Embed presentation
Downloaded 73 times

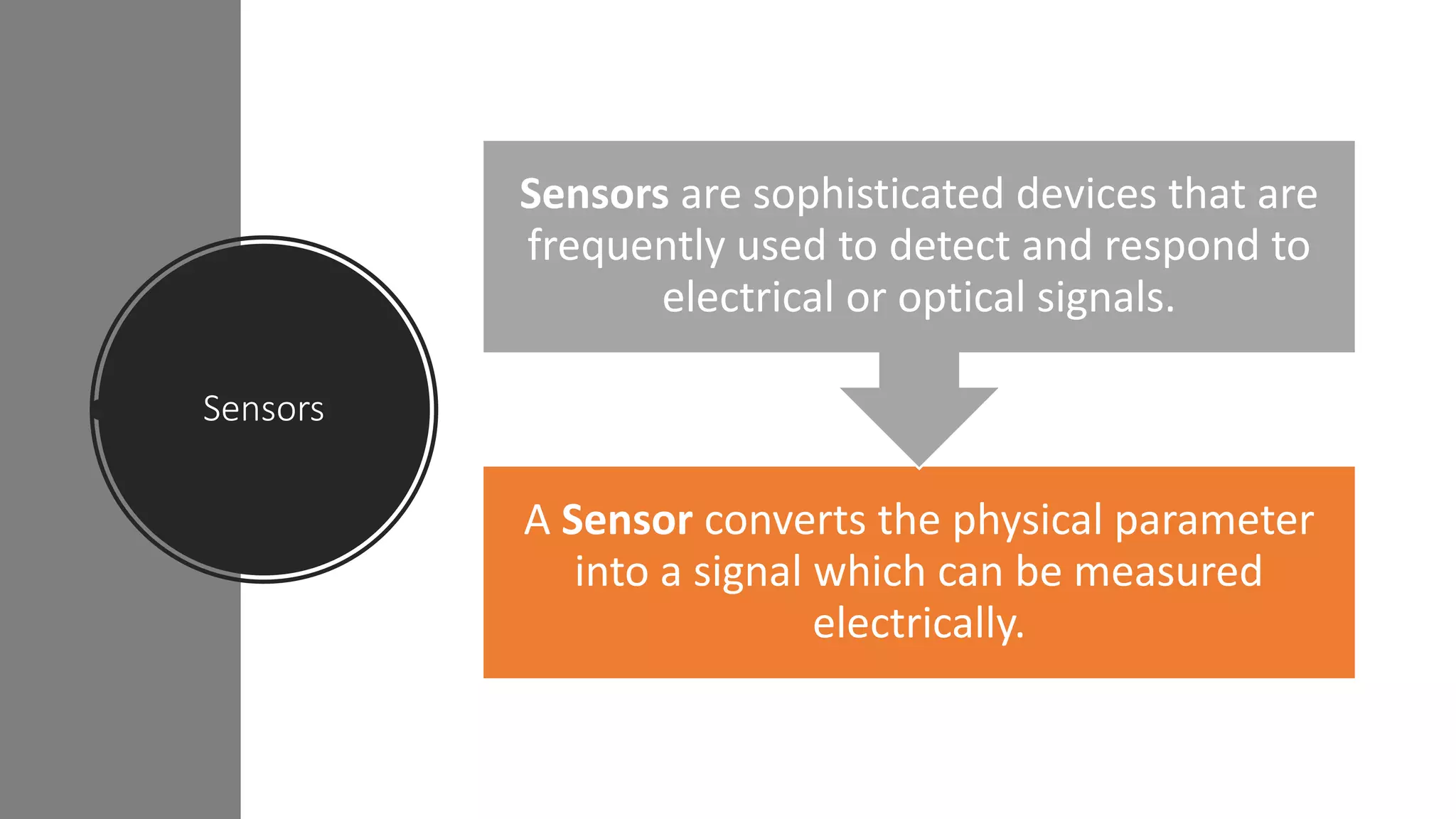

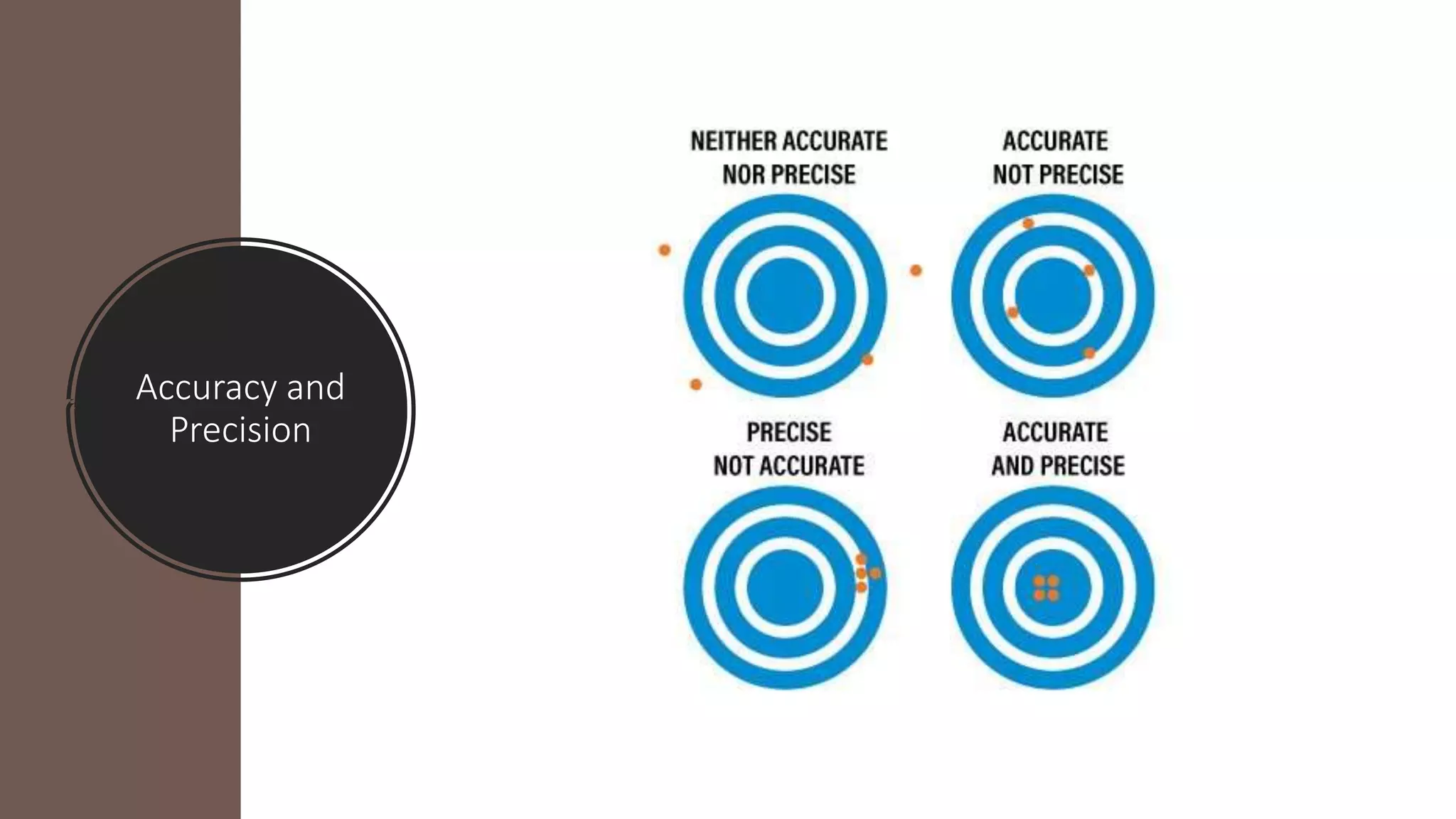


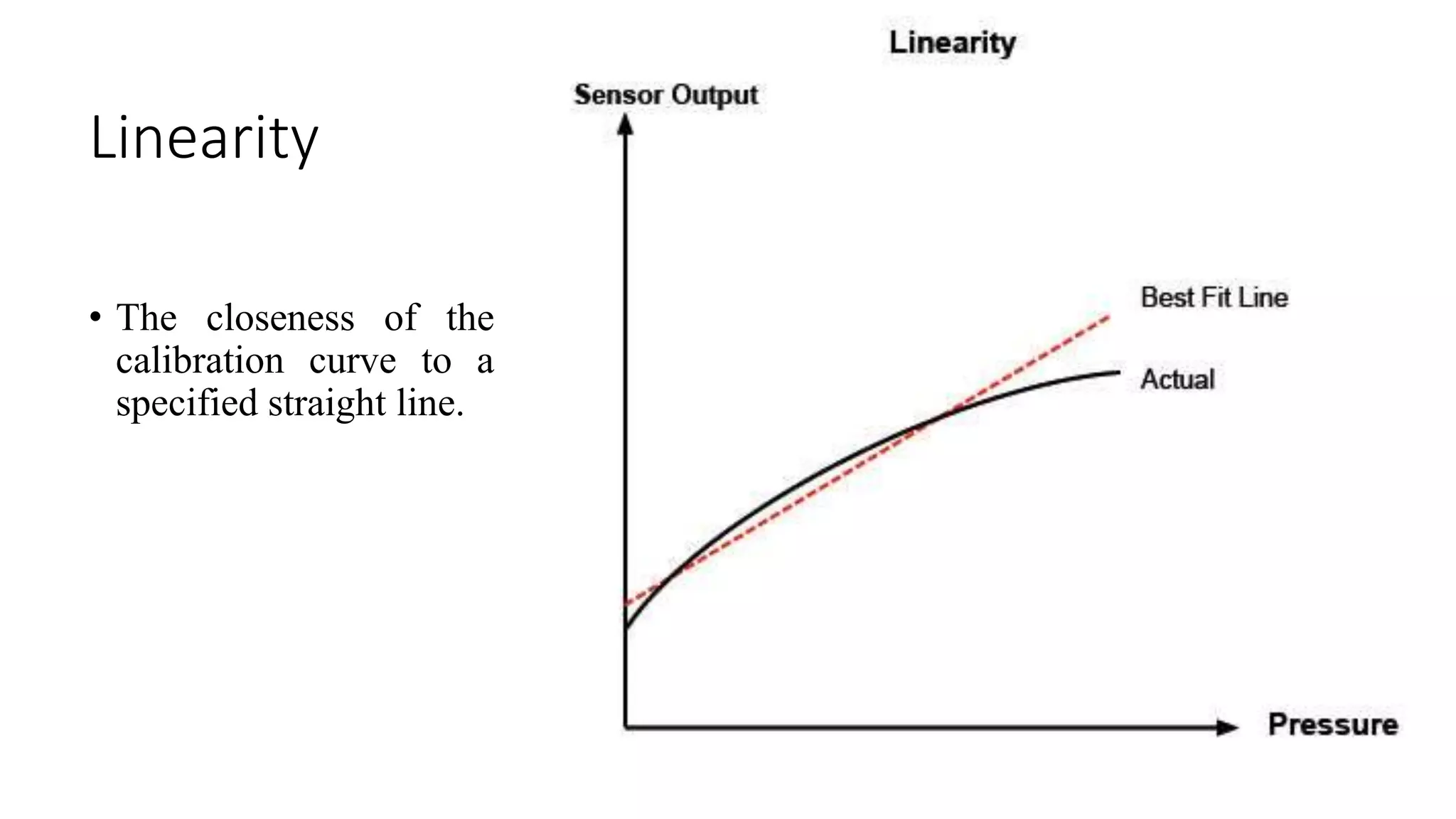
