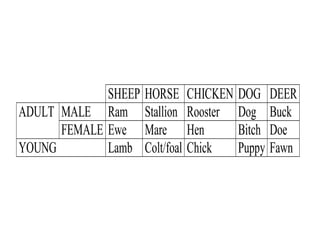
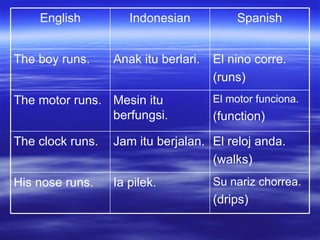
Characteristics of language that affect translation include:
1) Meaning components are packaged differently across languages. For example, the word for projector is described differently in Chipaya than English.
2) The same meaning can be expressed through multiple lexical items. In Indonesian there are several words that can be used to describe different ways of carrying something.
3) Individual words can have both primary and secondary meanings that become clear through context. The word "we" takes on different meanings depending on how it's used in a sentence.