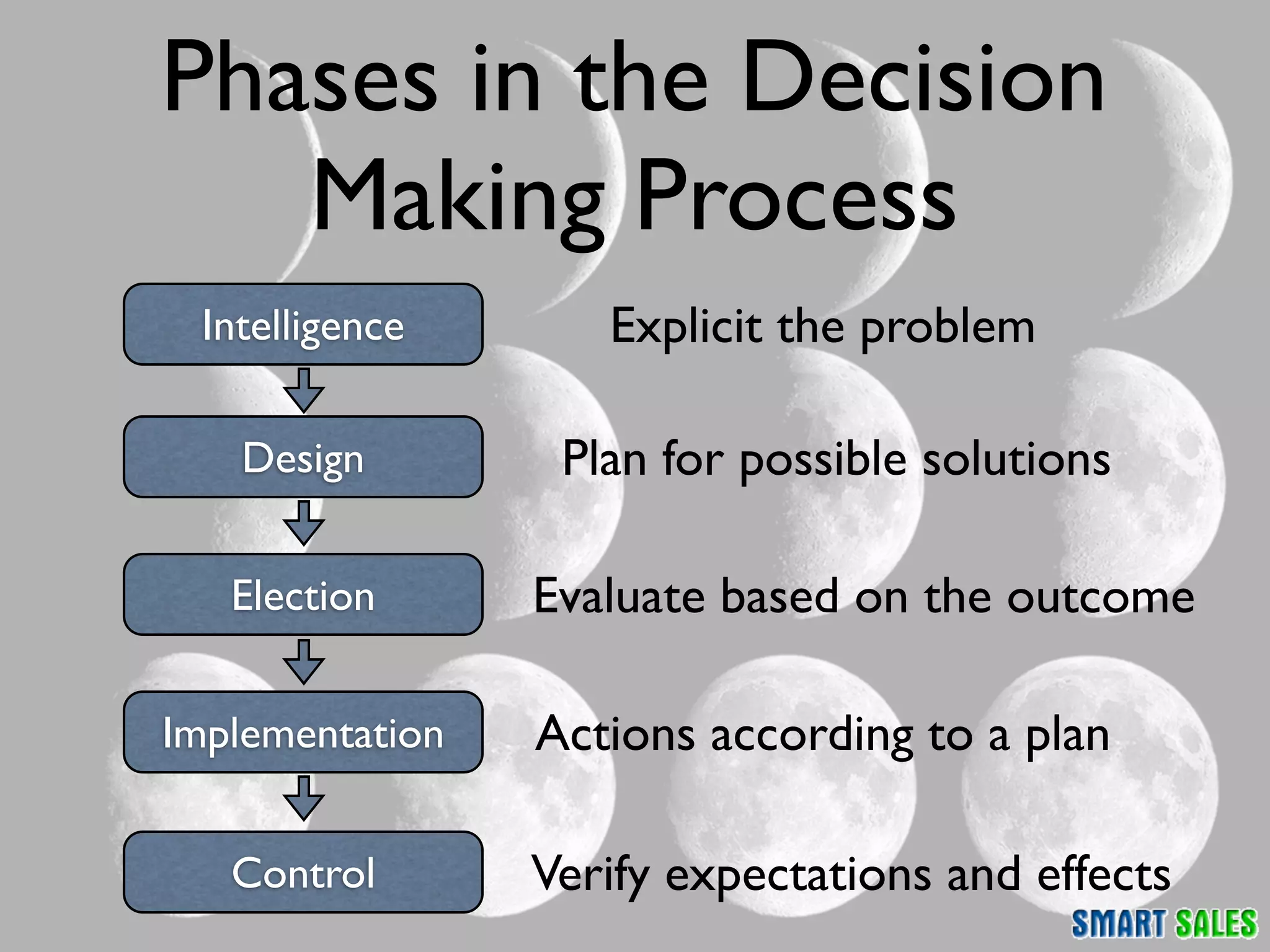
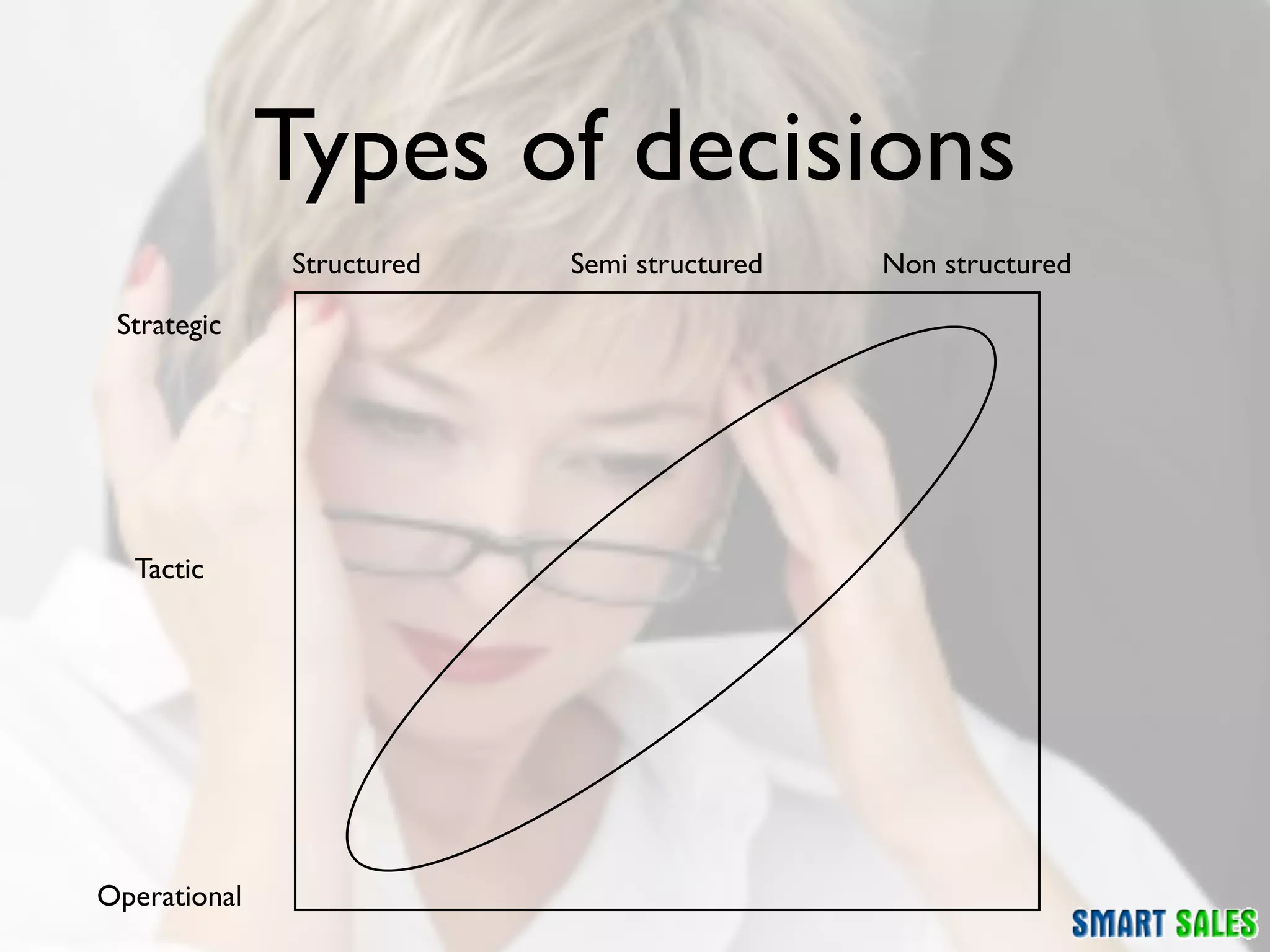
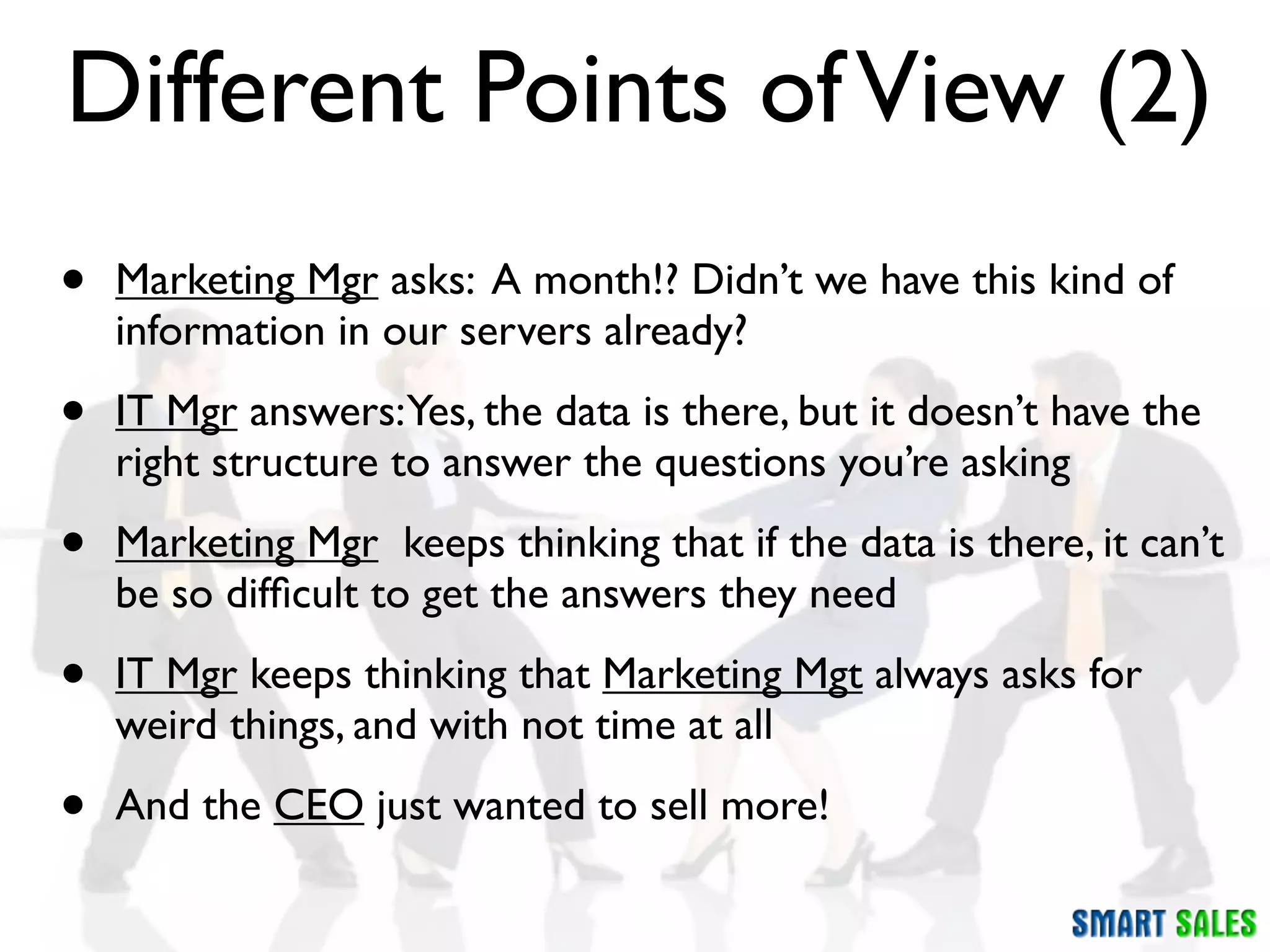
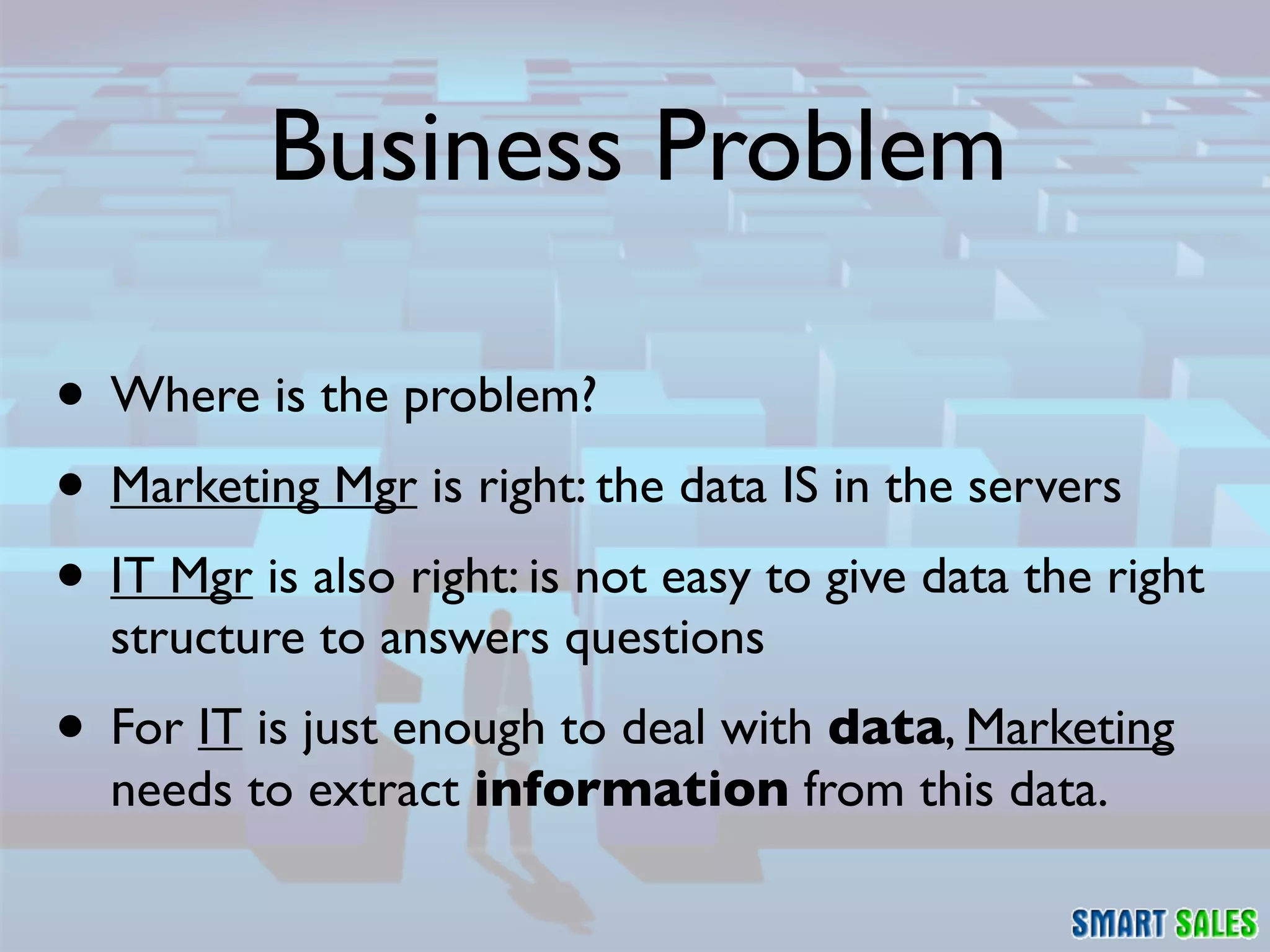
