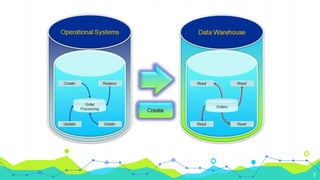
1) An operational database is a database used to manage and store real-time data that can be added or removed on the fly. It processes transactions like orders and deposits and is the source of data for data warehouses.
2) Examples of operational databases include databases that keep track of online store orders and inventory as well as bank databases that process transactions, maintain balances, and generate statements.
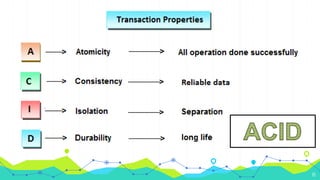
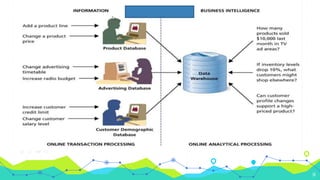
3) Operational databases use online transaction processing (OLTP) to handle current and constantly updated data needed for day-to-day business operations, while data warehouses use online analytical processing (OLAP) to analyze historical and summarized data for reports and decision making.