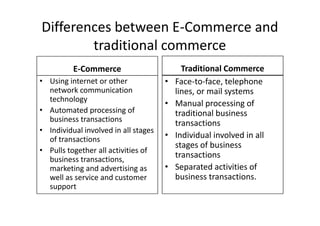
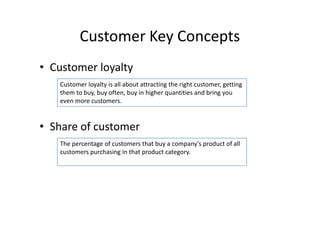
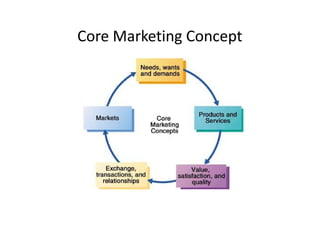
The document discusses e-commerce and marketing concepts, defining e-commerce as the process of buying and selling goods and services over the Internet and examining different types of e-commerce organizations and marketing channels. It also covers benefits of e-commerce such as reduced costs and increased access to global markets, as well as internet advertising methods like banners ads and their benefits and limitations.