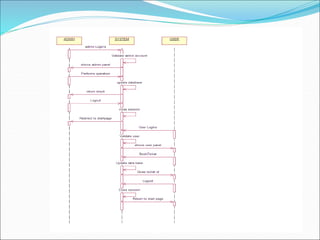
This document describes an airline reservation system that manages flight schedules, fares, passenger reservations, and tickets. It divides airline inventory into classes like economy, business, and first class with different prices and booking conditions. The system includes modules for registration, administration, and passengers. The registration module allows passengers to create accounts. The administrative module manages flight data and bookings. The passenger module lets users view flight schedules and book/cancel tickets.