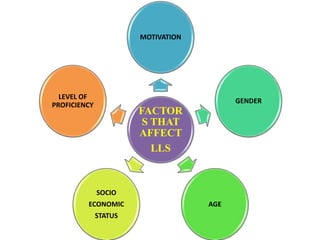
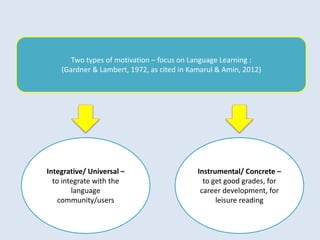
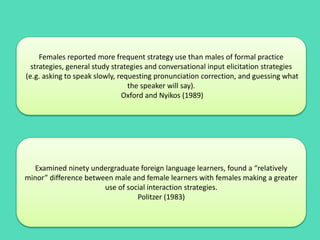
The document discusses various factors affecting language learning strategies (LLS), including motivation, gender, age, socioeconomic status, and proficiency level. Motivation is identified as the most significant factor influencing the choice of LLS, with gender differences noted in strategy usage, while socioeconomic status impacts access to learning resources. Proficient learners tend to employ a wider range of strategies compared to less proficient learners, highlighting the role of individual background in language acquisition.














![REFERENCES
Adel, A. R. 2011. Effects of L2 proficiency and gender on choice of language learning strategies by
university students majoring in English. The Asian EFL Journal Quarterly. 13 (1), 114-162. From
http://www.asian-efl-journal.com/PDF/March-2011.pdf#page=114 [March 25, 2014].
Farzad, S., Mahnaz, S. & NedaSalahshour. 2013. The relationship between language learning strategy
use, language proficiency level and learner gender. Procedia-Social and Behavioural Sciences 70.
634-643. From http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1877042813001043 [March 25, 2014]
Hong-Nam, K. & Leavell, A.G. 2006. Language learning strategy use of ESL students in an intensive Eng-
lish learning context. System 34: 399–415
Kamarul Shukri Mat Teh & Mohamed Amin Embi. 2012. Variasi Penggunaan Strategi Pembelajaran
Bahasa. Dlm. Strategi Pembelajaran Bahasa, hlm. 79-105. Kuala Lumpur: Penerbit Universiti Malaya
Karim Sadeghi & Mohammad Taghi Attar. 2013. The relationship between learning strategy use and
starting age of learning EFL. Procedia-Social and Behavioural Sciences 70. 387- 396. From
http://ac.els-cdn.com/S1877042813000773/1-s2.0-S1877042813000773- main.pdf?_tid=36c013ce-
b0a5-11e3-8861- 00000aab0f6b&acdnat=1395371118_c98afd0973232170bc0f6378edcf21d0
[March 20, 2014]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/factorsaffectlls-150401104917-conversion-gate01/85/5-Factors-that-Affect-Language-Learning-Strategies-18-320.jpg)
![Khamkhien, A. 2010. Factors affecting language learning strategy reported usage by Thai and Vietnamese EFL students.
Electronic Journal of Foreign Language Teaching. 7(1), 66- 85. From http://e-
flt.nus.edu.sg/v7n12010/khamkhien.pdf [March 20, 2014]
MacLeod, P. 2002. Take two language learners: A case study of the learning strategies of two successful learners of
English as a second language with instrumental motivation. Journal of Language and Linguistics 1: 1–13
Mohammad Rahimi, Abdolmehdi Riazi & Shahrzad Saif. 2008. An investigation into the factors affecting the use of
language learning strategies by Persian EFL learners. Canadian Journal of Applied Linguistics (CJAL). 11(2), 31-60.
From http://journals.hil.unb.ca/index.php/CJAL/article/view/19915/21770 [March 20, 2014]
O’Malley, J.M., Chamot, A.U., Stewner-Manzanares Küpper G.L., & Russo, R.P. 1985. Learning strategies used by beginning and intermediate
ESL students. Language Learning 35: 21–46
Oxford, R. 1994. Language Learning Strategies: An Update. ERIC Digest. From
http://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED376707.pdf [March 22, 2014]
Paul, P. 2011. Use of language learning strategies: an investigation of the use pattern of language learning strategies of
Bangladeshi learners and its correlation with the proficiency level. Thesis submitted to the Department of English
and Humanities of BRAC University In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Arts in
Applied Linguistics and ELT
Tam, K. C. 2013. A study on Language Learning Strategies (LLSs) of university students in Hong Kong. Taiwan Journal of
Linguistics, 11(2), 1-42. From http://tjl.nccu.edu.tw/volume11- 2/11.2.1.pdf [March 26, 2014]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/factorsaffectlls-150401104917-conversion-gate01/85/5-Factors-that-Affect-Language-Learning-Strategies-19-320.jpg)
