The document provides a comprehensive overview of nursing management for patients with chickenpox and smallpox, detailing definitions, causative agents, risk factors, transmission modes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention methods. It emphasizes the importance of vaccination, patient education, and supportive nursing interventions while comparing the two diseases in terms of their clinical manifestations and management. Additionally, it includes specific medical management strategies for chickenpox and highlights the historical context of smallpox eradication and current treatments.













![Inhalation of respiratory droplets
Virus infect upper respiratory tract mucosa
Viral proliferation in the regional lymph node of the
URT[ 2-4 days after initial infection]
Virus enters the blood
PRIMARY VIREMIA leads to fever, malaise,fatigue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomteaching1-240609125811-f78636c1/85/chicken-pox-and-small-pox-management-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![Virus starts to target lymphocytes in order to multiply
and spread even further
Viral replication in other organs [ liver and spleen]
Stage of secondary viremia at 14-16
days
Diffuse viral invasion of capillary endothelial cells and the epidermis
Viral infection of epidermal cells produces both intracellular
and intercellular edema resulting in vesicle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomteaching1-240609125811-f78636c1/85/chicken-pox-and-small-pox-management-pptx-17-320.jpg)

![SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
PRE-ERUPTIVE STAGE [ BEFORE THE ONSET OF RASHES]
Mild or moderate fever usually 1-2 days before the onset of
rashes 100-101 Fahrenheit
Pain in the back
Shivering and malaise
Loss of appetite
Headache
Sore throat](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomteaching1-240609125811-f78636c1/85/chicken-pox-and-small-pox-management-pptx-19-320.jpg)
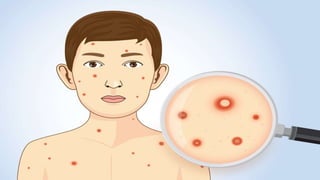
![ERUPTIVE STAGE
In children, Rash is often the first sign it comes on the day fever
starts usually during the secondary viremia stage [14- 16 days ]
1. DISTRIBUTION:
Rashes are symmetrical they first appear on the trunk where it
is abundant, then come on arms, face, and legs where it is less
abundant. Rashes also appear on the mucosal surface of the
buccal and pharyngeal.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomteaching1-240609125811-f78636c1/85/chicken-pox-and-small-pox-management-pptx-20-320.jpg)

![RAPID EVOLUTION
The rashes advance quickly through the stages
of Macule [small patches of skin that are altered in colour
but not elevated], Papules [ elevated solid lesion of skin less
than 1 cm ] Vesicles[ a thin-walled sac filled with a fluid,
usually clear and small less than 1 cm ] with in 24 hours.
The vesicles may form a crust without going
to pustular stage. Usually, they are superficial in site ,with
easily ruptured wall](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomteaching1-240609125811-f78636c1/85/chicken-pox-and-small-pox-management-pptx-22-320.jpg)



![PLEOMORPHISM
A characteristic feature of the rashes in
chickenpox is pleomorphism. That is all stages of rash
[papules, vesicles, and crusts] present simultaneously at one
time in the same area. This is due to rashes appearing
continuously for 4-5 days in the same area](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomteaching1-240609125811-f78636c1/85/chicken-pox-and-small-pox-management-pptx-26-320.jpg)
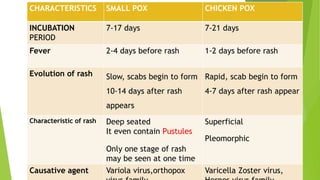
![The incubation period of chicken pox is about 15
days [range 7-21 days]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomteaching1-240609125811-f78636c1/85/chicken-pox-and-small-pox-management-pptx-27-320.jpg)

![DIAGNOSIS
• Chickenpox can be diagnosed with its classical symptoms
through physical examination
• Microscopic examination of the skin lesion can be done
for laboratory confirmation of the disease
• Examination of vesicle fluid under an electron microscope
• Detection of viral DNA by PCR [ Polymerase Chain
Reaction ]
• Serology to assess antibodies usually [IgG present against
VZV virus]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomteaching1-240609125811-f78636c1/85/chicken-pox-and-small-pox-management-pptx-29-320.jpg)






![STOCK PILES
Since 1984, small pox virus has been held in just
two places in world at
United States Centre for disease control and
prevention laboratory in Atlanta, Vector laboratory
Russia
Due to bioterrorism now they invented Antiviral
drug Tecovirimat [July2018 ] and Brincidovir [2021]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomteaching1-240609125811-f78636c1/85/chicken-pox-and-small-pox-management-pptx-38-320.jpg)










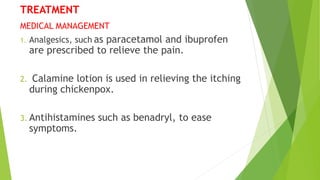
![QUESTIONS
1) Mention any two risk factors of chickenpox?
2) What are the stages of chicken pox symptoms?
3) Mention any two medical management for chickenpox ?
4) Mention any two complications of chicken pox?
5) Difference between smallpox and chicken pox [two point]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classroomteaching1-240609125811-f78636c1/85/chicken-pox-and-small-pox-management-pptx-50-320.jpg)