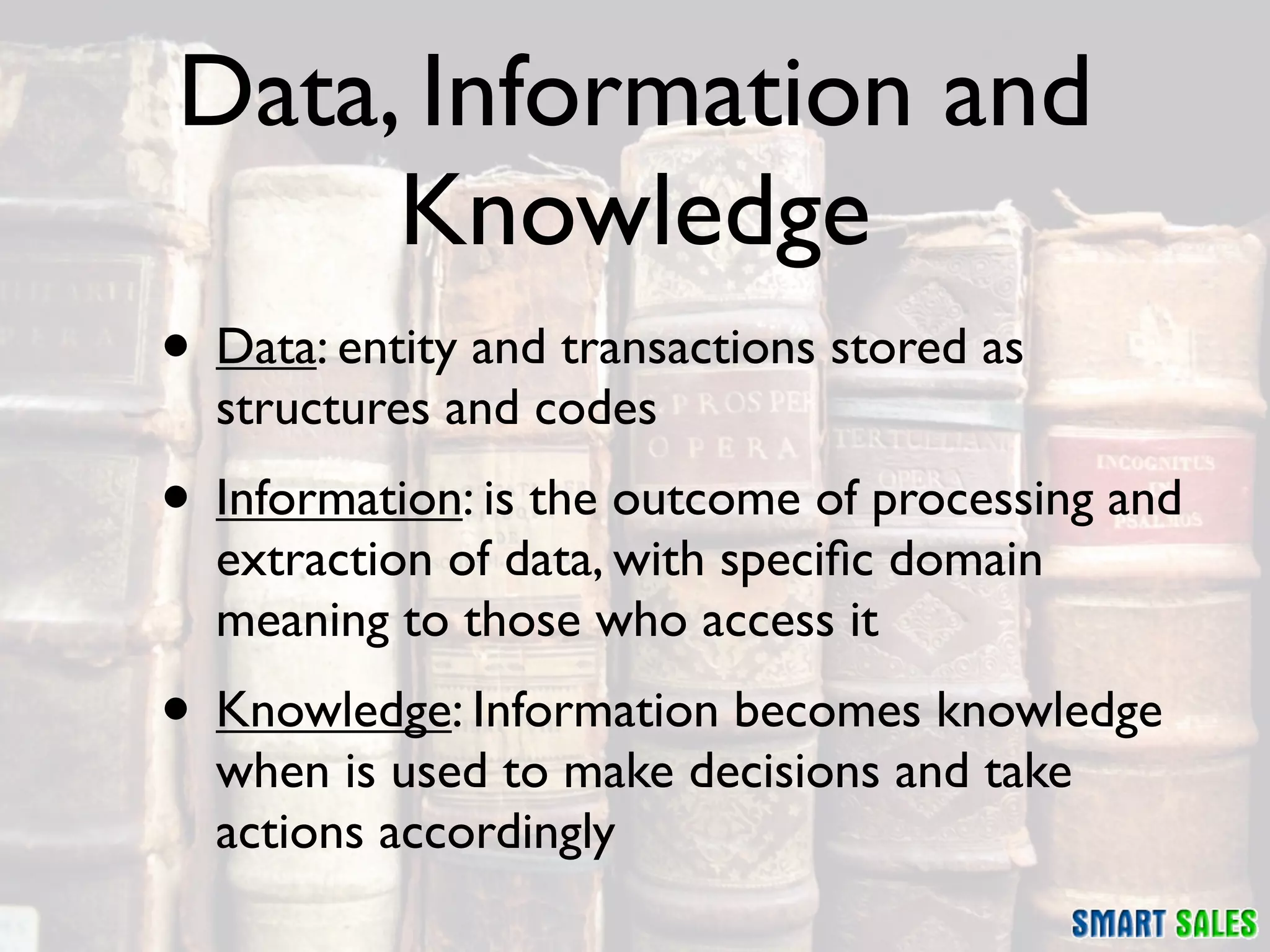
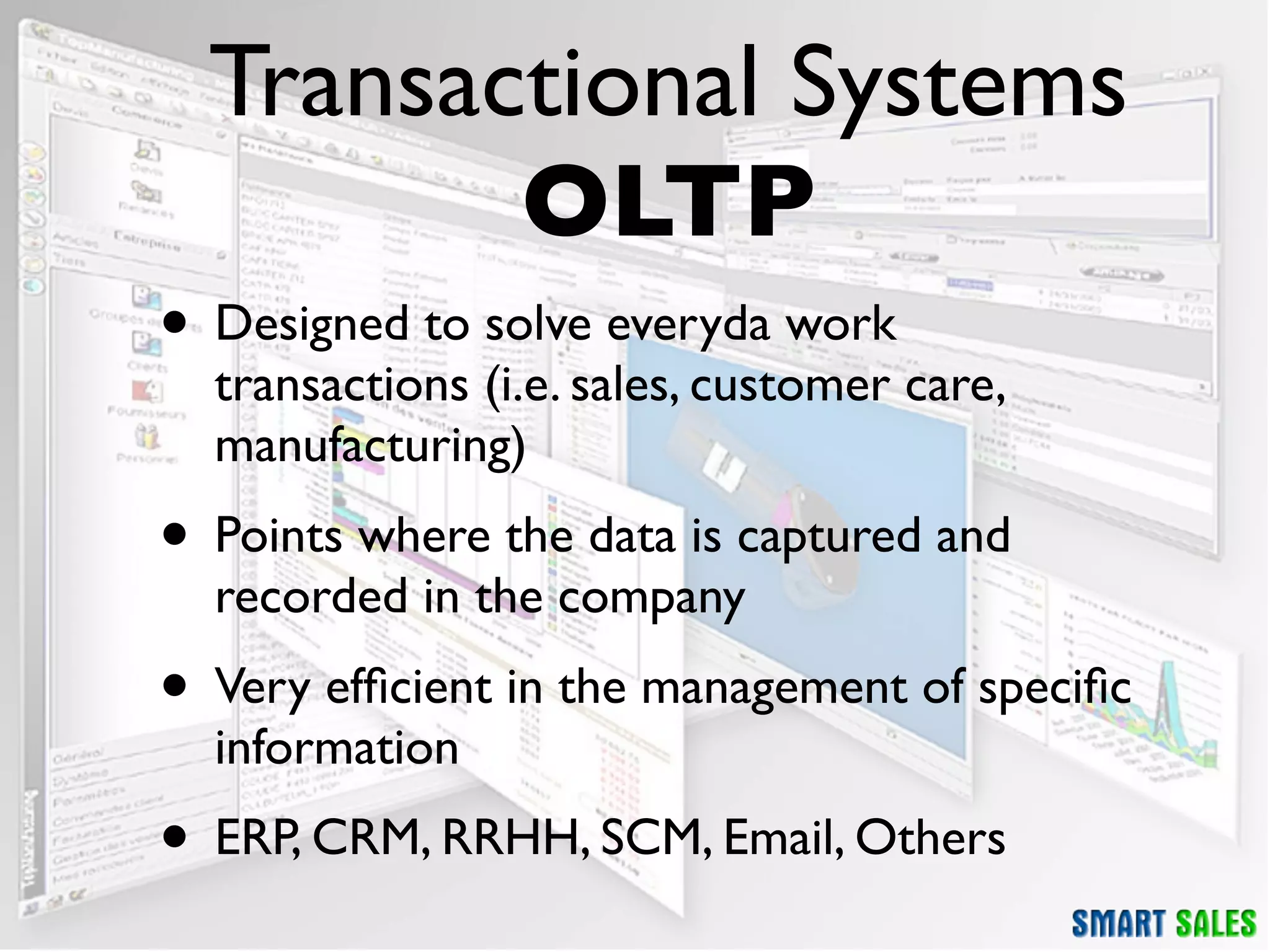
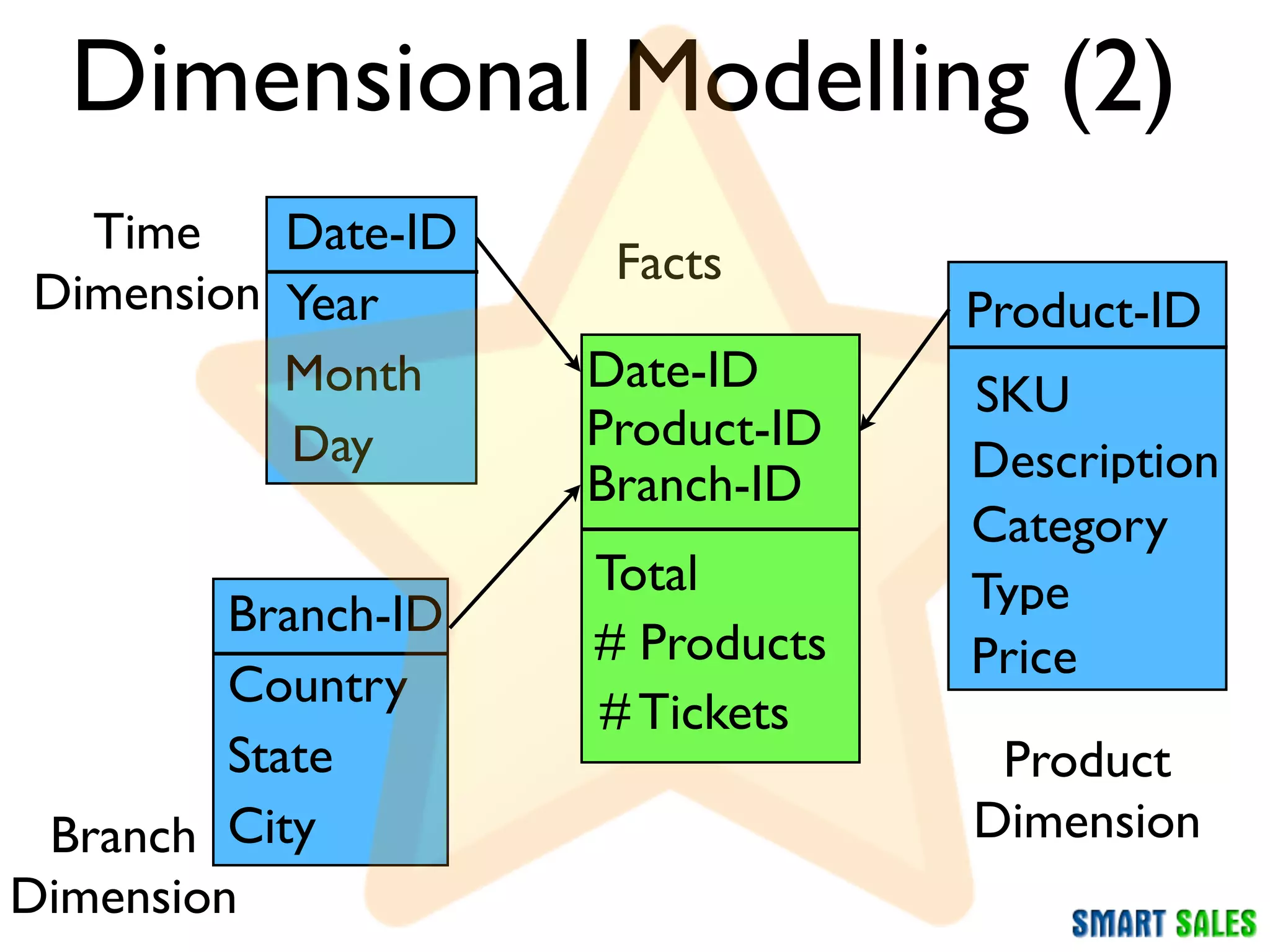
