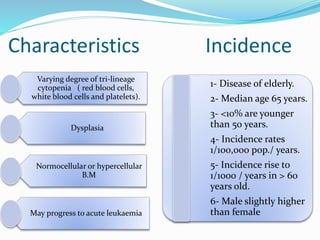
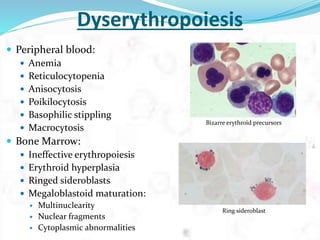
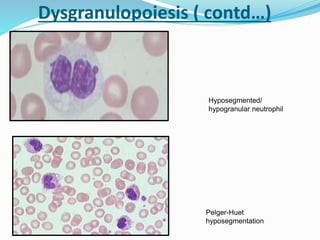
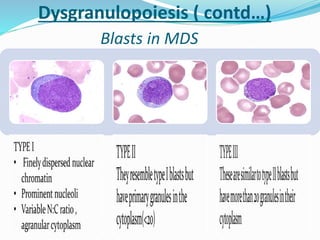
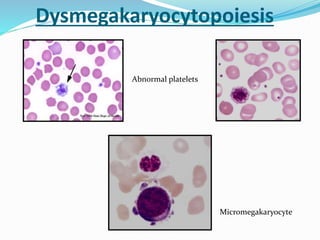
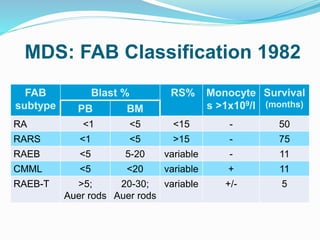
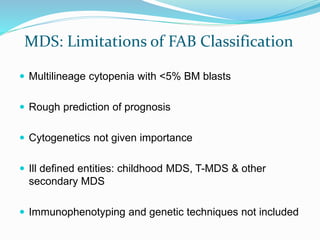
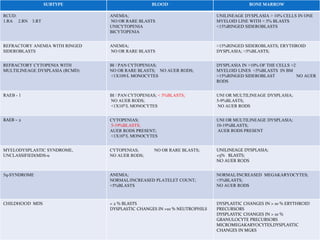
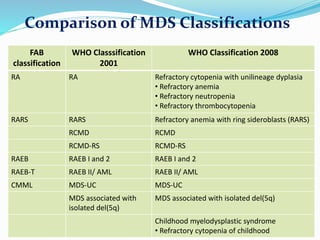
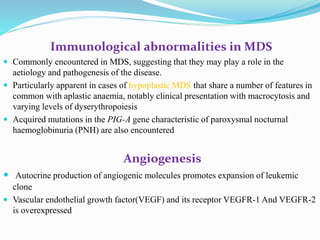
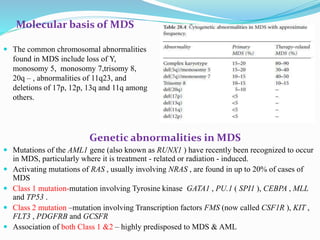
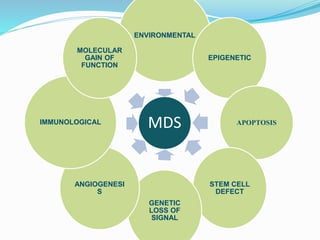
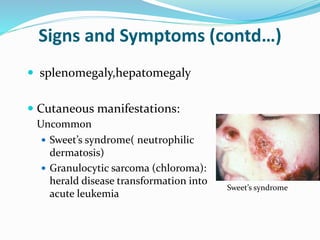
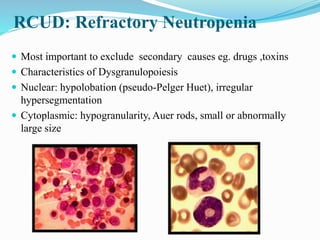
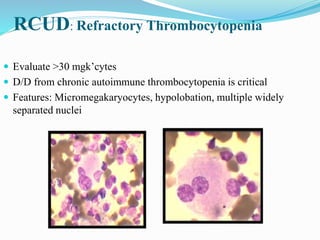
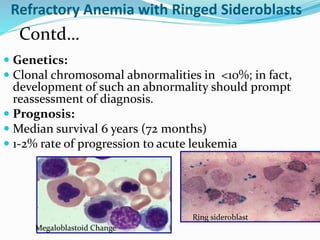
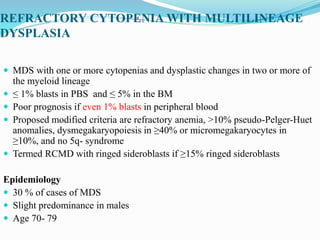
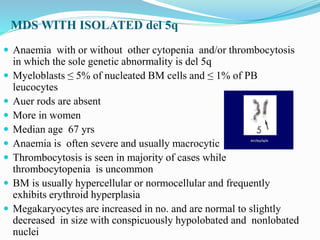
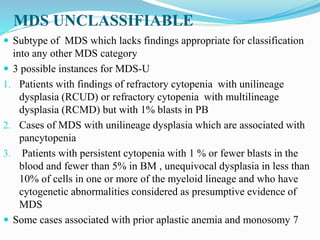
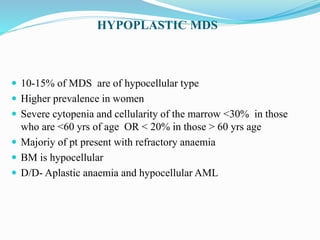
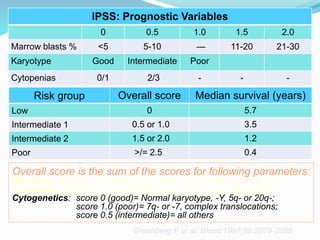
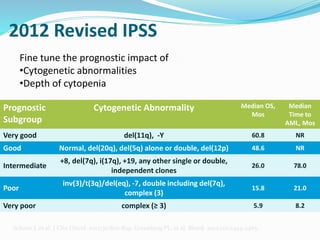
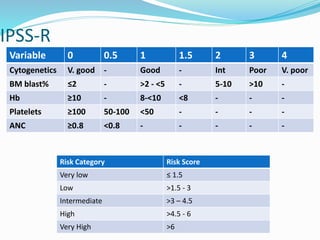
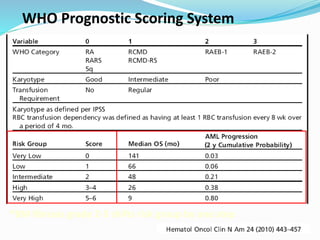
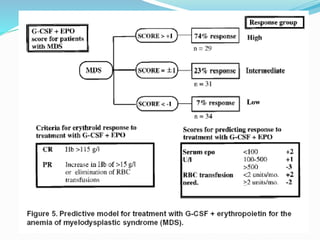