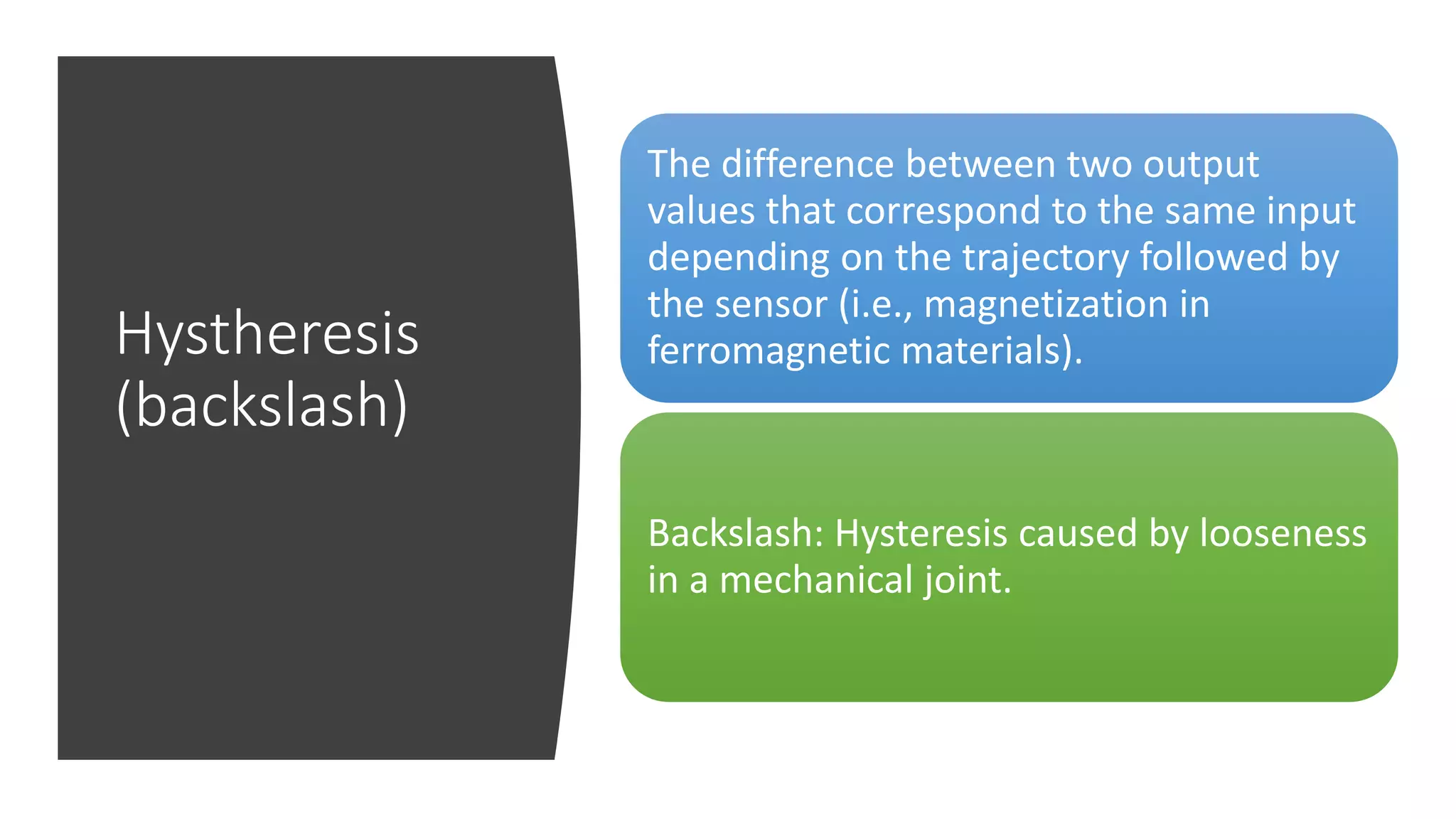


The document discusses the characteristics and selection criteria for sensors, which convert physical parameters into measurable electrical signals. Key characteristics include accuracy, precision, sensitivity, linearity, and hysteresis, while selection criteria encompass environmental conditions, calibration, resolution, cost, and repeatability. Understanding these factors is essential for effectively choosing and utilizing sensors in various applications.









