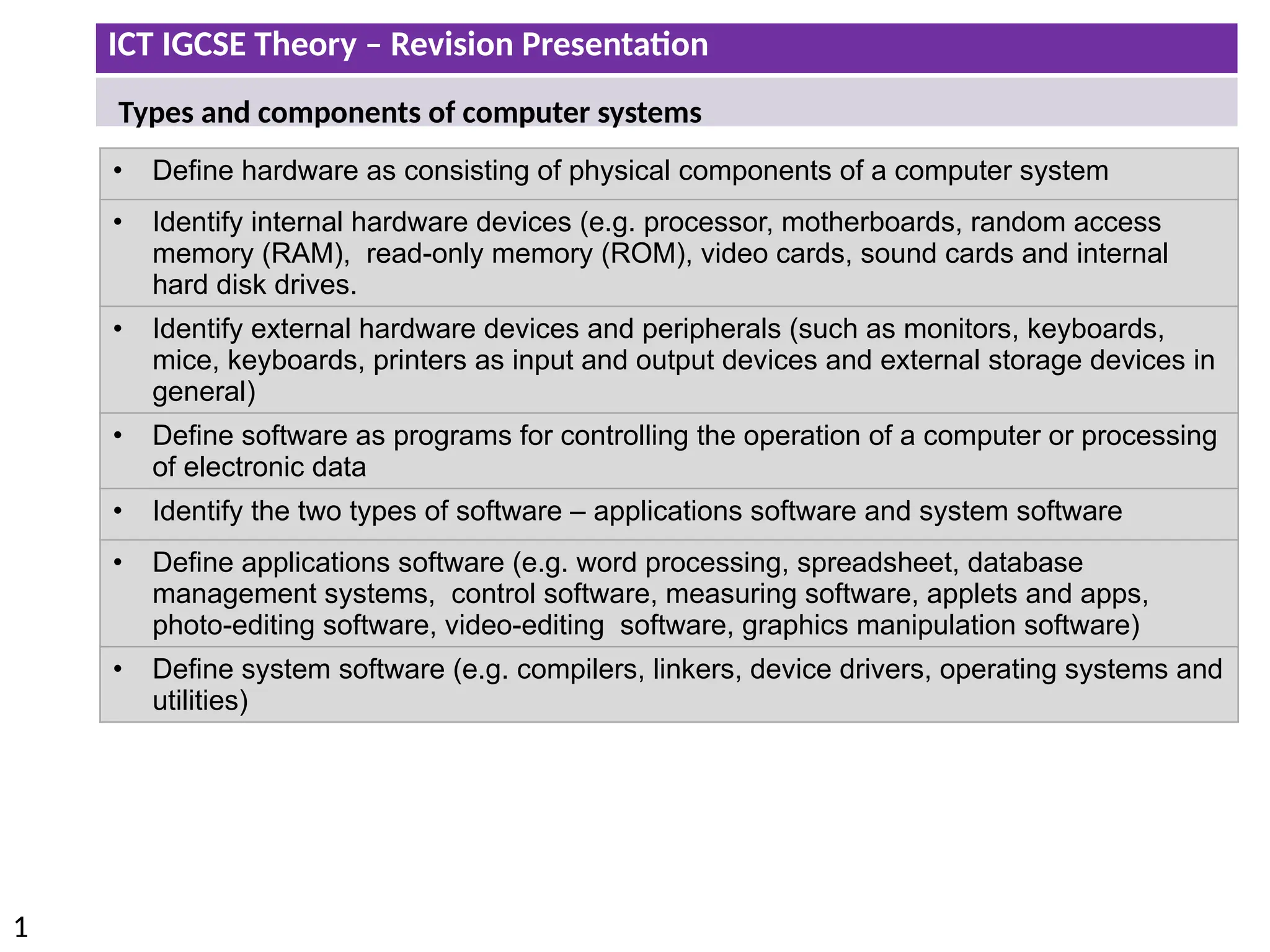
