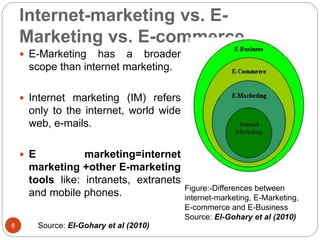
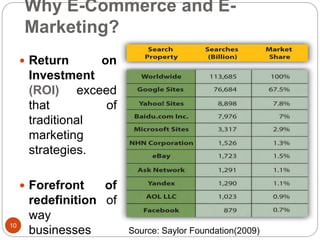
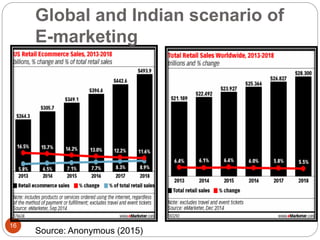
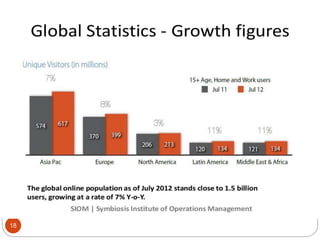
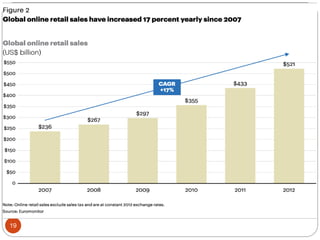
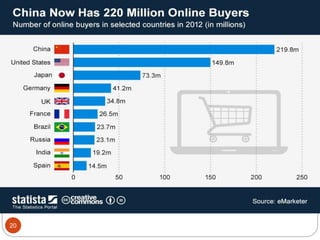
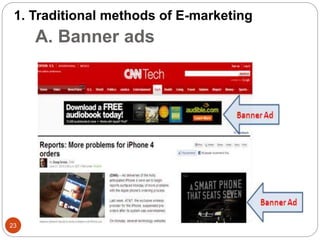
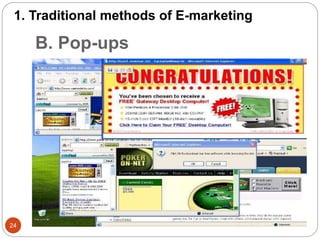
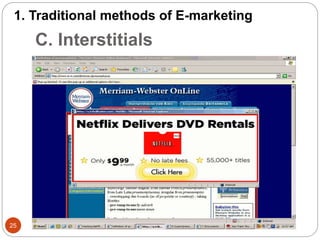
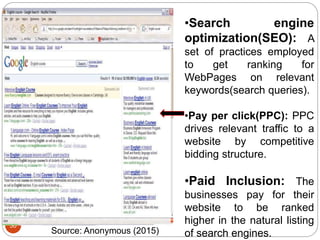
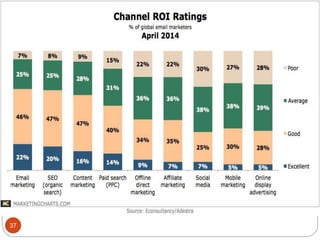
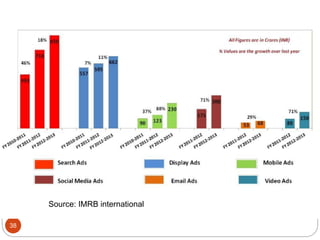
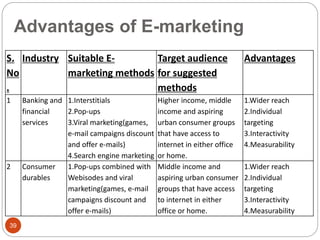
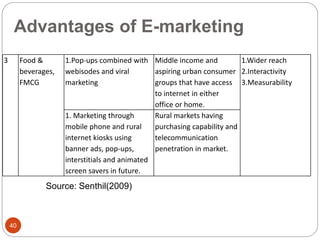
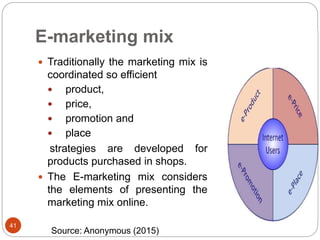
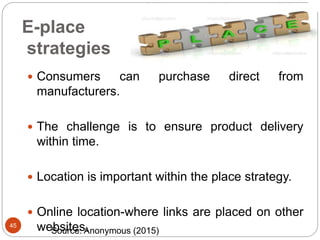
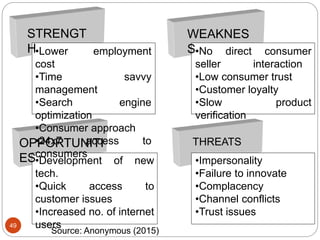
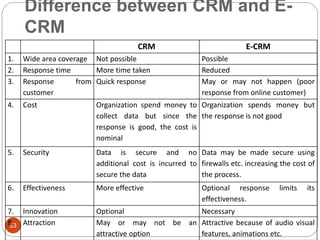
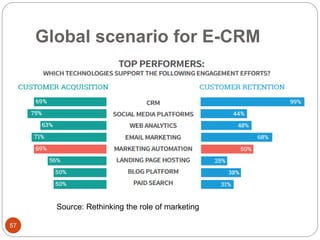
This document provides an overview of the key concepts of e-marketing. It begins by defining e-marketing and discussing how it uses digital media and the internet as an addition to traditional marketing approaches. It then explores the differences between internet marketing, e-marketing and e-commerce. The document outlines the objectives, global scenario, and various methods of e-marketing such as banner ads, pop-ups, viral marketing techniques. It also discusses the e-marketing mix, advantages of e-marketing, and concludes with two case studies about how companies have successfully used e-CRM and viral marketing strategies.