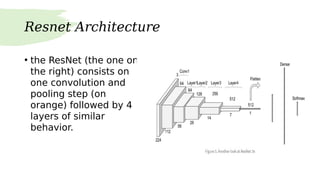
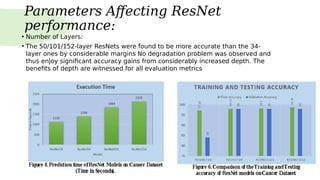
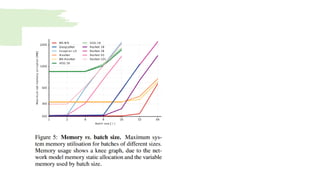
Residual neural networks (ResNets) solve the vanishing gradient problem through shortcut connections that allow gradients to flow directly through the network. The ResNet architecture consists of repeating blocks with convolutional layers and shortcut connections. These connections perform identity mappings and add the outputs of the convolutional layers to the shortcut connection. This helps networks converge earlier and increases accuracy. Variants include basic blocks with two convolutional layers and bottleneck blocks with three layers. Parameters like number of layers affect ResNet performance, with deeper networks showing improved accuracy. YOLO is a variant that replaces the softmax layer with a 1x1 convolutional layer and logistic function for multi-label classification.




![shortcut connections
• The formulation of F(x)+x can be realized by feed for-ward
neural networks with “shortcut connections” (Fig. 2).Shortcut
connections are those skipping one or more layers. In our case,
the shortcut connections simply perform identity mapping, and
their outputs are added to the outputs of the stacked layers
• Identity short-cut connections add neither extra parameter nor
computational complexity.
• Helps to attain early convergence of models. [2]
• Helps to increase accuracy of deep networks. [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/resnet-200327074748/85/Resnet-6-320.jpg)






![References
• https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-and-visu
alizing-resnets-442284831be8
• Original Resnet Paper
• Performance Comparison of Pretrained Convolutional
Neural Networks on Crack Detection in Buildings- Ç.F.
Özgenelaand A.GönençSorguç [2018]
• AN ANALYSIS OF DEEP NEURAL NETWORK MODELS FOR
PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS- Alfredo Canziani, Eugenio
Culurciello and Adam Paszke [2017]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/resnet-200327074748/85/Resnet-16-320.jpg)