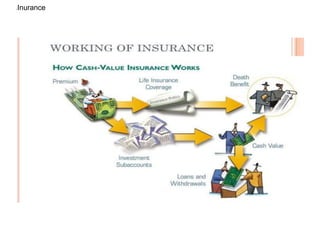
The document outlines the fundamentals of insurance, defining it as a social mechanism for managing pure risk among large groups, contrasting it with gambling and hedging. It details key concepts such as risk transfer, underwriting, insurable risks, and unique characteristics of insurance contracts. Additionally, it discusses the benefits and functions of insurance, emphasizing its role in providing financial protection and supporting economic stability.