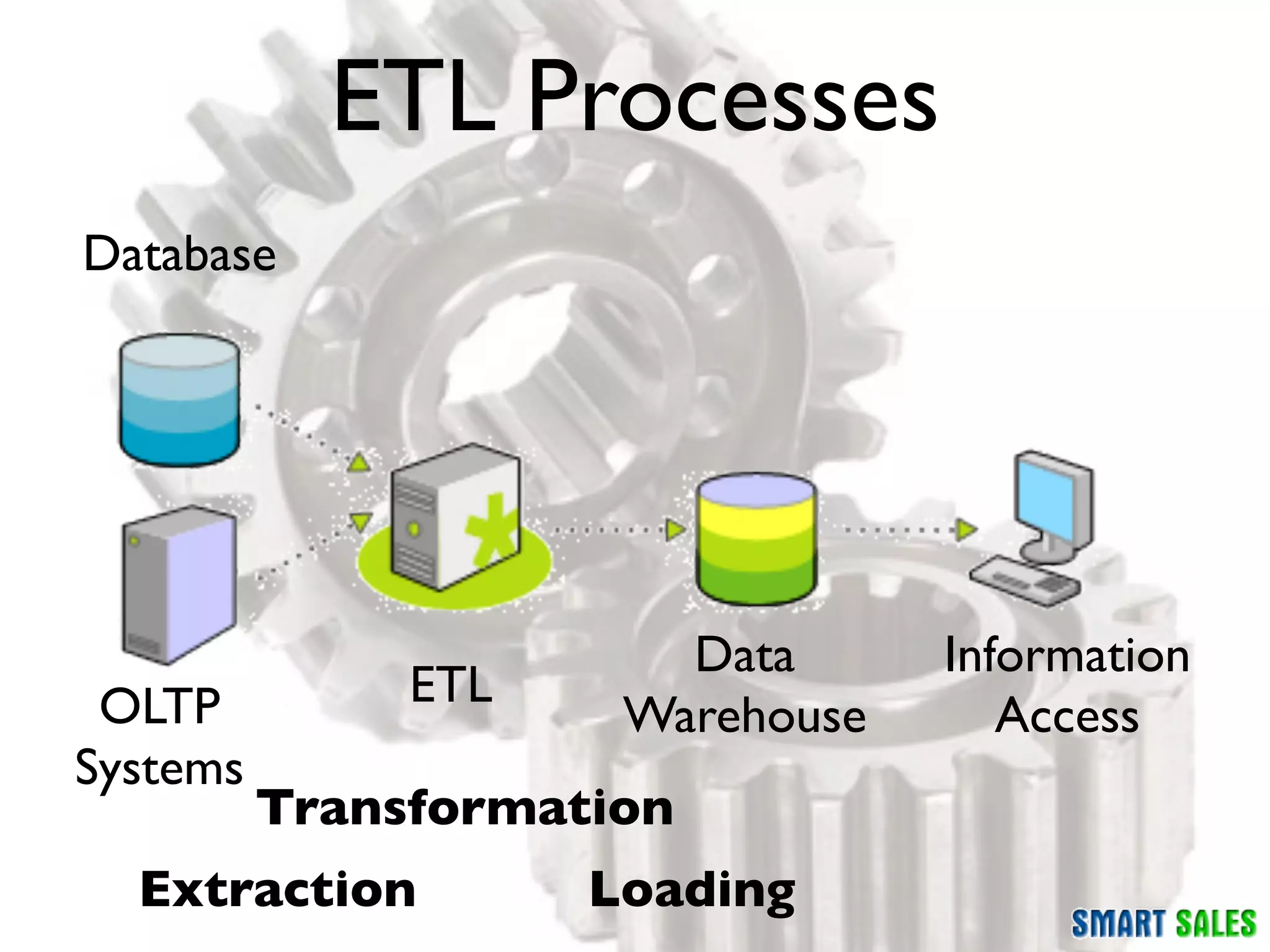
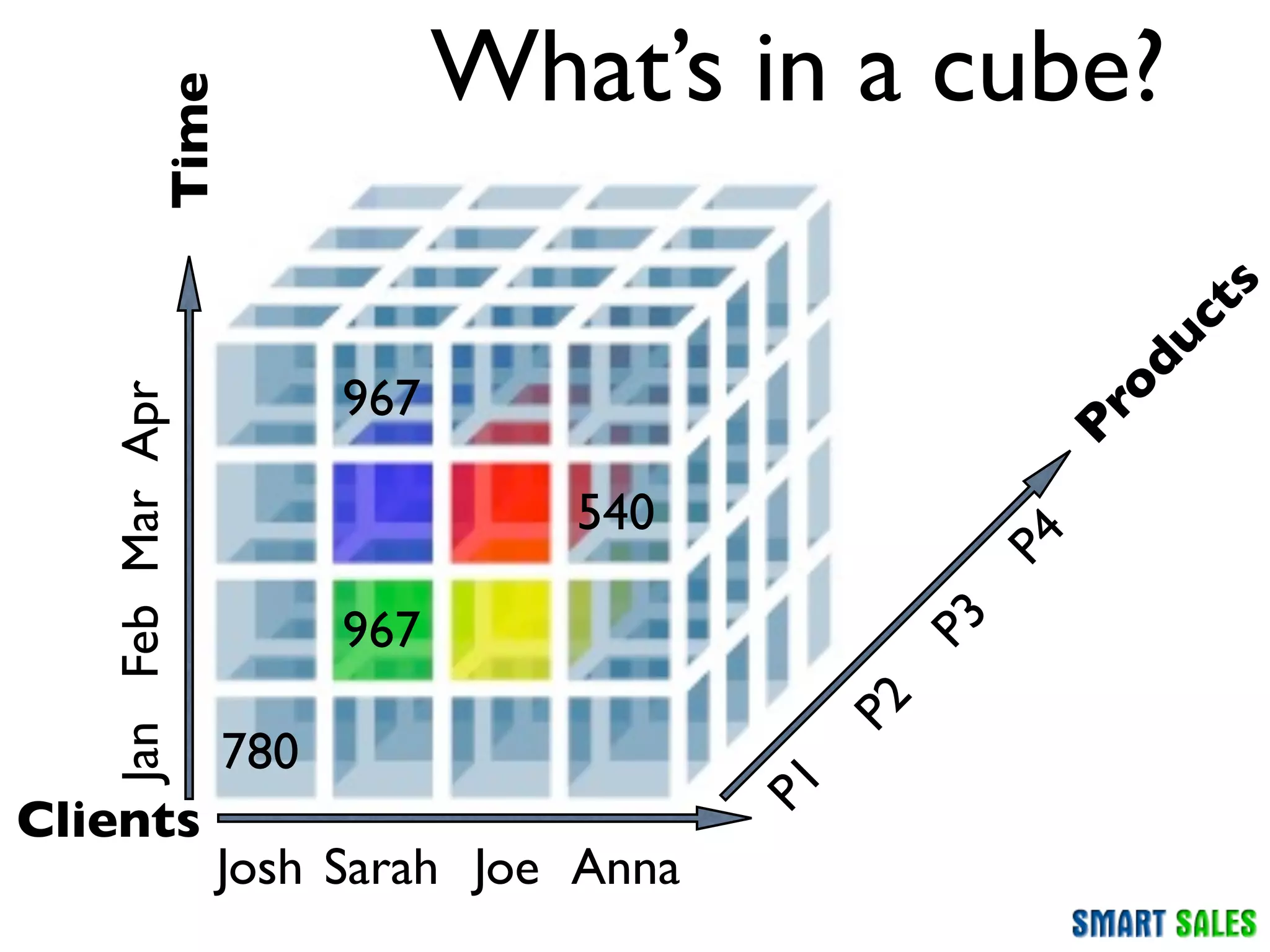
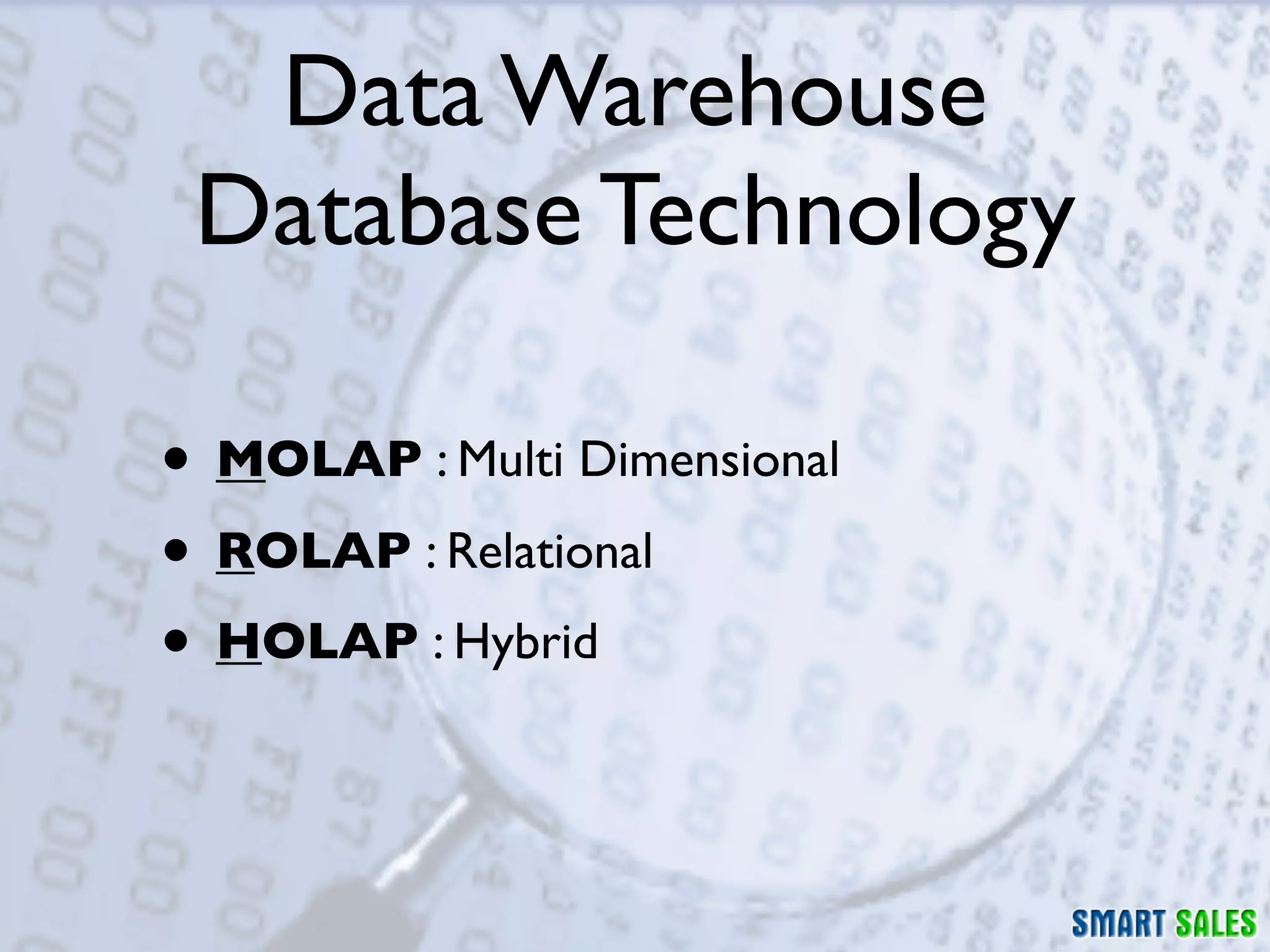
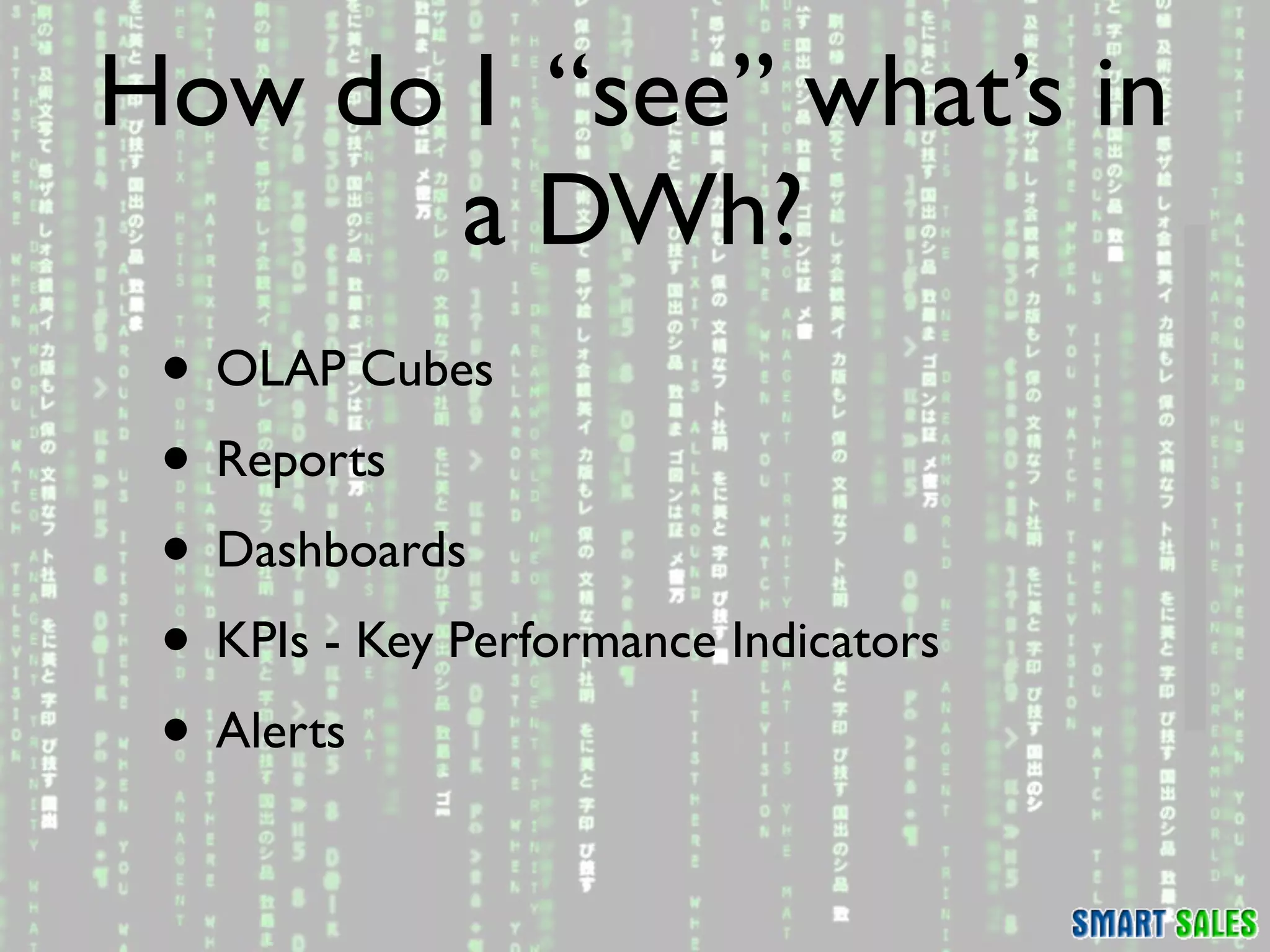