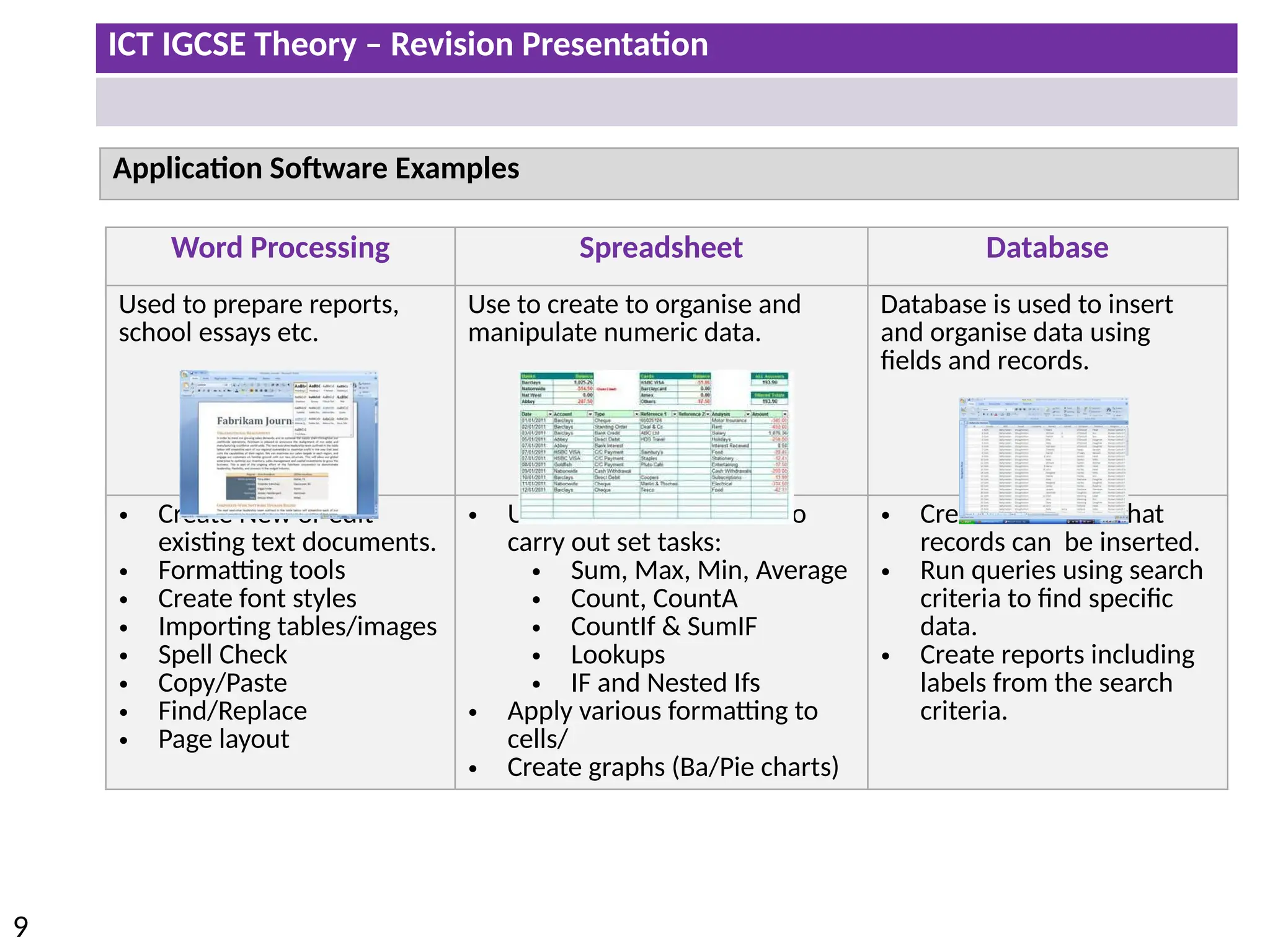
