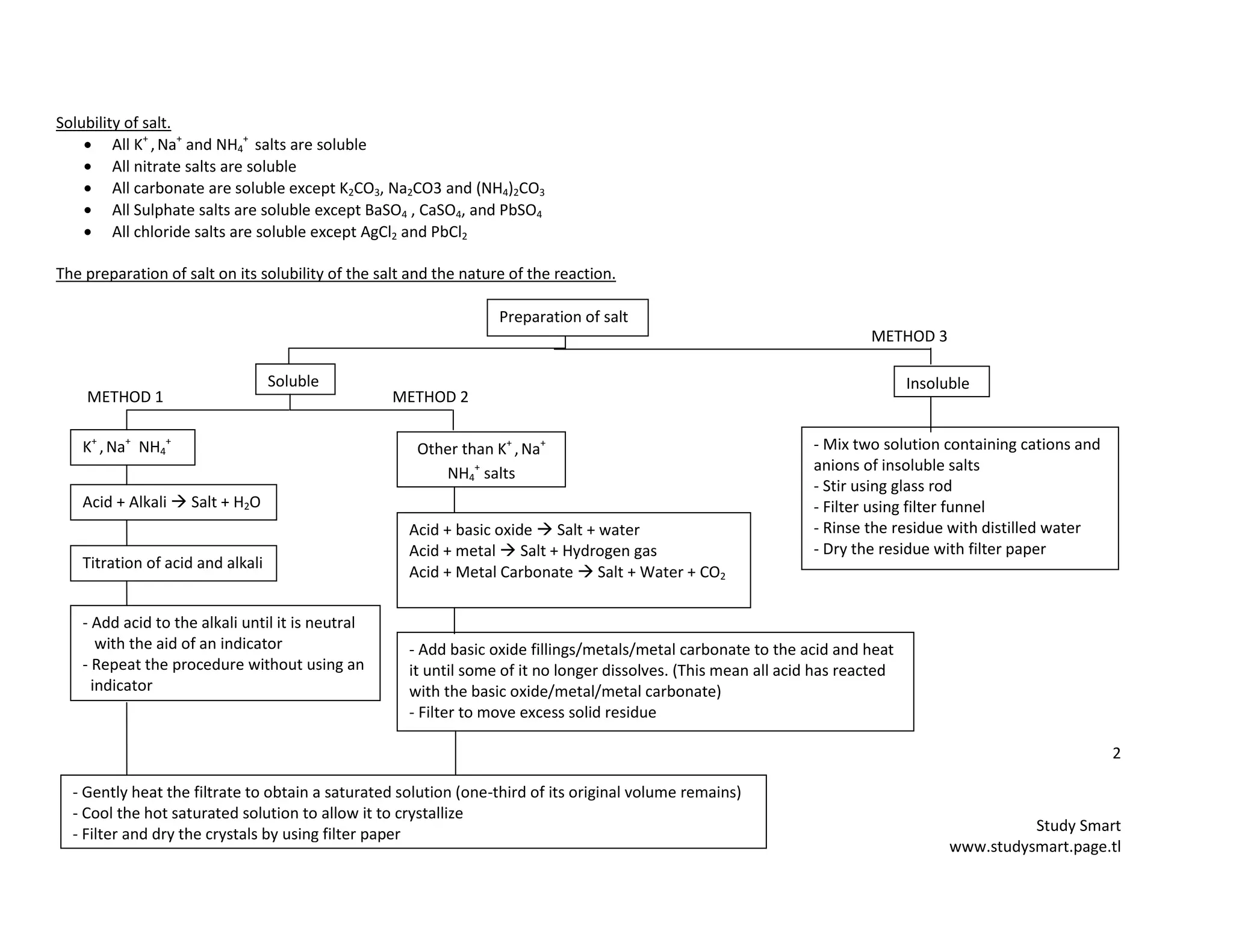
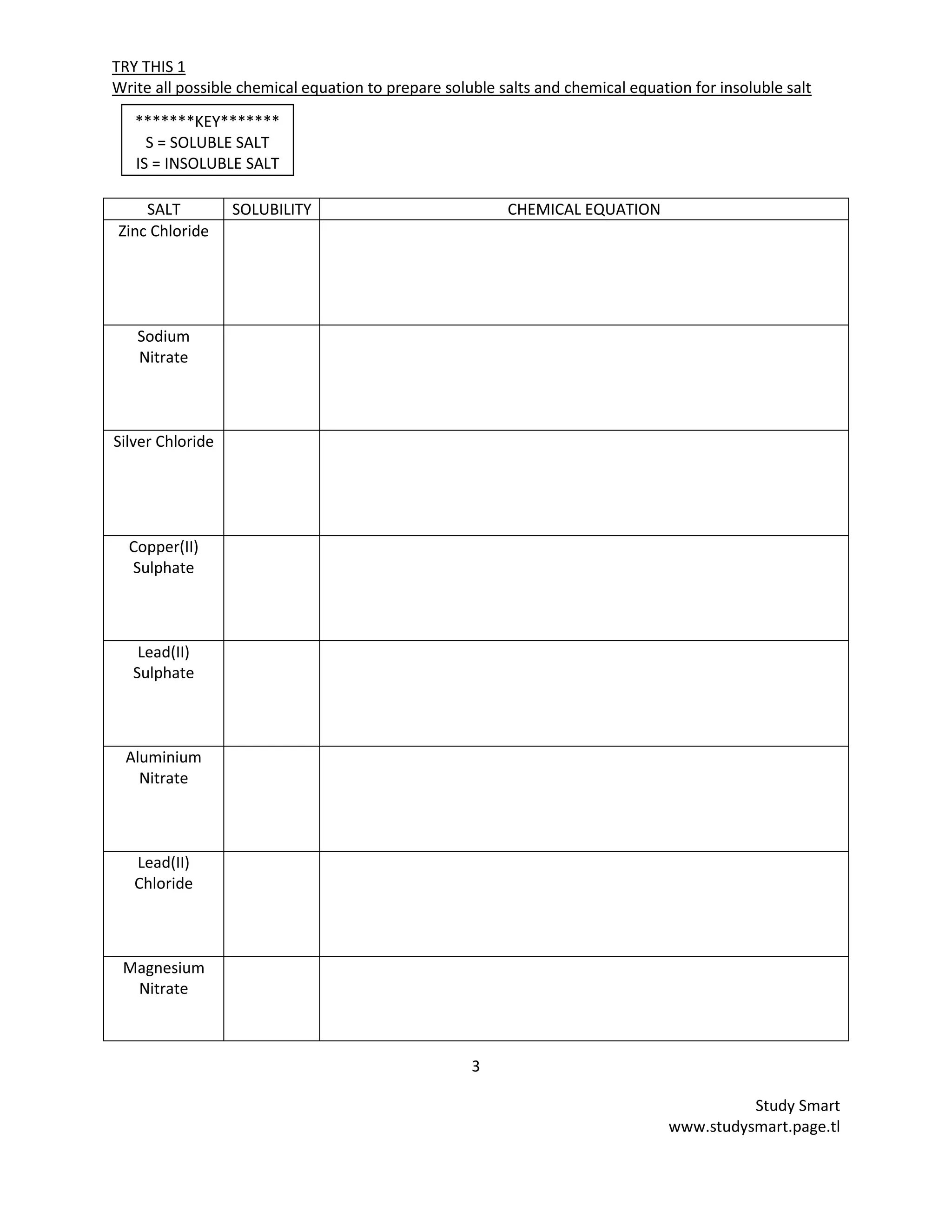
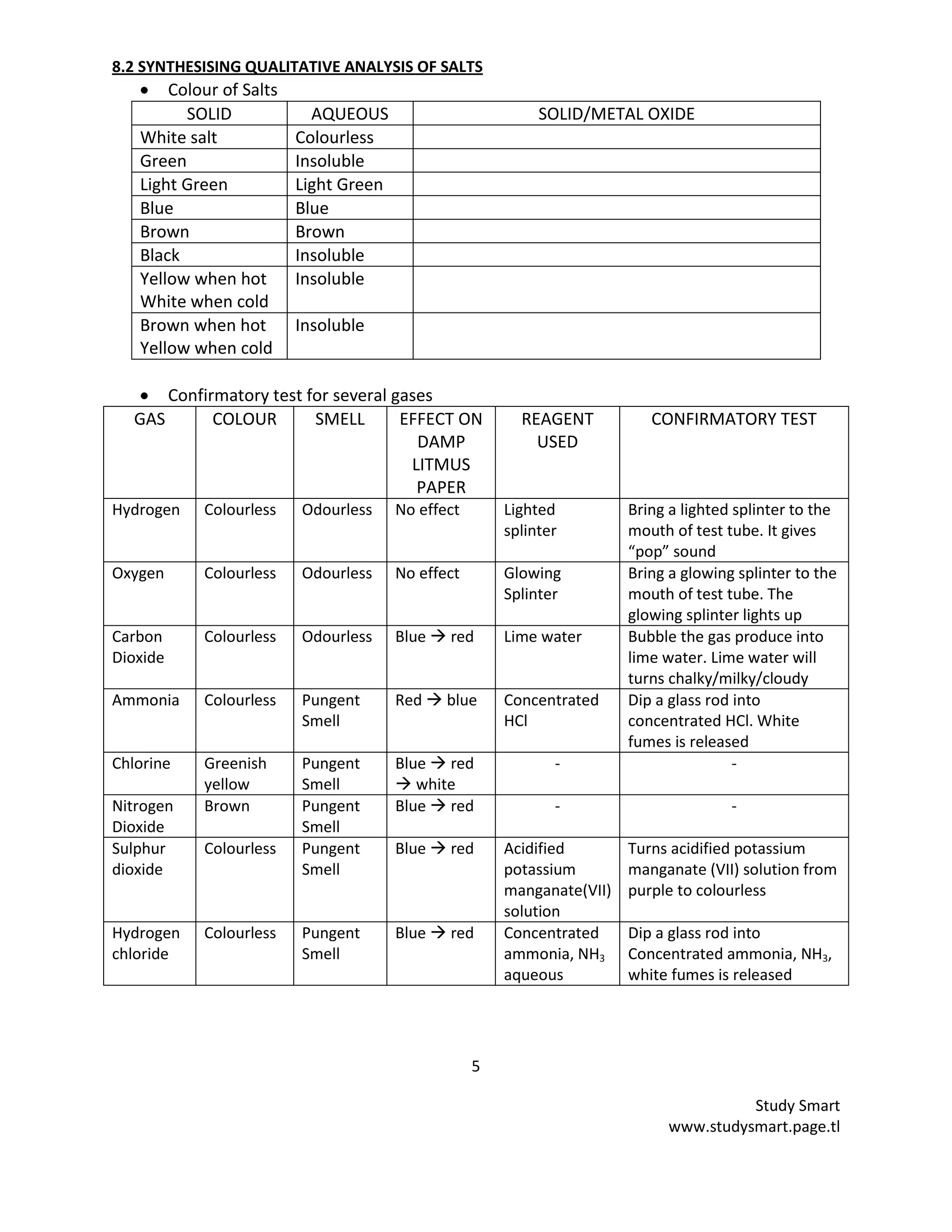
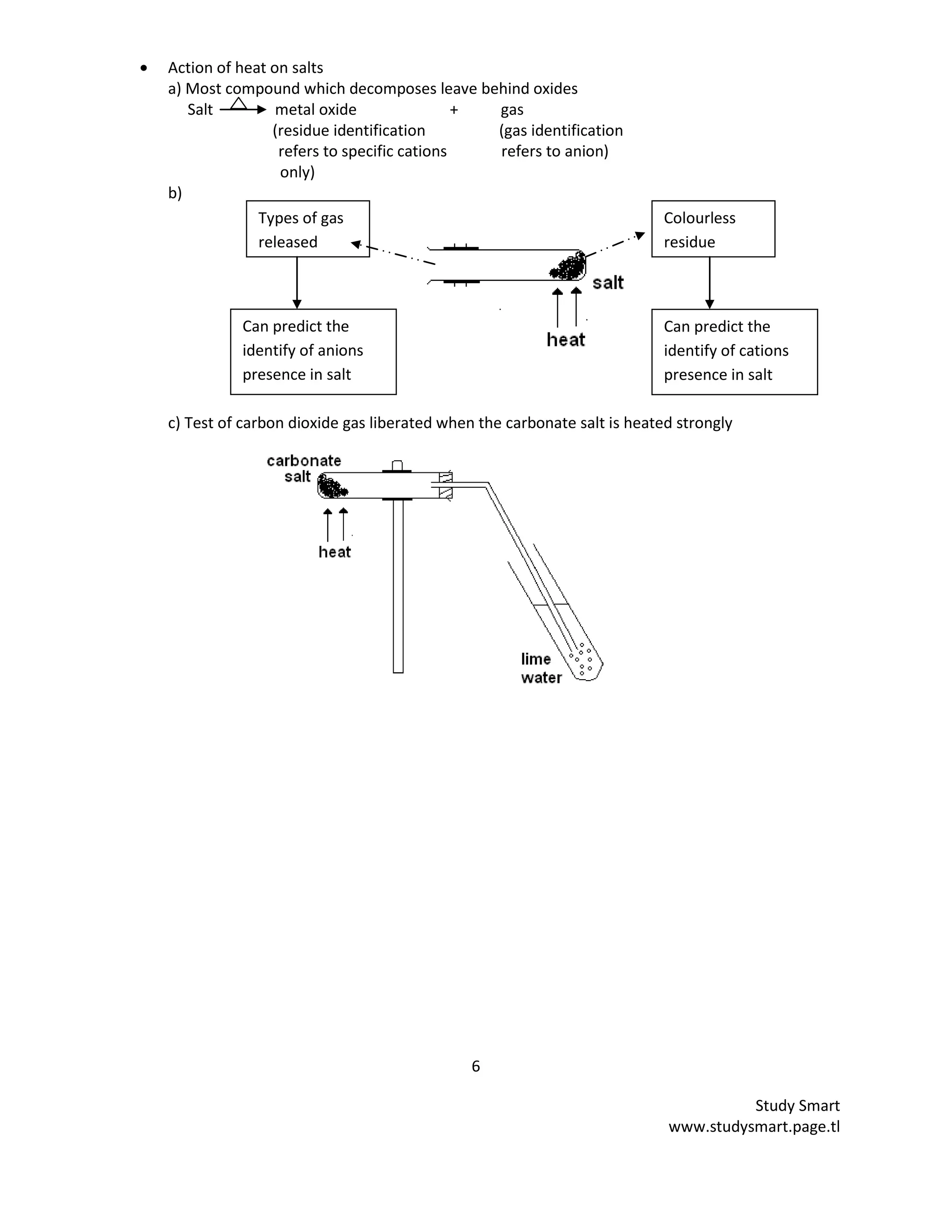
This document provides information on synthesizing and qualitatively analyzing salts. It discusses how salts are formed by replacing hydrogen ions in acids with metal ions or ammonium ions. Common salt reactions and solubility rules for various salts are presented. Methods for synthesizing soluble and insoluble salts are described. Qualitative salt analysis involves tests to identify cations using sodium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide solutions and tests to identify anions using reagents like barium chloride and silver nitrate solutions. Color changes, gas evolution and precipitate formation are observed to determine the present ions.

![4
Study Smart
www.studysmart.page.tl
Potassium
Chloride
Lead(II)
Nitrate
Barium
Sulphate
Ammonium
Sulphate
Numerical problem involving stoichiometry reactions in the preparation of salts
A student prepare copper(II) nitrate, Cu(NO3)2 by reacting copper(II) oxide, CuO with 100 cm3 of 1.5
mol dm-3
nitric acid, HNO3. Calculate the mass of copper(II) oxide, CuO needed to react
completely with the acid. [RAM : Cu,64 ; O,16]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studysmartchapter8-121211185514-phpapp02-160827081650/75/Studysmartchapter8-121211185514-phpapp02-4-2048.jpg)
![7
Study Smart
www.studysmart.page.tl
d) Write down the chemical equation for the reactions that occur.
