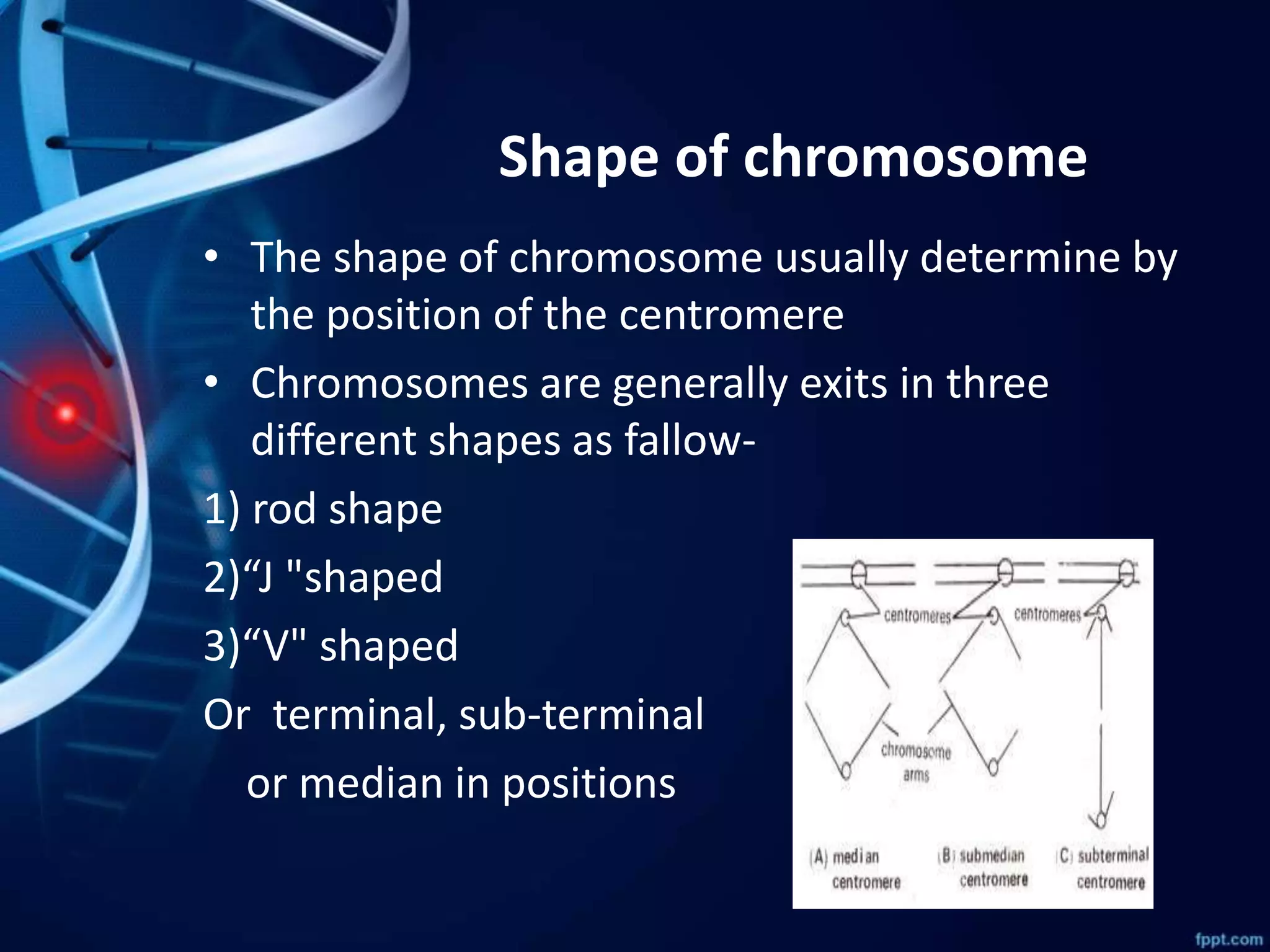
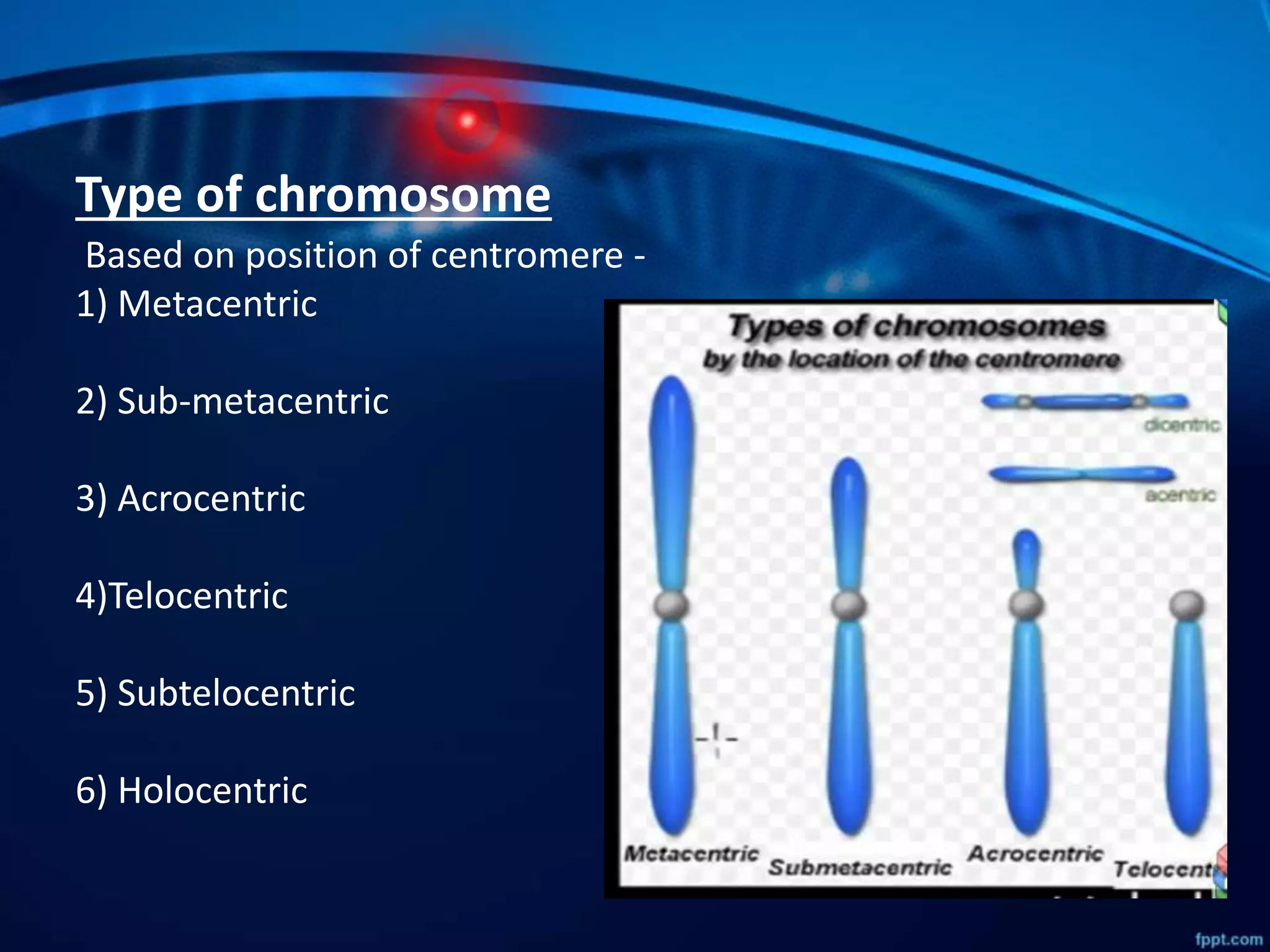
Chromosomes are thread-like structures found within cell nuclei that package DNA. They are only visible during cell division. Species have characteristic chromosome numbers that vary, with humans having 46. Chromosomes exist in rod, J, or V shapes depending on centromere position. Human chromosomes include autosomes and allosomes (X and Y sex chromosomes) and differ in centromere number and position.


![ Chromosome number
• Each species has its own characteristic number of
chromosomes and varies from some species to species.
• Sexually reproducing species Somatic or body cells, which
are DIPLOID [2n] having two sets of chromosomes, one
from the mother and one from the father
• Asexually reproducing species have one set of
chromosomes that are the same in all body cells. However,
asexual species
can be either haploid or diploid
Organisms Chromosom
e no
Human 46
Chimpanzee 48
House mouse 40
Maize 20
Concept of
1)euploidy
2)aneuploidy](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chromosomeppt-181027100657/75/Chromosome-shape-and-size-ppt-3-2048.jpg)