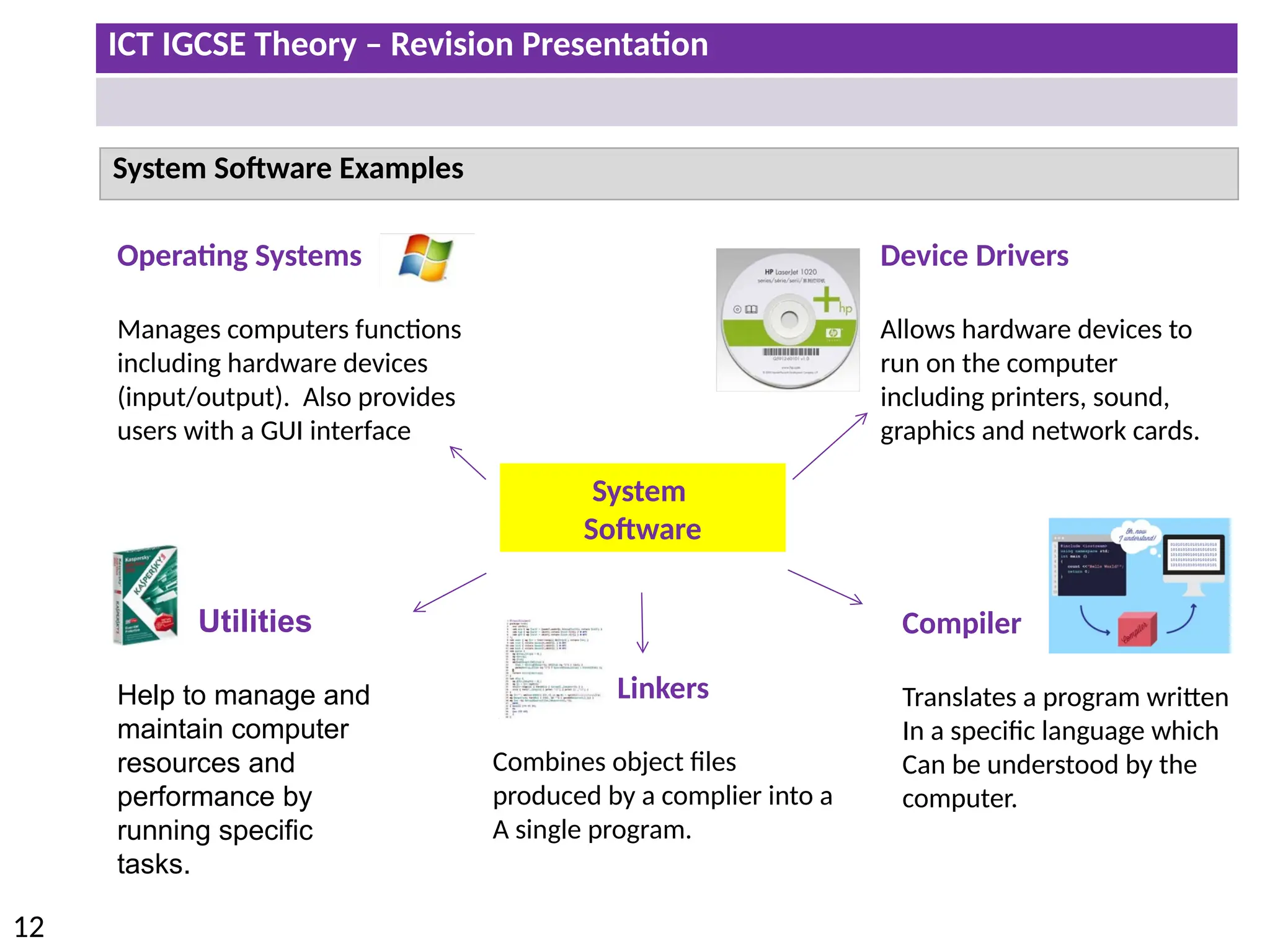
