The document describes procedures for identifying an unknown salt sample. Various tests are performed to identify the cation and anion present in the salt. Cation tests include adding reagents like sodium hydroxide, ammonium chloride and ammonium hydroxide to observe color changes or precipitate formation. Anion tests involve adding acids or bases and observing gas evolution or precipitate formation. Confirmatory tests are also outlined to verify the identity of ions like chloride, nitrate, sulfate and acetate. A list of common salts is presented with their chemical formulae and physical states.
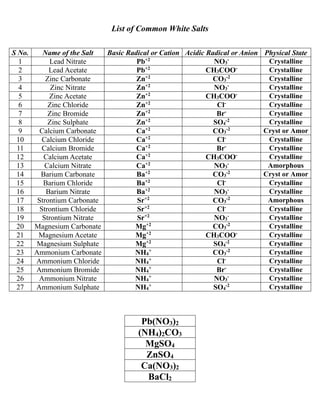
![Salt Analysis
S.no Experiment Observation Inference
1. Preliminary Tests
1) Colour:
Blue or Bluish green, Light Green, Light
pink, Greenish, Pink.
May be Cu+2, Fe+2, Mn+2,
Ni+2, Co+2 Salts.
Colourless Absence of the above salts.
2) Physical state: Crystalline / Amorphous -
3)
Action of heat:
A pinch of salt is taken in a dry
test tube & heated strongly.
White sublimate is formed. May be NH4
+ salt.
Reddish brown vapours are evolved. May be NO3
- salt.
Crackling sound is observed. May be Pb+2 salt.
Characteristic vinegar like smell. May be CH3COO- salt.
Yellow when hot & white when cold. May be Zn+2 salt.
Water drops are formed along the inner
walls of the test tube.
May be hydrated salt.
4)
Flame test:
A paste of salt with Con.HCl is
prepared & put on top of the
flame.
i) Brick red flame May be Ca+2 salt.
ii) Apple green flame May be Ba+2 salt.
iii) Crimson red flame May be Sr+2 salt.
iv) Green flashes May be Zn+2 salt.
v) Dull Bluish White May be Pb+2 salt.
No characteristic flame is observed. Absence of the above salts.
2. Identification of Anion
1)
Test with dil.HCl:
A pinch of salt is taken in a dry test
tube & dil.HCl is added to it.
i) Colourless & Odourless gas of CO2 is
evolved with brisk effervescence which
puts out flame & turns lime water milky.
CO3
-2 may be present.
ii) Colourless vapours of CH3COOH with
vinegar smell are evolved, which turns
blue litmus red.
CH3COO- may be present.
No characteristic reaction was observed. CO3
-2 & CH3COO- (Absent)
2)
Test with Con.H2SO4:
Take a small quantity of salt in a
dry test tube & add Con.H2SO4.
i) Colourless gas with pungent smell (HCl)
is evolved. It produced white dense fumes
when a glass rod dipped in NH4OH is
placed at the mouth of the test tube.
Cl- may be present.
ii) Reddish brown vapours with pungent
smell (Br2) are evolved.
Br- may be present.
No characteristic reaction is observed. Cl- & Br- are absent.
3)
Test with BaCl2:
To the salt solution add BaCl2
solution.
White crystalline precipitate (BaSO4) is
formed.
SO4
-2 may be present.
No precipitate is formed. SO4
-2 is absent.
4)
Test with Con.H2SO4 [Hot Condition]:
Take a small quantity of the salt in a
test tube, add Con.H2SO4 & heat it.
Reddish brown vapours of NO2 are
evolved.
NO3
- may be present.
Reddish brown vapours of NO2 are not
evolved.
NO3
- is absent.
Test with Copper turnings &
Con H2SO4:
Take a small quantity of the salt in
a test tube, add Copper turnings,
Con. H2SO4 & heat it strongly.
Deep reddish brown vapours of NO2 are
evolved & the solution turns pale blue.
NO3
- may be present.