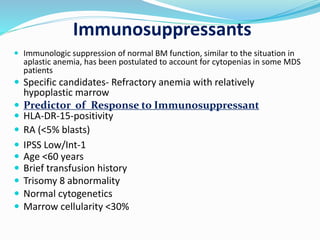
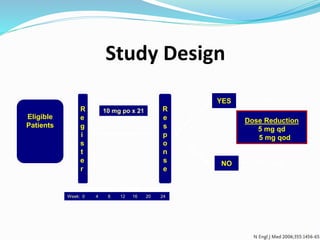
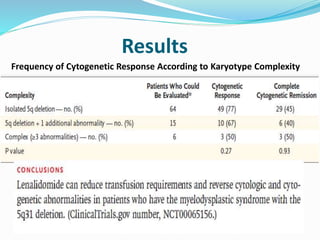
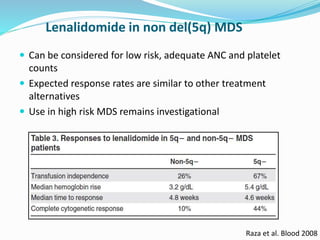
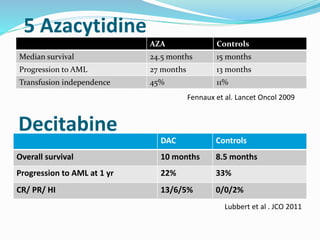
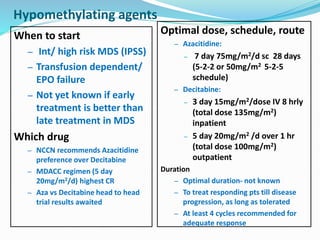
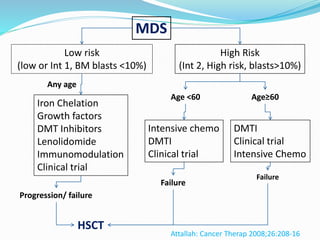
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is a heterogeneous group of clonal stem cell disorders where the bone marrow cannot produce blood cells effectively. Patients present with varying degrees of cytopenias. MDS may progress to acute leukemia. The WHO classification system recognizes subtypes based on blast percentage and cytogenetics that provide prognostic information. MDS results from genetic mutations and epigenetic changes in hematopoietic stem cells. Presenting signs include anemia, infections, and bleeding due to cytopenias. Evaluation involves blood tests, bone marrow aspiration/biopsy, and cytogenetics. Refractory cytopenia with unilineage dysplasia is the most common subtype.