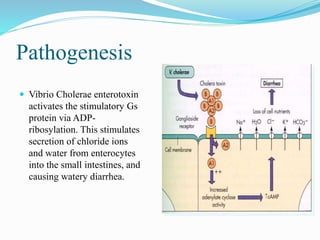
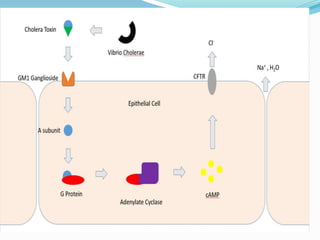
Vibrio cholerae is a Gram-negative, comma-shaped bacterium that is the cause of cholera. It produces a cholera toxin that increases cyclic AMP in intestinal cells, causing an efflux of chloride ions and water into the intestines and resulting in profuse watery diarrhea. Transmission occurs through ingestion of food or water contaminated with the feces or vomit of infected individuals. Treatment focuses on oral rehydration with fluids and electrolytes as well as antibiotics like doxycycline.