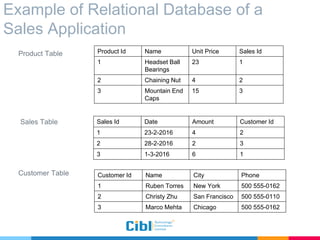
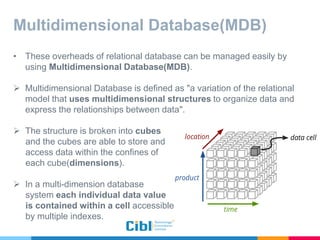
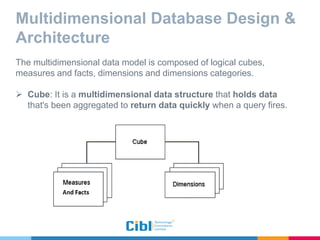
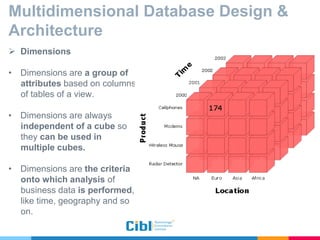
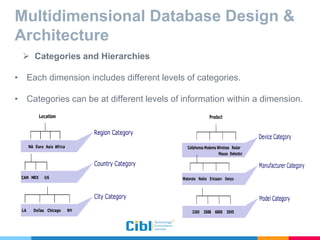
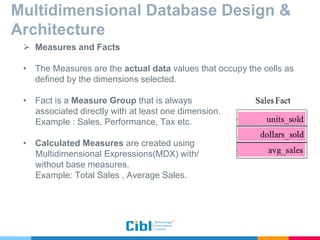
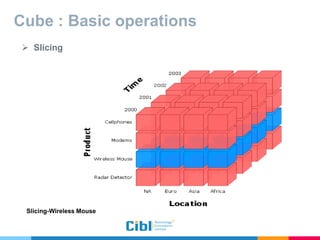
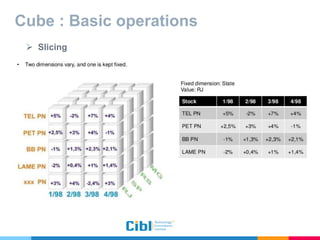
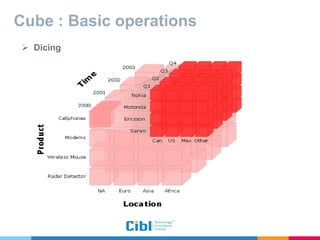
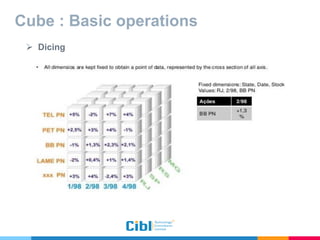
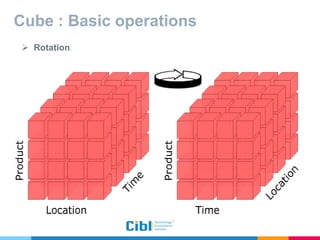
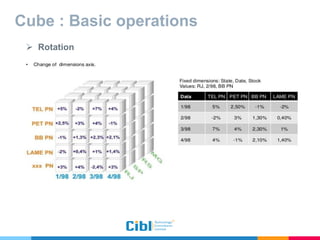
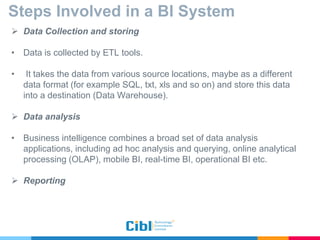
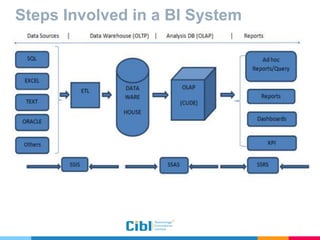
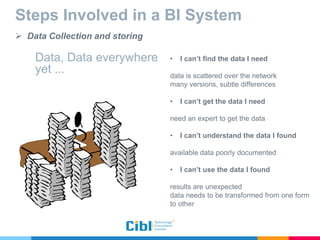
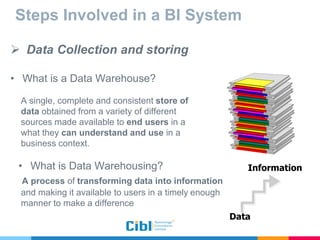
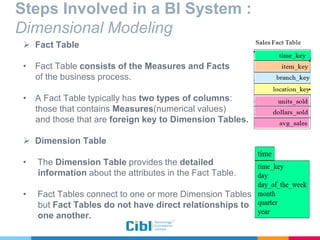
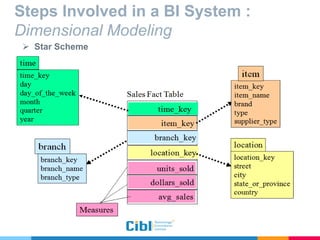
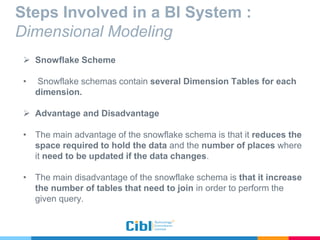
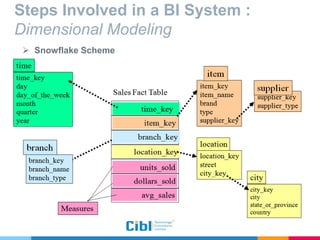
The document outlines the use of multidimensional databases (MDB) in business intelligence systems, highlighting their advantages over traditional relational databases for data analysis and retrieval. It details the architecture of MDB, including cubes, dimensions, and operations like slicing and dicing, and discusses the steps involved in setting up a business intelligence system, including data collection, dimensional modeling, and online analytical processing (OLAP). The content also touches upon the application of OLAP in various industries and tools for reporting.