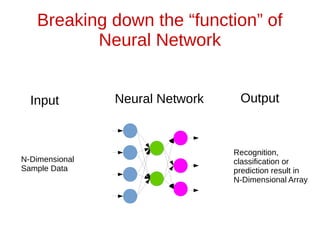
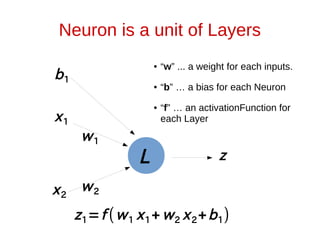
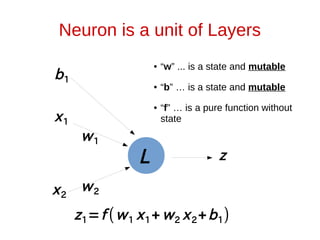
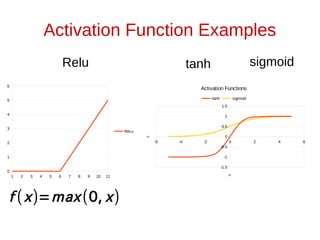
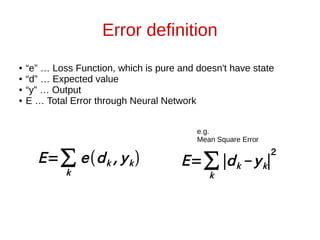
The document discusses neural networks and how they can be viewed as functions. It describes how neural networks take input data and produce output predictions or classifications. The document outlines how neural networks have a layered structure where each layer is a function, and how the layers are composed together. It explains that neurons are the basic units of computation in each layer and how they operate. The document also discusses how neural network training works by optimizing the weights and biases in each layer to minimize error, and how matrix operations in neural networks can benefit from parallel processing on GPUs.



![Simplest case:
Classification of Iris
Neural Network
Features
[5.1 1.5 1.8 3.2]
Probability of each class
[0.9 0.02 0.08]
ResultSample](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-8-320.jpg)
![Neural Network is like a
Function1[INDArray, INDArray]
Neural Network
Features
[5.1 1.5 1.8 3.2]
Probability of each class
[0.9 0.02 0.08]
ResultSample
W:INDArray => INDArray
W](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-9-320.jpg)
![Dealing with multiple samples
Neural Network
Features
[
5.1 1.5 1.8 3.2
4.5 1.2 3.0 1.2
⋮ ⋮
3.1 2.2 1.0 1.2
]
Probability of each class
[
0.9 0.02 0.08
0.8 0.1 0.1
⋮ ⋮
0.85 0.08 0.07
]
ResultsIndependent
Samples](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-10-320.jpg)
![Generalized Neural Network
Function
ResultsNeural Network
[
X11 X12 ⋯ X1 p
X21 X2 p
⋮ ⋮
Xn 1 Xn2 ⋯ Xnp
] [
Y11 Y12 ⋯ Y1 m
Y21 Y2 m
⋮ ⋮
Yn1 Yn2 ⋯ Ynm
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-11-320.jpg)
![NN Function deals with multiple
samples as it is (thx to Linear Algebra!)
ResultIndependent
Samples
Neural Network
[
X11 X12 ⋯ X1 p
X21 X2 p
⋮ ⋮
Xn 1 Xn2 ⋯ Xnp
] [
Y11 Y12 ⋯ Y1 m
Y21 Y2 m
⋮ ⋮
Yn1 Yn2 ⋯ Ynm
]
W:INDArray => INDArray
W](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-12-320.jpg)

