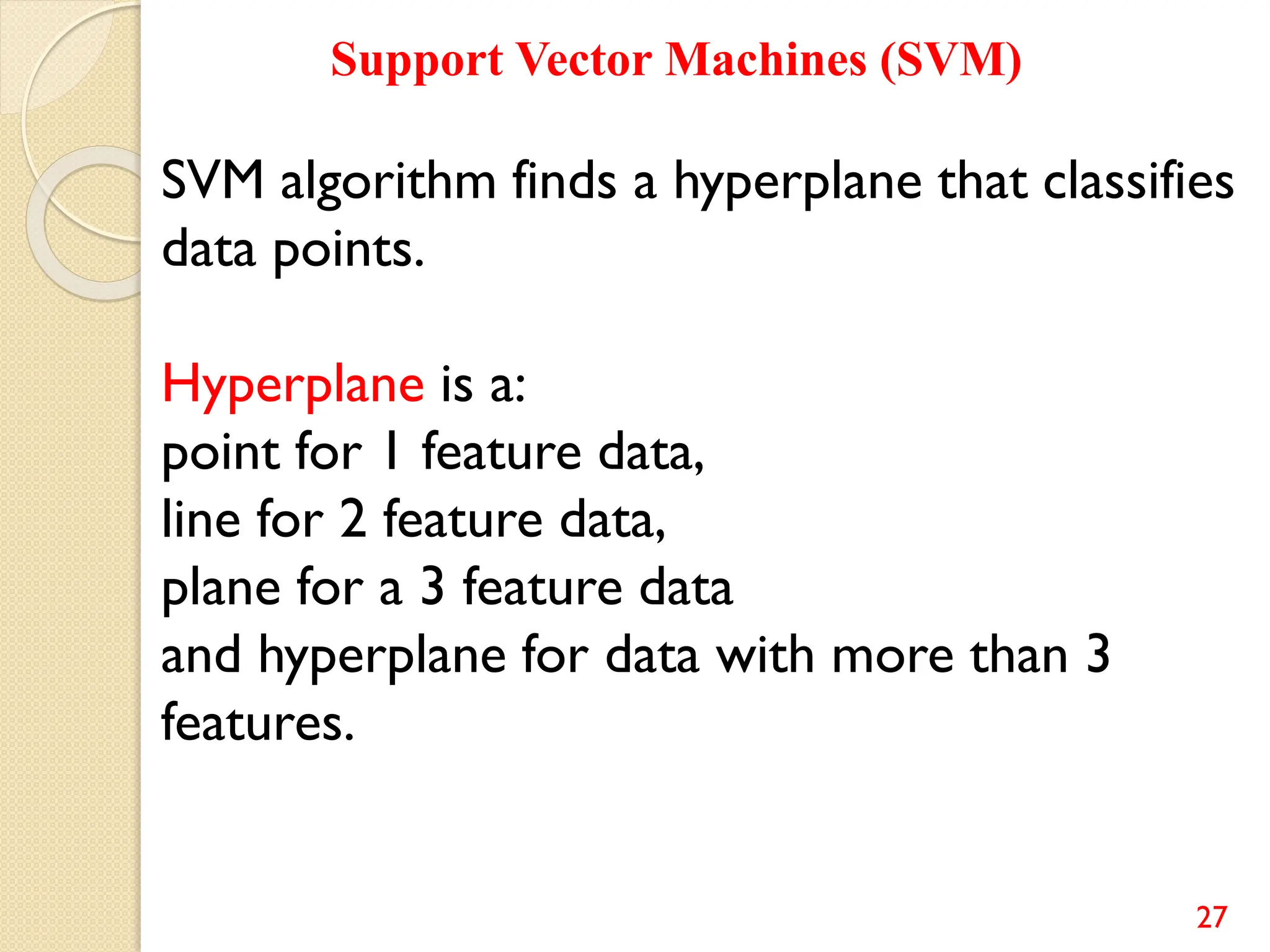
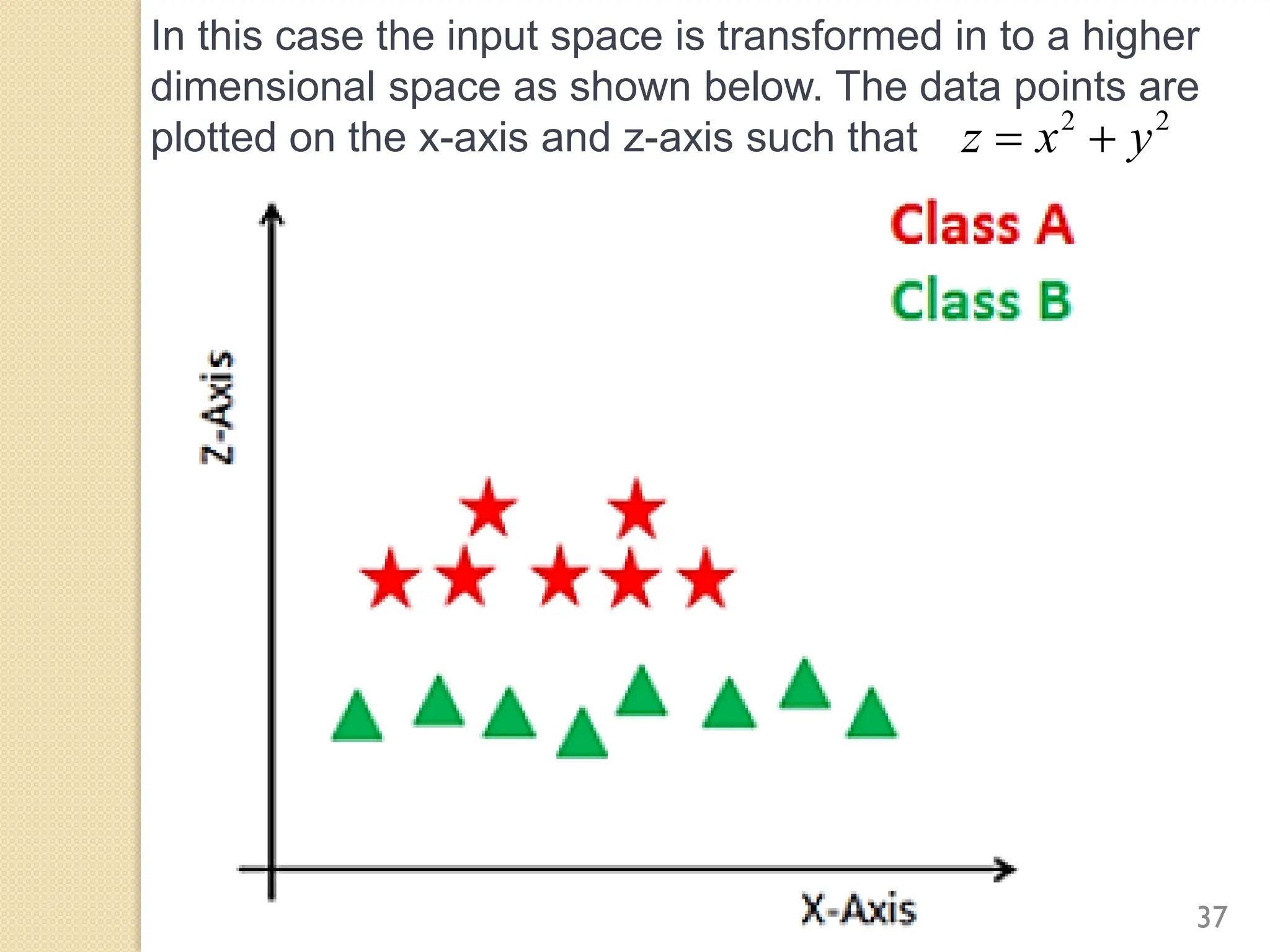
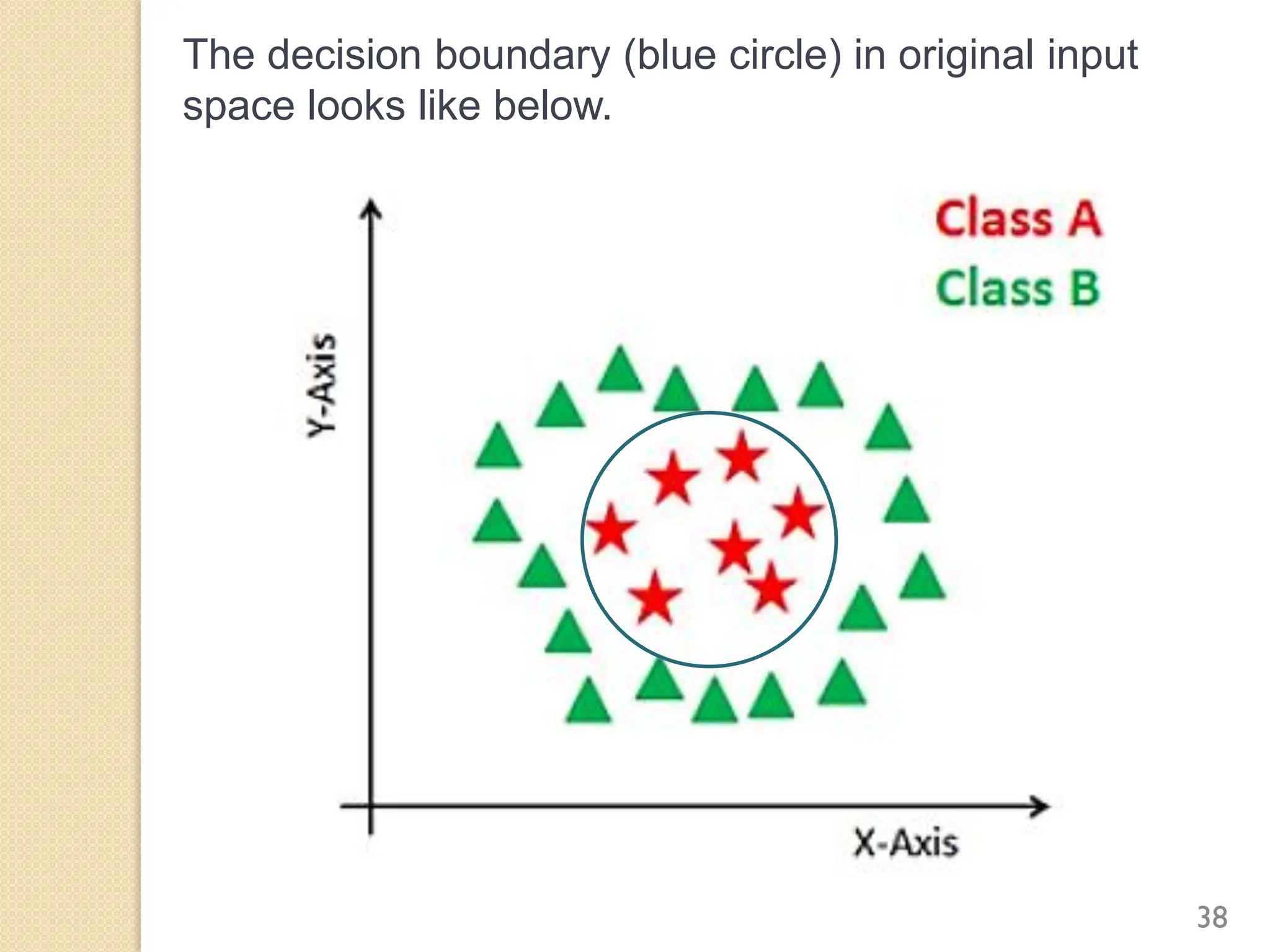
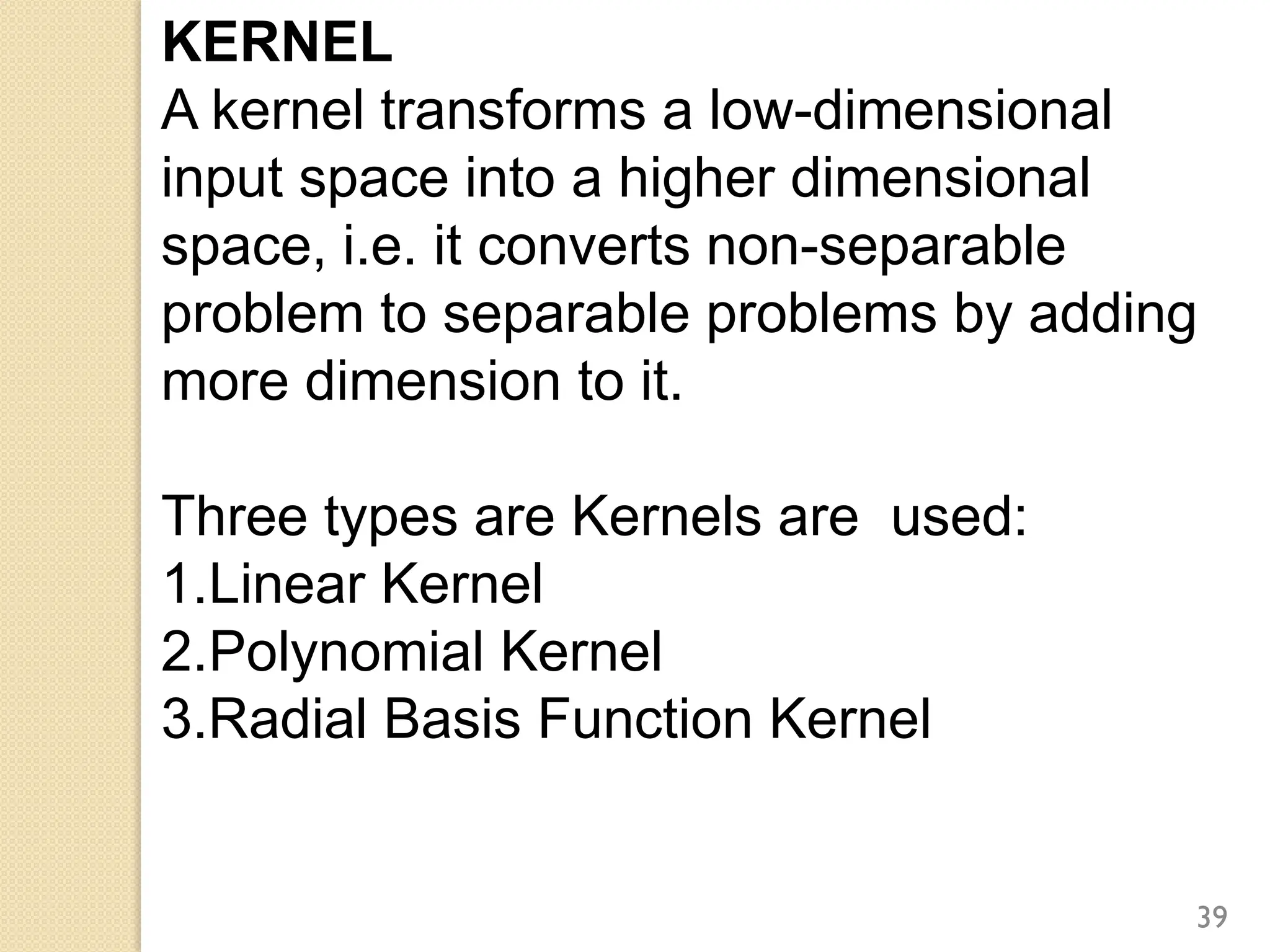
This document discusses various classification algorithms including logistic regression, Naive Bayes, support vector machines, k-nearest neighbors, decision trees, and random forests. It provides examples of using logistic regression and support vector machines for classification tasks. For logistic regression, it demonstrates building a model to classify handwritten digits from the MNIST dataset. For support vector machines, it uses a banknote authentication dataset to classify currency notes as authentic or fraudulent. The document discusses evaluating model performance using metrics like confusion matrix, accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score.



![11
Python Example: Digits Dataset
The digits dataset is included in scikit-learn.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
digits = load_digits()
print(digits.data.shape)
plt.matshow(digits.images[1796])
plt.show()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20memechpart3-classification-231029162927-7bdcdeba/75/20MEMECH-Part-3-Classification-pdf-11-2048.jpg)










![(1) Dividing the data into attributes and
labels
X = bankdata.drop('Class', axis=1) #1
y = bankdata['Class’] #2
#1 The drop() command drops whole column
labeled ‘Class’ (axis=1 means whole column,
not just values are deleted)
#2 Only the class column is being stored in
the y variable.
Now, X variable contains features while y
variable contains corresponding labels.
44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20memechpart3-classification-231029162927-7bdcdeba/75/20MEMECH-Part-3-Classification-pdf-44-2048.jpg)