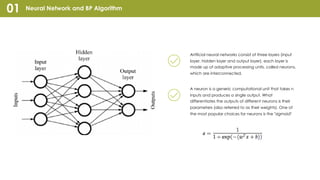
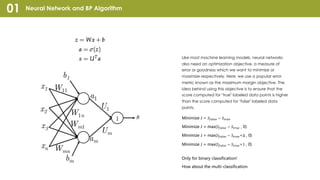
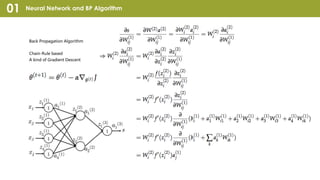
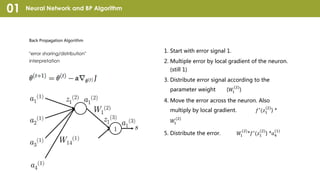
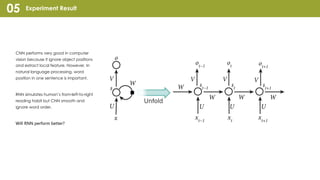
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a type of neural network that can take in an input image, assign importance to areas in the image, and distinguish objects in the image. CNNs use convolutional layers and pooling layers, which help introduce translation invariance to allow the network to recognize patterns and objects regardless of their position in the visual field. CNNs have been very effective for tasks involving visual imagery like image classification but may be less effective for natural language processing tasks that rely more on word order and sequence. Recurrent neural networks (RNNs) that can model sequential data may perform better than CNNs for some natural language processing tasks like text classification.











![Reference
[1] Yoon Kim. ”Convolutional Neural Networks for
Sentence Classification” EMNLP 2014.
LINK: http://aclweb.org/anthology/D/D14/D14-
1181.pdf
[2] Peng Wang, Jiaming Xu. ”Semantic Clustering and
Convolutional Neural Network for Short Text
Categorization” 2015.
LINK: http://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P15-2058
Question
Time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/convolutionalneuralnetwork-200419005424/85/Convolutional-neural-network-22-320.jpg)