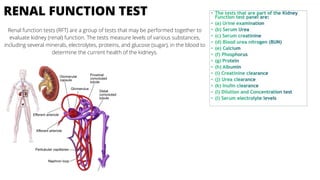
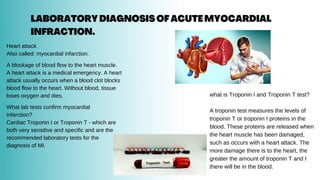
Sakshi Shah conducted a seminar on different diagnostic methods and tests in pathology guided by Dr. Rohini Thakare and Dr. Sachin Agrawal. The seminar covered various lab tests including HB test, laboratory diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction using troponin tests, fine needle aspiration biopsy, Widal test, gram staining for diagnosis of infections, laboratory diagnosis of malaria, diabetes, pyogenic meningitis, BTCT, lepromin test, renal function tests, VDRL test for syphilis, and urine examination.


![FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION BIOPSY
what is fine needle aspiration
biopsy?
During a fine needle aspiration
(FNA), a small amount of
breast tissue or fluid is
removed from a suspicious
area with a thin, hollow needle
and checked for cancer cells.
Applications of needle aspiration biopsy
1] palpable mass lesions -
a] lymph node .
b] breast
c]thyroid
d] salivary glands
e]soft tissue masses
f] bones](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-221101164908-3239a1d4/85/SEMINAR-pdf-5-320.jpg)
![Non palpable mass lesions in-
a]Abdominal cavity
liver mass.
pancreatic mass
retroperitonel masses
b]Thorasic cavity masses-
lung mass
mediastinum mas
c]Scrotal FNAC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seminar-221101164908-3239a1d4/85/SEMINAR-pdf-6-320.jpg)