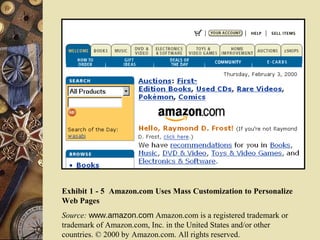
This document discusses e-marketing and provides details on various e-marketing strategies and models. It begins by defining e-marketing as using technology to increase marketing efficiency and profitability. It then covers the ten rules of e-marketing, various e-marketing challenges and opportunities, different online marketing methods like email marketing and social media marketing, and models for areas like distribution, communication, and relationship building. The document concludes by outlining the typical tasks involved in developing an e-marketing plan.