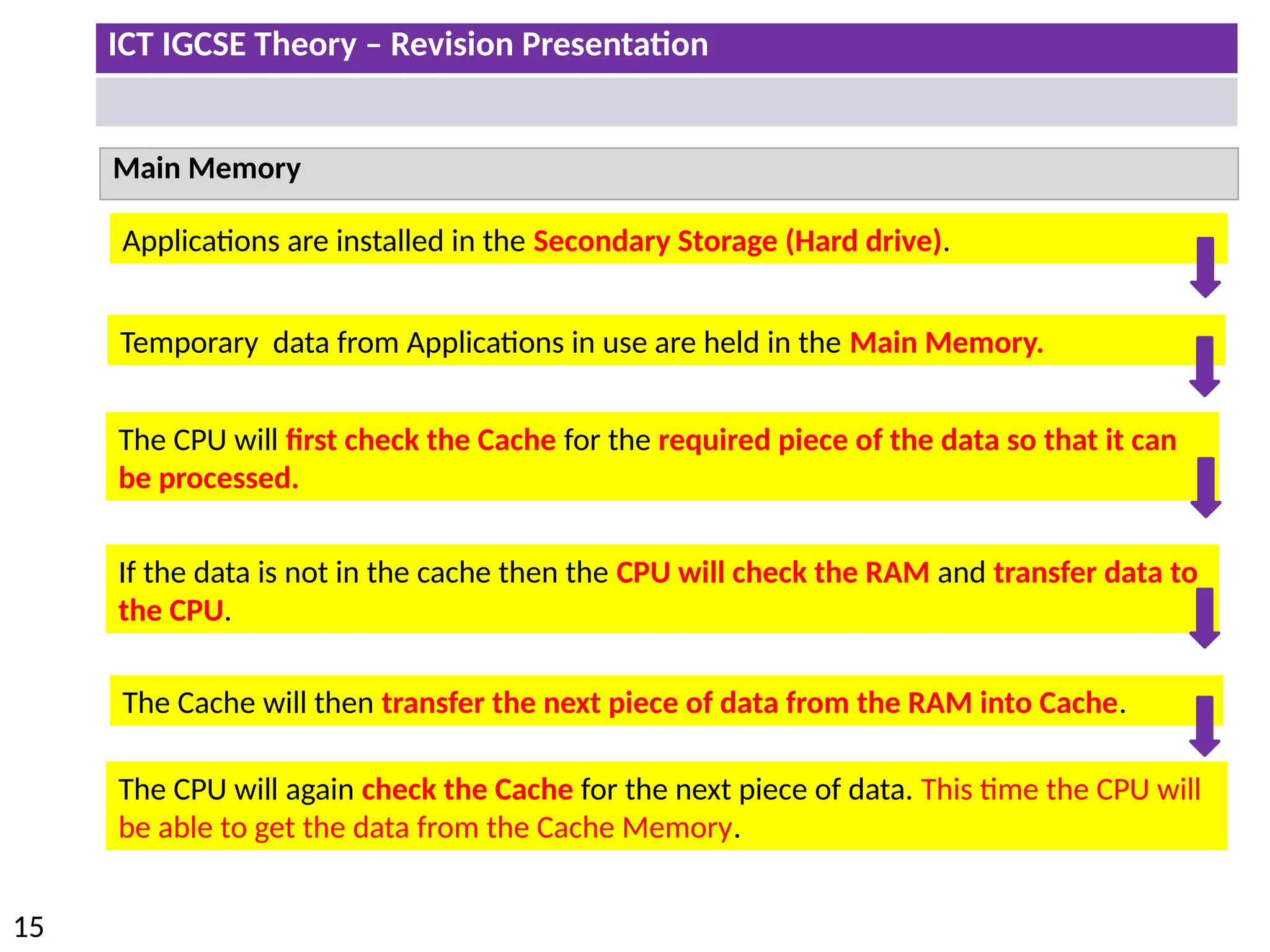