Ion Carbonate Salt Nitrate Salt
Is not decomposed by heat Decompose into O2 gas and metal nitrate
K+
Na+
Ca2+
Decompose into metallic oxide and CO2 Decompose into metal oxide, NO2 and O2
Mg2+
Al3+
Zn2+
Fe2+
Fe3+
Pb2+
Cu2+
Sulphate salts usually do not decompose
Chloride salts do not decompose except NH4Cl
NH4Cl (s) NH3 (g) + HCl (g) [sublimation]
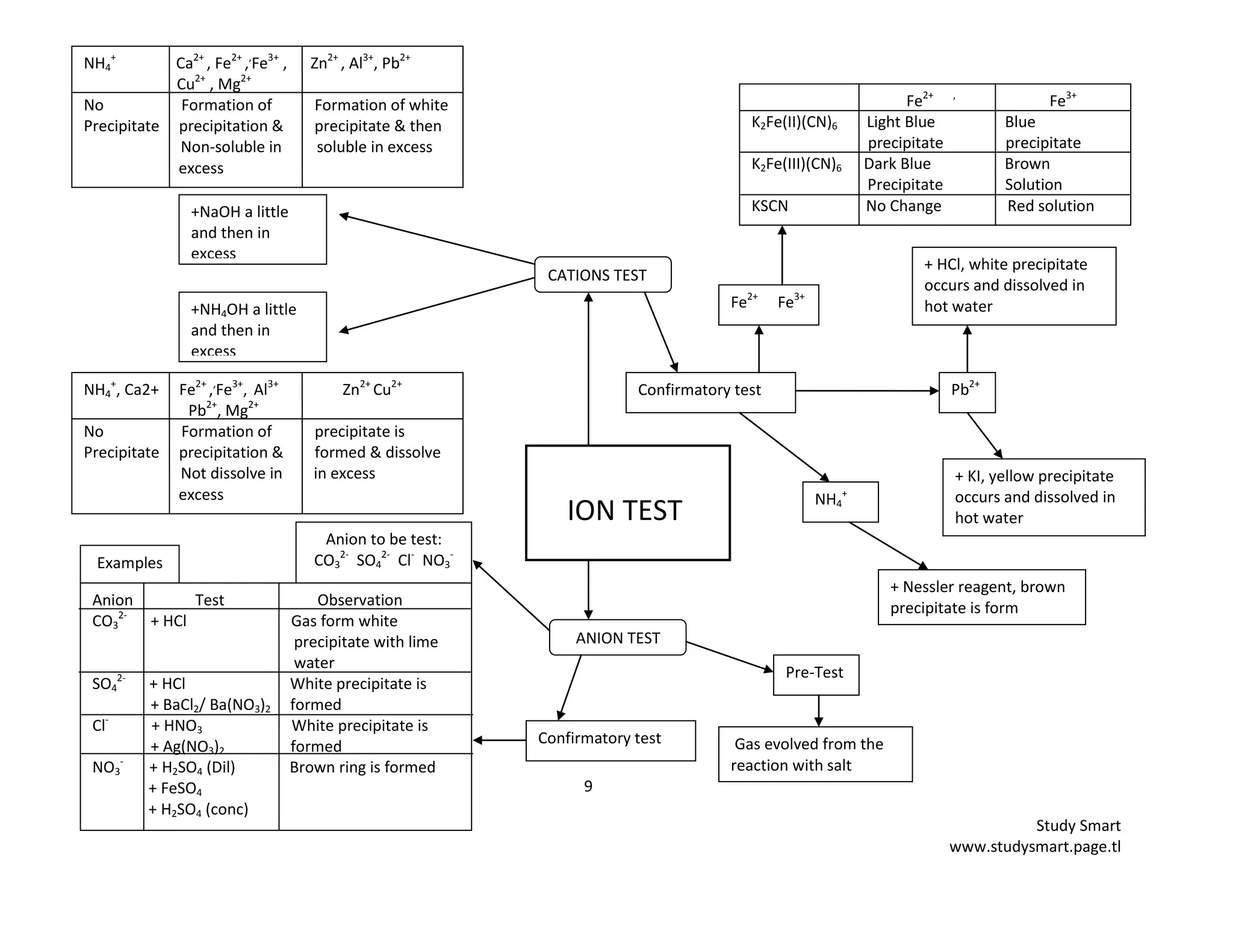
Confirmatory test for anions
