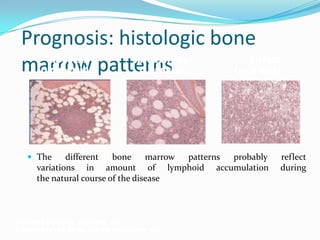
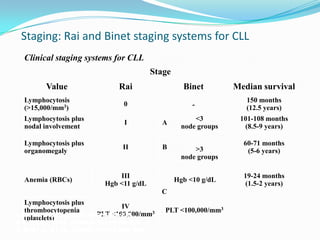
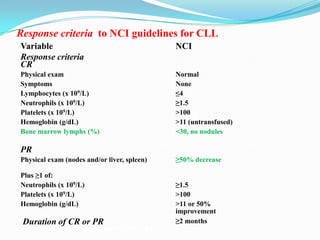
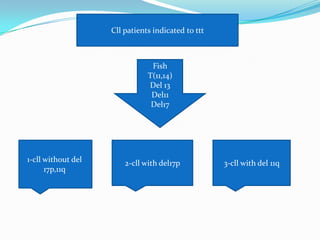
This document provides information on chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), including its definition, diagnosis, incidence, aetiology, clinical features, diagnostic tests, staging systems, prognostic factors, and treatment approaches.
Some key points include:
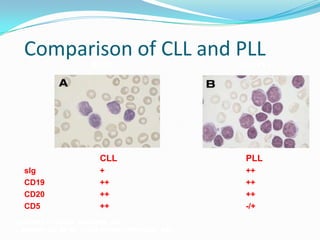
- CLL is defined as the progressive accumulation of long-lived, functionally incompetent B lymphocytes.
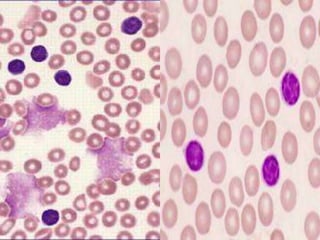
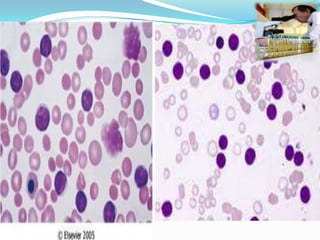
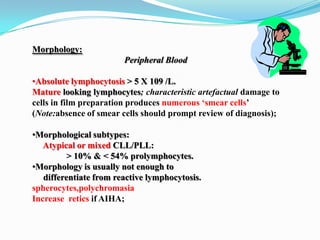
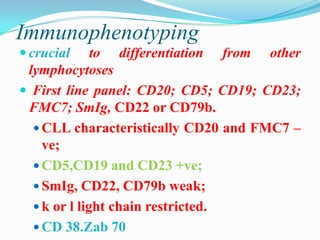
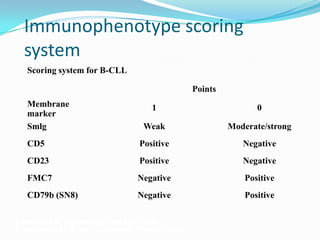
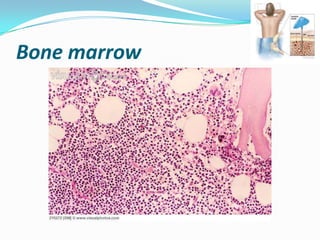
- Diagnosis involves evaluating lymphocyte counts, immunophenotyping, bone marrow biopsy, and cytogenetic/molecular testing.
- Incidence is highest in Western adults over age 65 and is more common in men.
- Prognostic factors include genetic abnormalities, IgV gene mutation status, and response to initial therapy.
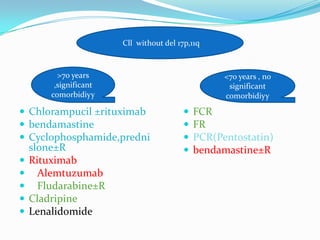
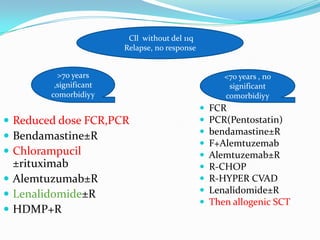
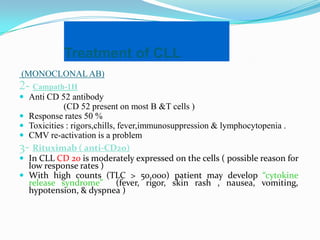
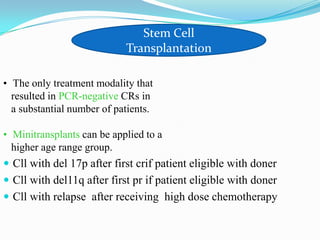
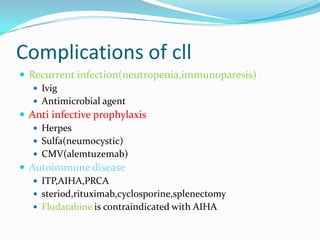
- Treatment depends on