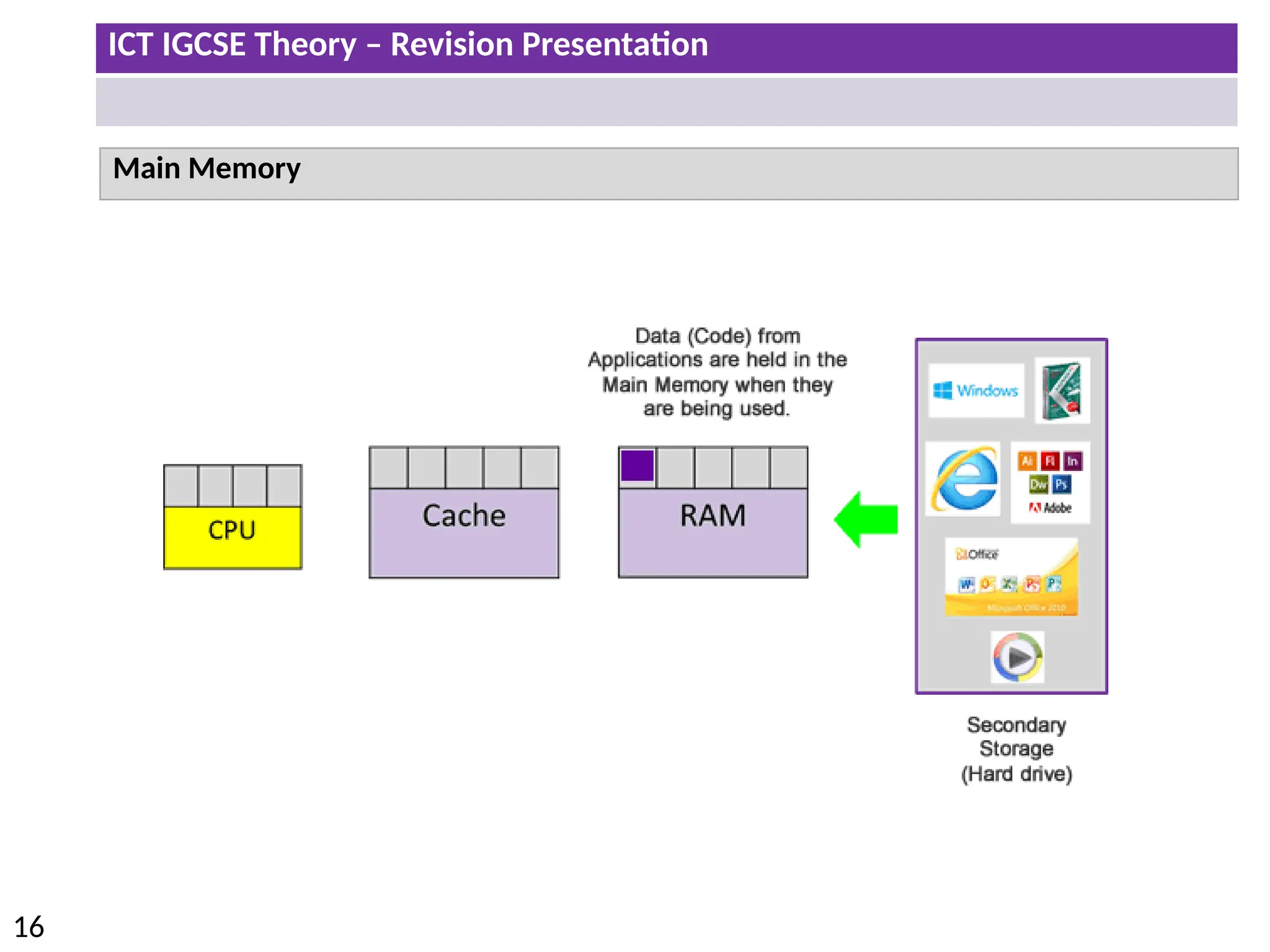