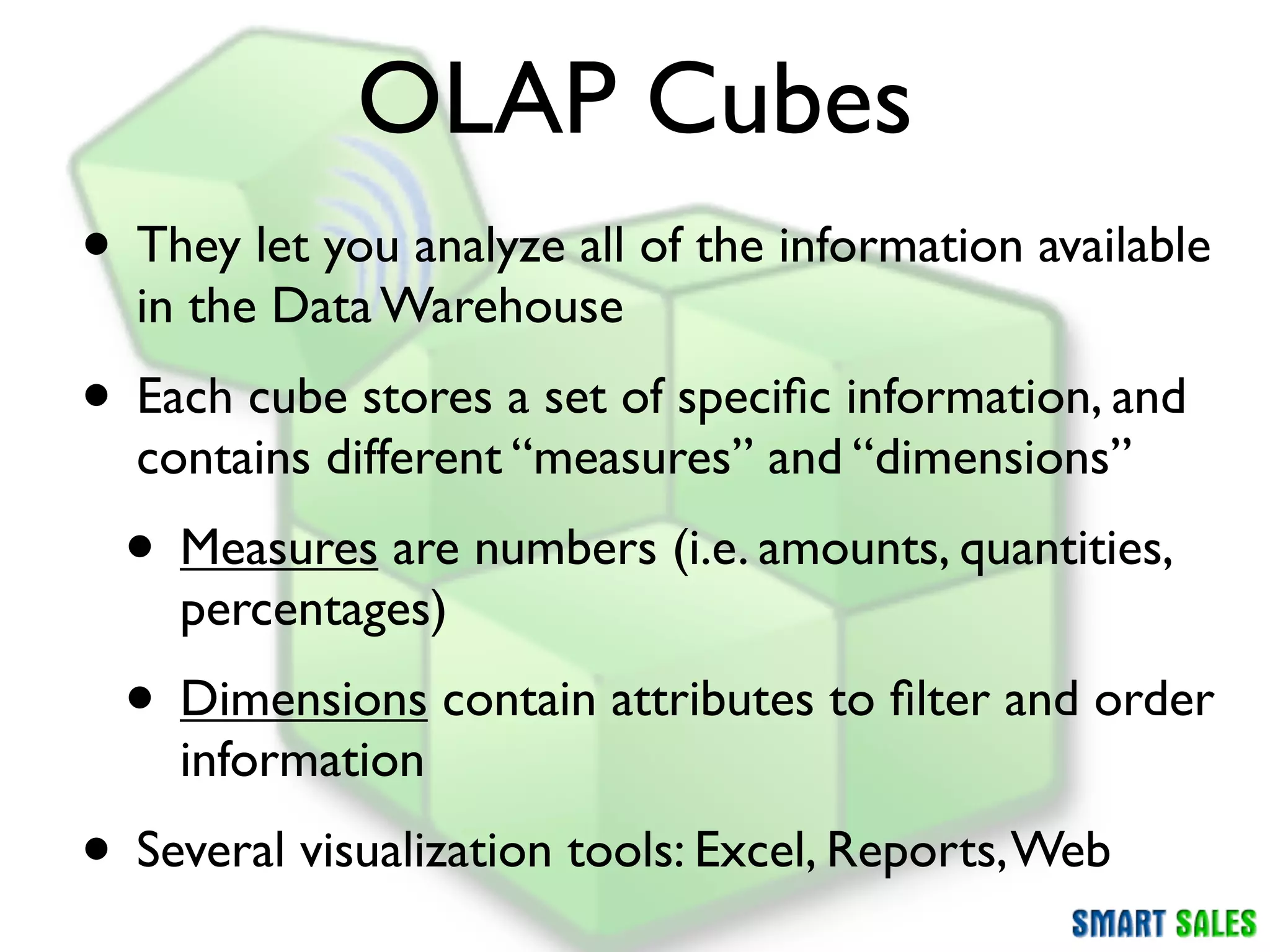
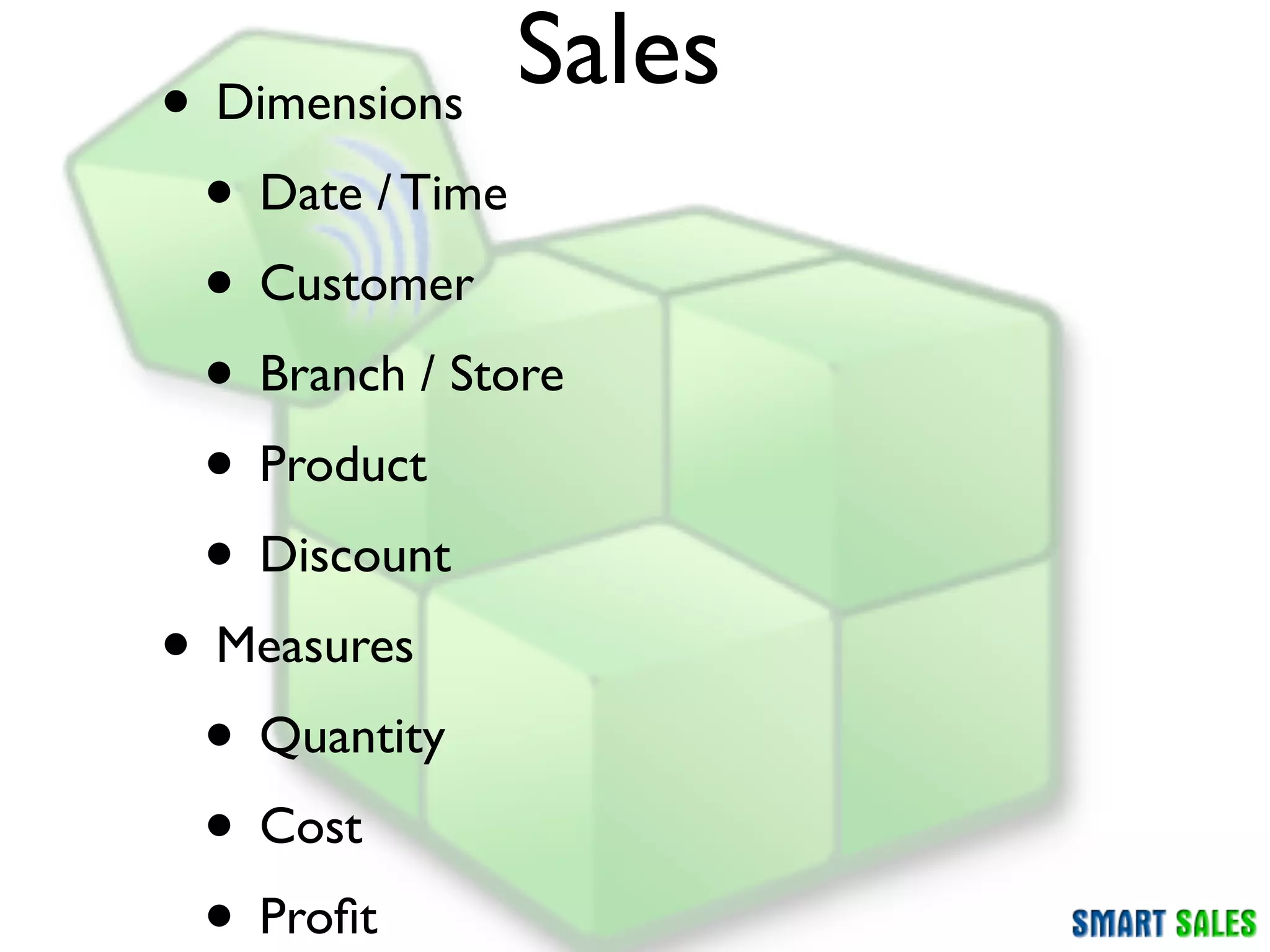
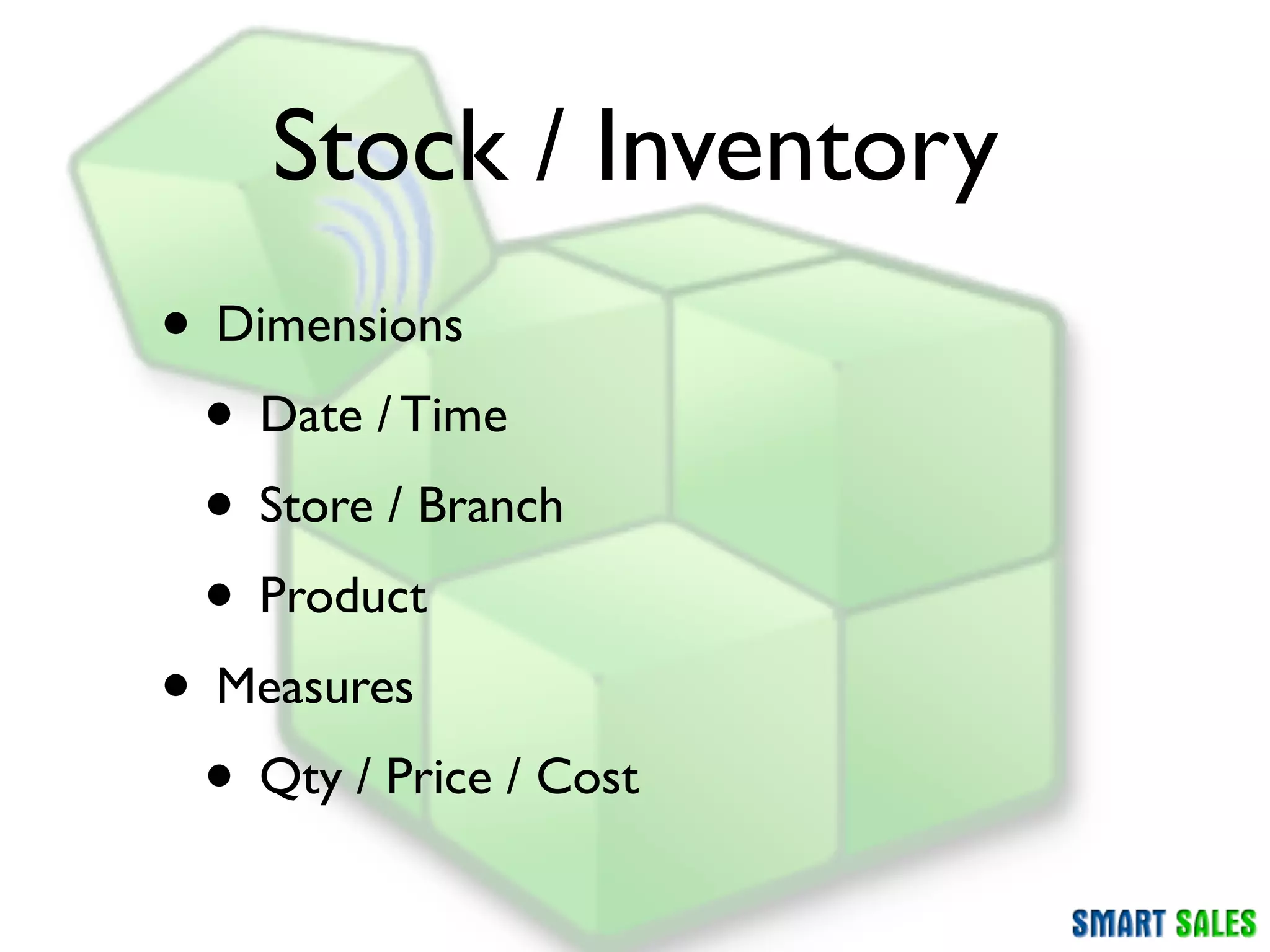
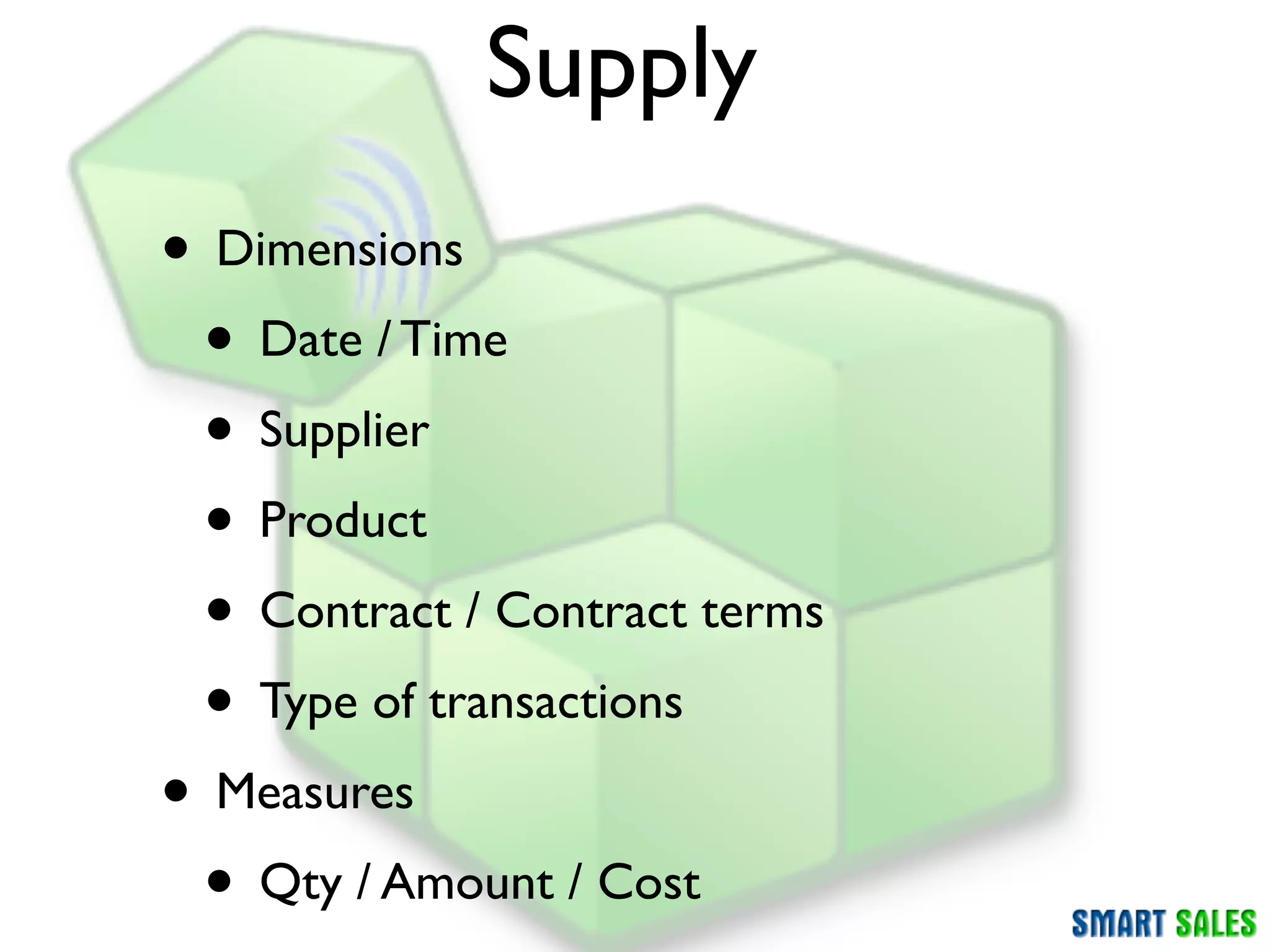