No reddish brown vapours are evolved. NO3
- is absent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saltanalysis2-231006150958-40db1a5f/85/Salt-Analysis-2-0-pdf-1-320.jpg)
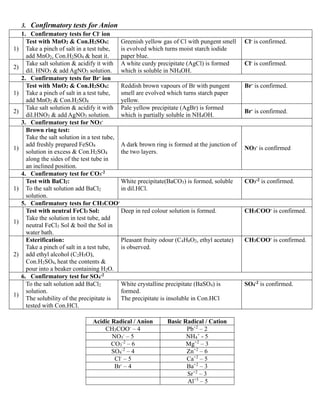
![4. Identification of Cation
1)
Analysis of NH4
+
:
Take a small quantity of salt in a test tube,
add NaOH & heat it.
Colourless gas with characteristic NH4
+
smell
is evolved, which gives dense white fumes
when a glass rod dipped in Con.HCl is
brought near the mouth of the test tube.
NH4
+
may be present.
❖ Preparation of Original solution
1) The salt is dissolved in H2O or dil.HCl solvent. Clear & transparent solution is formed. It is Original solution(O.S).
❖ Analysis of Cation groups
1. Analysis of Group – I
1) To the O.S add dil.HCl. White precipitate is formed. Group-I (Pb+2
) is present
2. Analysis of Group – II
1) To the O.S add dil.HCl and pass H2S gas. Black precipitate is formed. Group-II (Cu+2
) is present
3. Analysis of Group – III
1) To the O.S add solid NH4Cl, excess of NH4OH.
White gelatinous precipitate is formed. Group-III (Al+3
) is present.
Light green precipitate is formed. Group-III (Fe+3
) is present.
4. Analysis of Group – IV
1)
To the O.S add solid NH4Cl, excess of NH4OH
and pass H2S gas.
Flesh Coloured precipitate is formed. Group-IV (Mn+2
) is present.
Black precipitate is formed. Group-IV (Ni+2
) is present.
Dull White precipitate is formed. Group-IV (Zn+2
) is present.
5. Analysis of Group – V
1)
To the O.S add solid NH4Cl, excess of NH4OH
& (NH4)2CO3 solution.
White precipitate is formed.
Group - V (Ba+2
, Ca+2
, Sr+2
) is
present.
5. Confirmatory tests for Cation
1. Confirmatory test for NH4
+
1)
To the salt solution add Nessler’s reagent
(K2[HgI4] /Potassium mercuric iodide).
Reddish brown precipitate (NH2HgOHgI, Iodide of
Millon’s base) is formed.
NH4
+
is confirmed.
2. Confirmatory tests for Pb+2
[Group-I]
1)
Dissolve the white precipitate in hot water
& divide it into two parts.
2)
i) To the 1st
part add K2CrO4 solution.
Yellow precipitate is formed which dissolves in
NaOH solution.
Pb+2
is confirmed.
ii) To the 2nd
part add KI solution.
Yellow precipitate is formed which dissolves in hot
water & on cooling the solution forms golden
spangles.
Pb+2
is confirmed.
3. Confirmatory test for Al+3
[Group –III]
1) To the O.S add NaOH solution.
White gelatinous precipitate is formed, which is
soluble in excess of NaOH.
Al+3
is confirmed.
4. Confirmatory test for Zn+2
[Group –IV]
1) To the O.S add NaOH solution.
White precipitate is formed, which is soluble in
excess of NaOH.
Zn+2
is confirmed.
5. Confirmatory tests for Ba+2
, Ca+2
& Sr+2
[Group -V]
1) To the O.S add K2CrO4 solution.
Yellow precipitate (BaClO4) is formed, which is
soluble in Con.HCl.
Ba+2
is confirmed.
Yellow colour is formed. Ca+2
is confirmed.
2)
To the O.S add (NH4)2SO4 solution & warm
it. Scratch the inner sides of the test tube
with a glass rod.
White precipitate is formed. Sr+2
is confirmed.
6. Confirmatory test for Mg+2
[Group –VI]
1) To the O.S add NH4Cl, NH4OH & Na2PO4. White precipitate is formed. Mg+2
is confirmed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/saltanalysis2-231006150958-40db1a5f/85/Salt-Analysis-2-0-pdf-3-320.jpg)