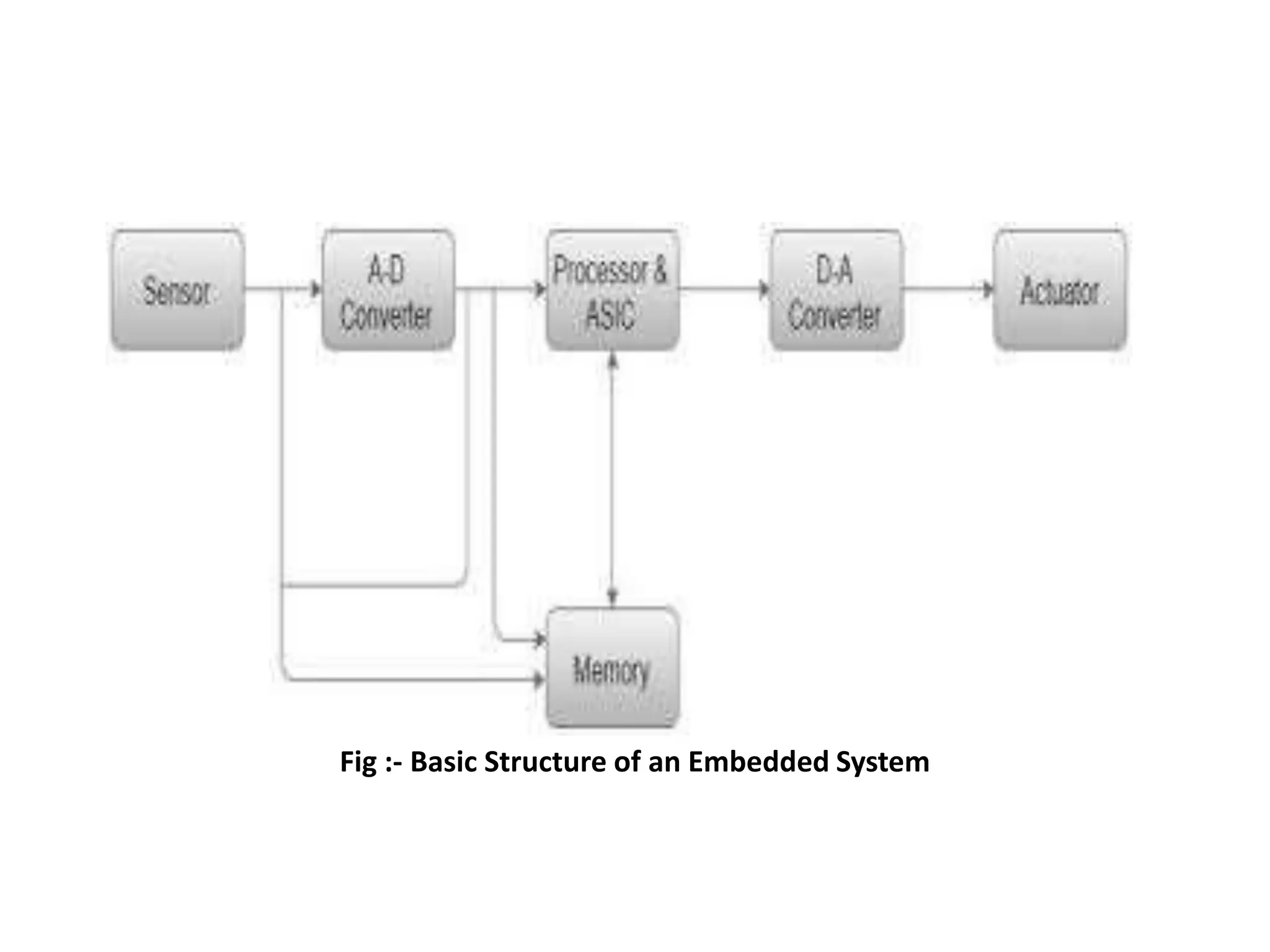
The document discusses emerging trends in computer engineering, specifically focusing on the Internet of Things (IoT). It defines embedded systems and their basic components. It then discusses IoT in depth, including its characteristics, enabling technologies, communication models, protocols, issues, and applications in various domains. The document also discusses embedded processors, cloud computing, and big data analytics as relevant technologies in computer engineering.