+ H2SO4 dilute
+ dilute +HNO3 + HNO3 + FeSO4
acid + AgNO3 + Ba(NO3)2 + H2SO4 conc
Confirmatory test for cations
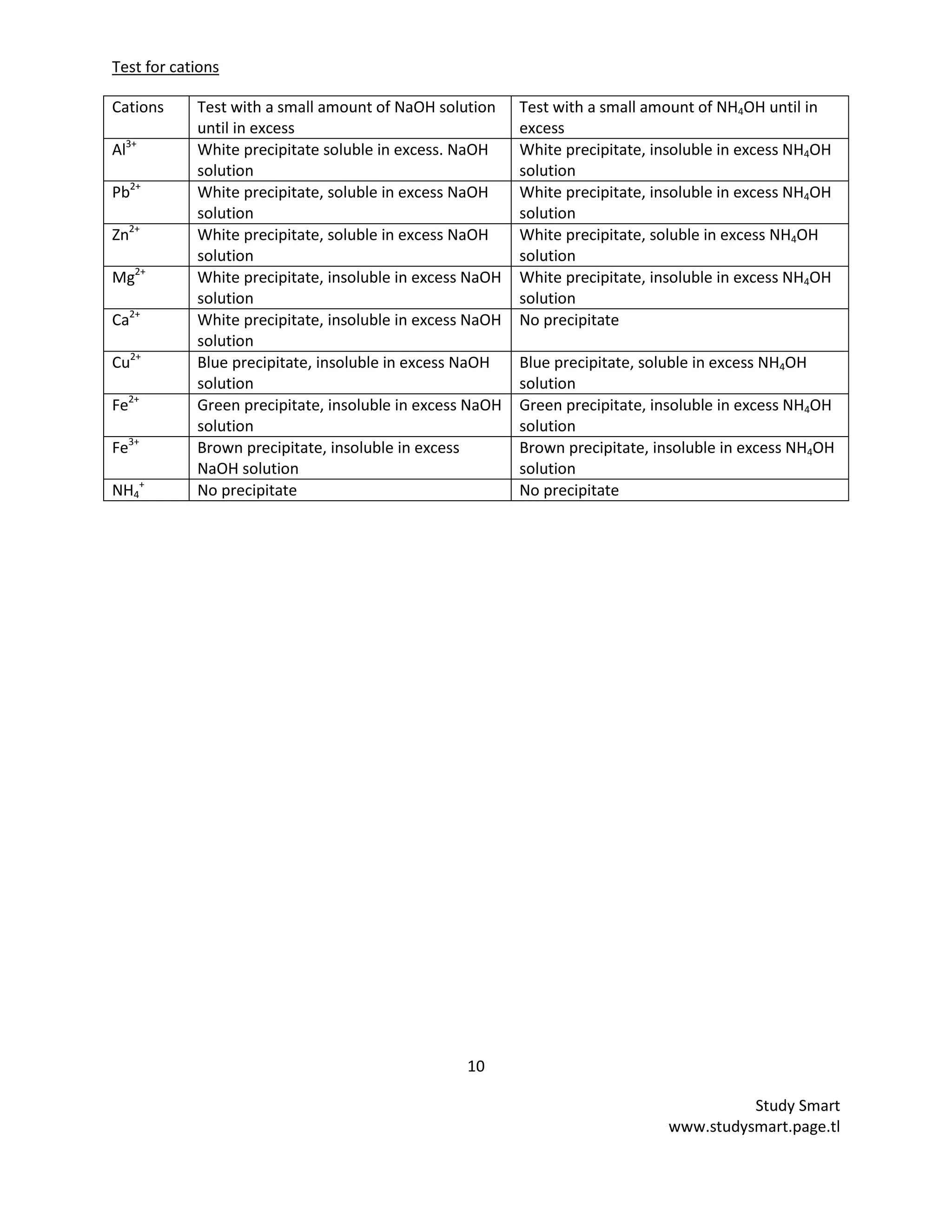
a) The presence of cation can be detected by using two common bench alkalis namely
i) _____________________________ solution
ii) _____________________________ solution
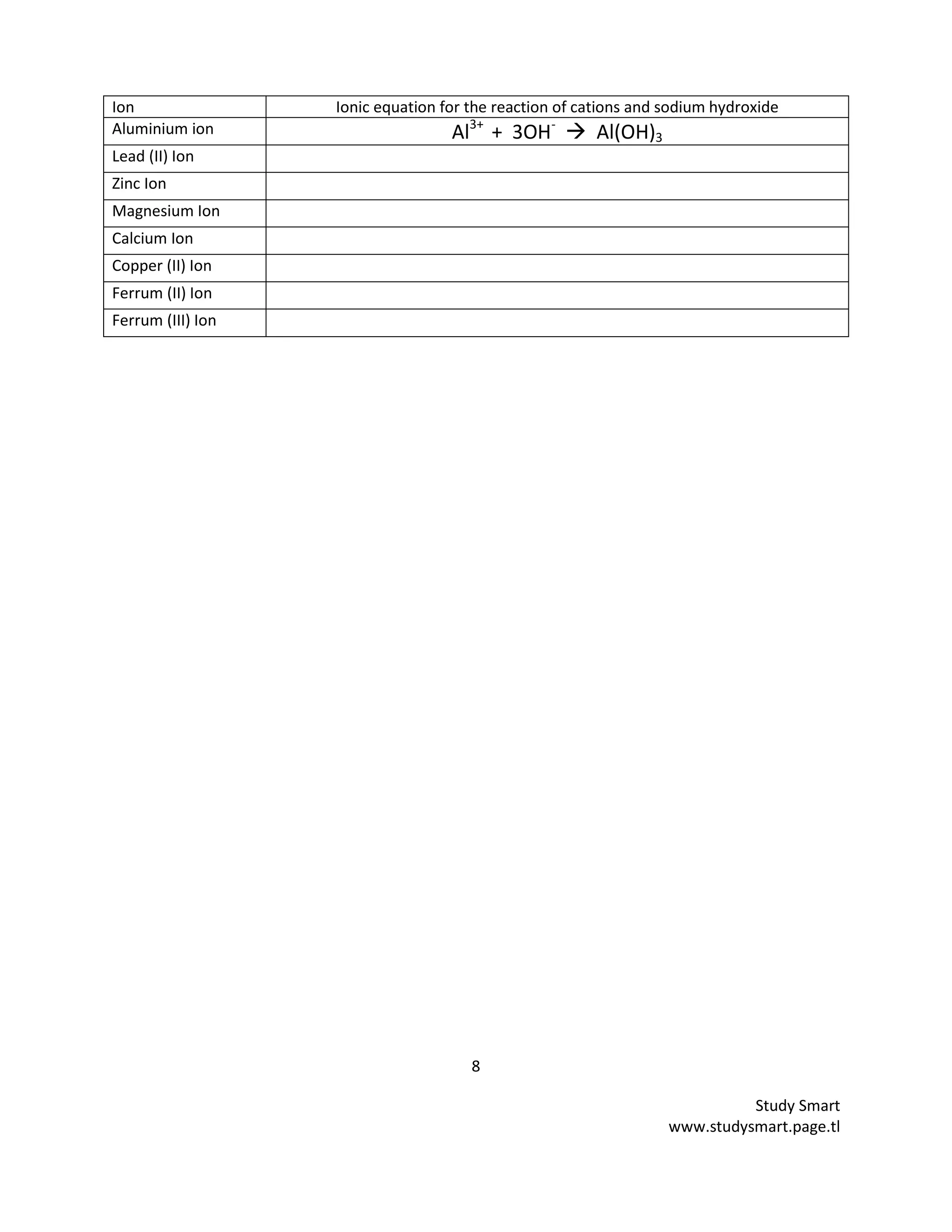
b) Write the ionic equation for the reaction of cations and sodium hydroxide
Unknown Salt Solution
Gas turns
limewater
__________
__________
Precipitate
formed
__________
precipitate
formed
________
________
__
The function of the alkalis is to produce a precipitate that is
Metal hydroxide
METAL + HYDROXIDE ION METAL HYDROXIDE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/studysmartchapter8-121211185514-phpapp02-160827081650/75/Studysmartchapter8-121211185514-phpapp02-7-2048.jpg)