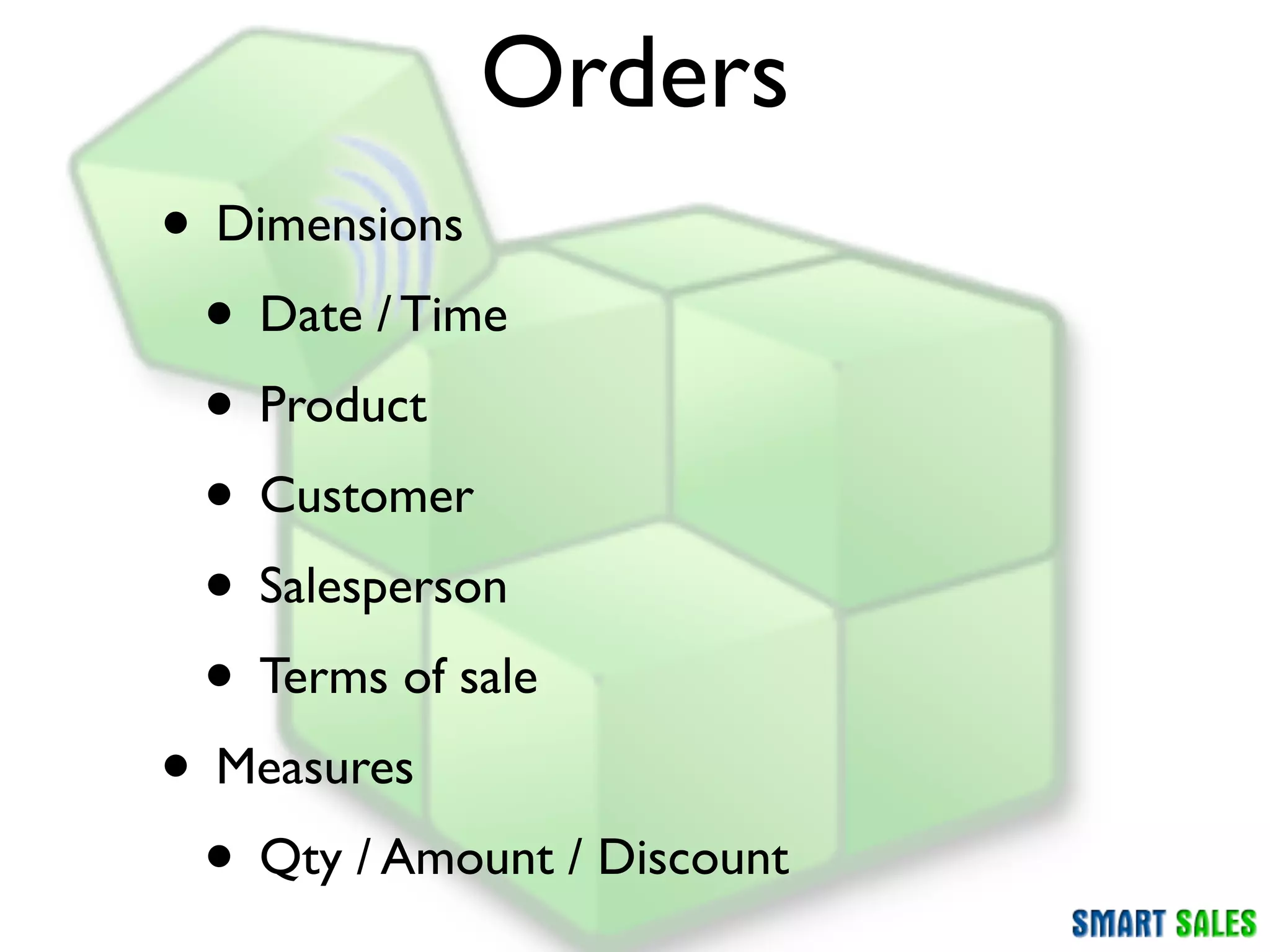
The document discusses business intelligence (BI) as a set of processes and technologies used to support decision making in organizations, emphasizing the importance of data collection, structuring, and analysis. It highlights the differences between operational systems (OLTP) and analytical systems (OLAP), as well as the role of data warehouses in centralizing and managing data for effective reporting and analytics. The document also outlines the methodologies for decision making and key performance indicators (KPIs) vital for measuring business success.