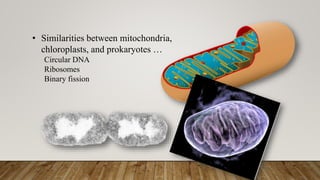
Plastids are membrane-bound organelles found in plant and algal cells that often contain pigments used in photosynthesis. There are several types of plastids that serve different functions: chloroplasts contain chlorophyll and are the site of photosynthesis; chromoplasts contain carotenoids and synthesize and store pigments; gerontoplasts are involved in chloroplast degradation during senescence; and leucoplasts like amyloplasts, elaioplasts, and proteinoplasts store starches, lipids, and proteins respectively. It is believed that plastids evolved from endosymbiotic cyanobacteria that were engulfed by plant cells and eventually became specialized organelles.