![Neural Network is a layered
structure
[
X11 X12 ⋯ X1 p
X21 X2 p
⋮ ⋮
Xn 1 Xn2 ⋯ Xnp
] [
Y11 Y12 ⋯ Y1 m
Y21 Y2 m
⋮ ⋮
Yn1 Yn2 ⋯ Ynm
]
L1 L2 L3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-14-320.jpg)
![Each Layer is also a function which
maps samples to output
[
X11 X12 ⋯ X1 p
X21 X2 p
⋮ ⋮
Xn 1 Xn2 ⋯ Xnp
]
L1
[
Z11 Z12 ⋯ Z1 q
Z21 Z2 p
⋮ ⋮
Zn1 Zn2 ⋯ Znp
]
Output
of Layer1
L1 :INDArray => INDArray](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-15-320.jpg)
![NN Function is composed of
Layer functions.
W=L1andThenL2andThenL3
W ,L1 ,L2 ,L3 :INDArray => INDArray
[
X11 X12 ⋯ X1 p
X21 X2 p
⋮ ⋮
Xn 1 Xn2 ⋯ Xnp
] [
Y11 Y12 ⋯ Y1 m
Y21 Y2 m
⋮ ⋮
Yn1 Yn2 ⋯ Ynm
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-16-320.jpg)
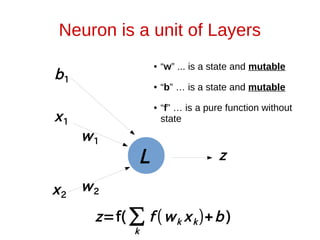
![How does L1 function look like?
L1 (X)=( X・
[
W11 W12 ⋯ W1q
W21 W2q
⋮ ⋮
Wp1 Wp2 ⋯ Wpq
]+
[
b11 b12 ⋯ b1q
b21 b2q
⋮ ⋮
bn 1 bn 2 ⋯ bnq
]) map f
Weight Matrix Bias Matrix
L1 :INDArray => INDArray](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-22-320.jpg)
![L1
(
[
X11 X12 ⋯ X1p
X21 X2p
⋮ ⋮
Xn1 Xn 2 ⋯ Xnp
]・
[
W11 W12 ⋯ W1 q
W21 W2 q
⋮ ⋮
Wp1 Wp2 ⋯ Wpq
]+
[
b11 b12 ⋯ b1 q
b21 b2 q
⋮ ⋮
bn 1 bn 2 ⋯ bnq
]) map f
Input
Feature Matrix Weight Matrix Bias Matrix
=
[
Z11 Z12 ⋯ Z1 q
Z21 Z2 p
⋮ ⋮
Zn 1 Zn 2 ⋯ Znp
]
Output of Layer1
How does L1 function look like?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-23-320.jpg)

![Training of Neural Network
● Optimizing Weight Matrices and Bias Matrices in each layer.
● Optimizing = Minimizing Error, in this context.
● How are Neural Network errors are defined?
Weight Matrix Bias Matrix
L (X)=( X・
[
W11 W12 ⋯ W1q
W21 W2q
⋮ ⋮
Wp1 Wp2 ⋯ Wpq
]+
[
b11 b12 ⋯ b1q
b21 b2q
⋮ ⋮
bn 1 bn 2 ⋯ bnq
]) map f](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-25-320.jpg)
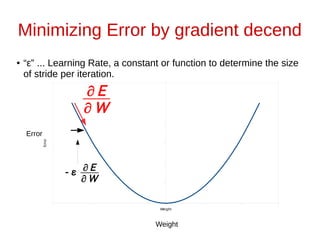
![Minimize Error by gradient decend
● “ε” ... Learning Rate, a constant or function to determine the size
of stride per iteration.
[
W11 W12 ⋯ W1q
W21 W2q
⋮ ⋮
Wp1 Wp2 ⋯ Wpq
] -= ε
[
∂E
∂ W11
∂E
∂ W12
⋯ ∂ E
∂ W1q
∂E
∂ W21
∂ E
∂ W2q
⋮ ⋮
∂E
∂ Wp1
∂E
∂ Wp2
⋯ ∂ E
∂ Wpq
]
[
b11 b12 ⋯ b1q
b21 b2q
⋮ ⋮
bp1 Wp2 ⋯ bpq
] -= ε
[
∂ E
∂ b11
∂ E
∂ b12
⋯ ∂ E
∂ b1q
∂ E
∂ b21
∂ E
∂ b2q
⋮ ⋮
∂ E
∂bp1
∂ E
∂bp2
⋯ ∂ E
∂ bpq
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-28-320.jpg)

![Matrix Calculation in Parallel
● Matrix calculation can be run in parallel, such as multiplication,
adding,or subtraction.
● GPGPU works well matrix calculation in parallel, with around
2000 CUDA cores per NVIDIA GPU and around 160GB / s
bandwidth.
[
W11 W12 ⋯ W1 q
W21 W2 q
⋮ ⋮
Wp1 Wp 2 ⋯ Wpq
] -= ε
[
∂ E
∂ W11
∂ E
∂ W12
⋯
∂ E
∂ W1 q
∂ E
∂ W21
∂ E
∂ W2 q
⋮ ⋮
∂ E
∂ Wp 1
∂ E
∂ Wp 2
⋯ ∂ E
∂ Wpq
]
(
[
X11 X12 ⋯ X1p
X21 X2p
⋮ ⋮
Xn1 Xn2 ⋯ Xnp
]・
[
W11 W12 ⋯ W1q
W21 W2q
⋮ ⋮
Wp 1 Wp2 ⋯ Wpq
]+
[
b11 b12 ⋯ b1q
b21 b2q
⋮ ⋮
bn1 bn2 ⋯ bnq
]) map f](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2015scalaworld-150927123309-lva1-app6892/85/Neural-Network-as-a-function-30-320.jpg)