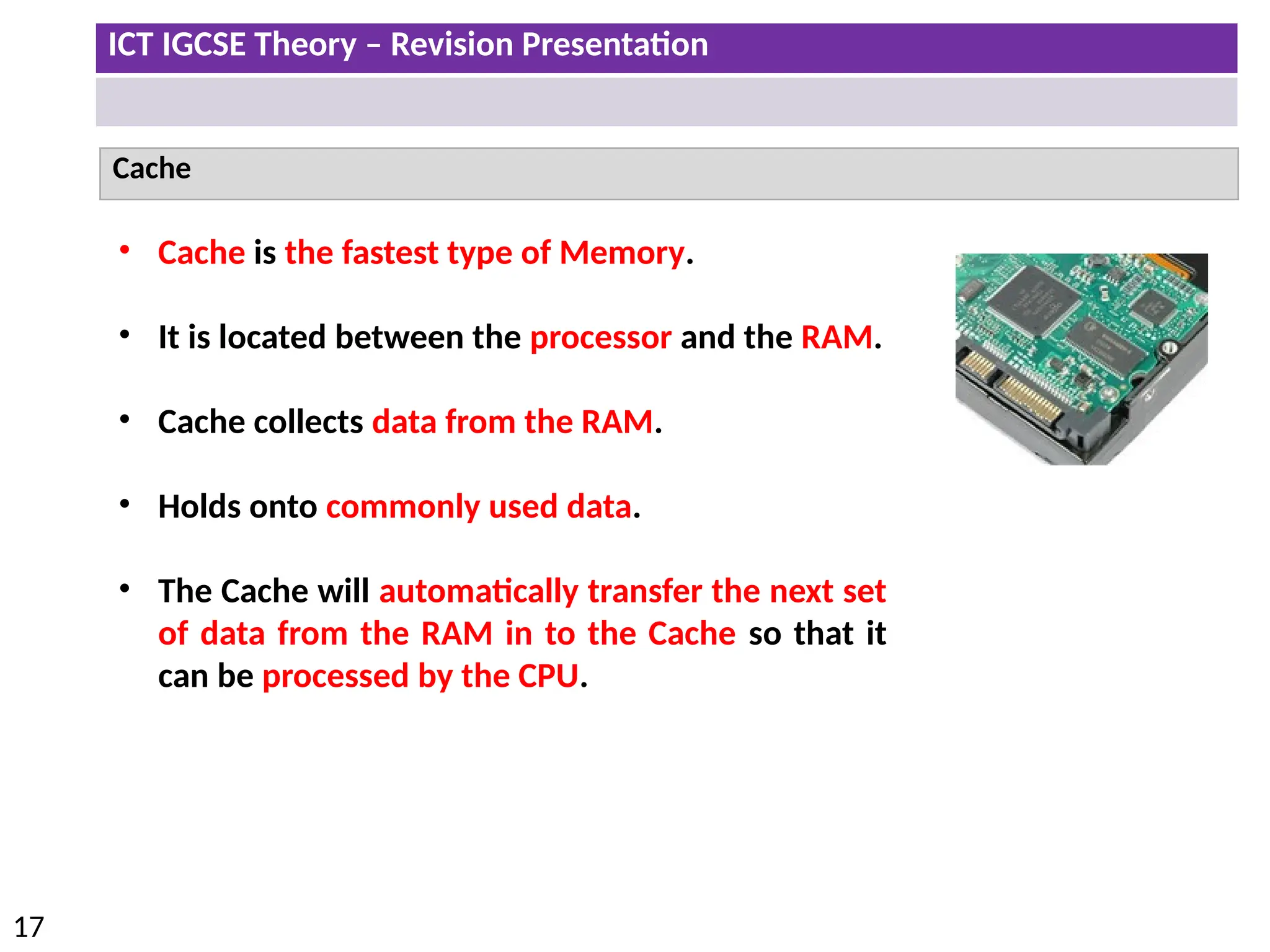
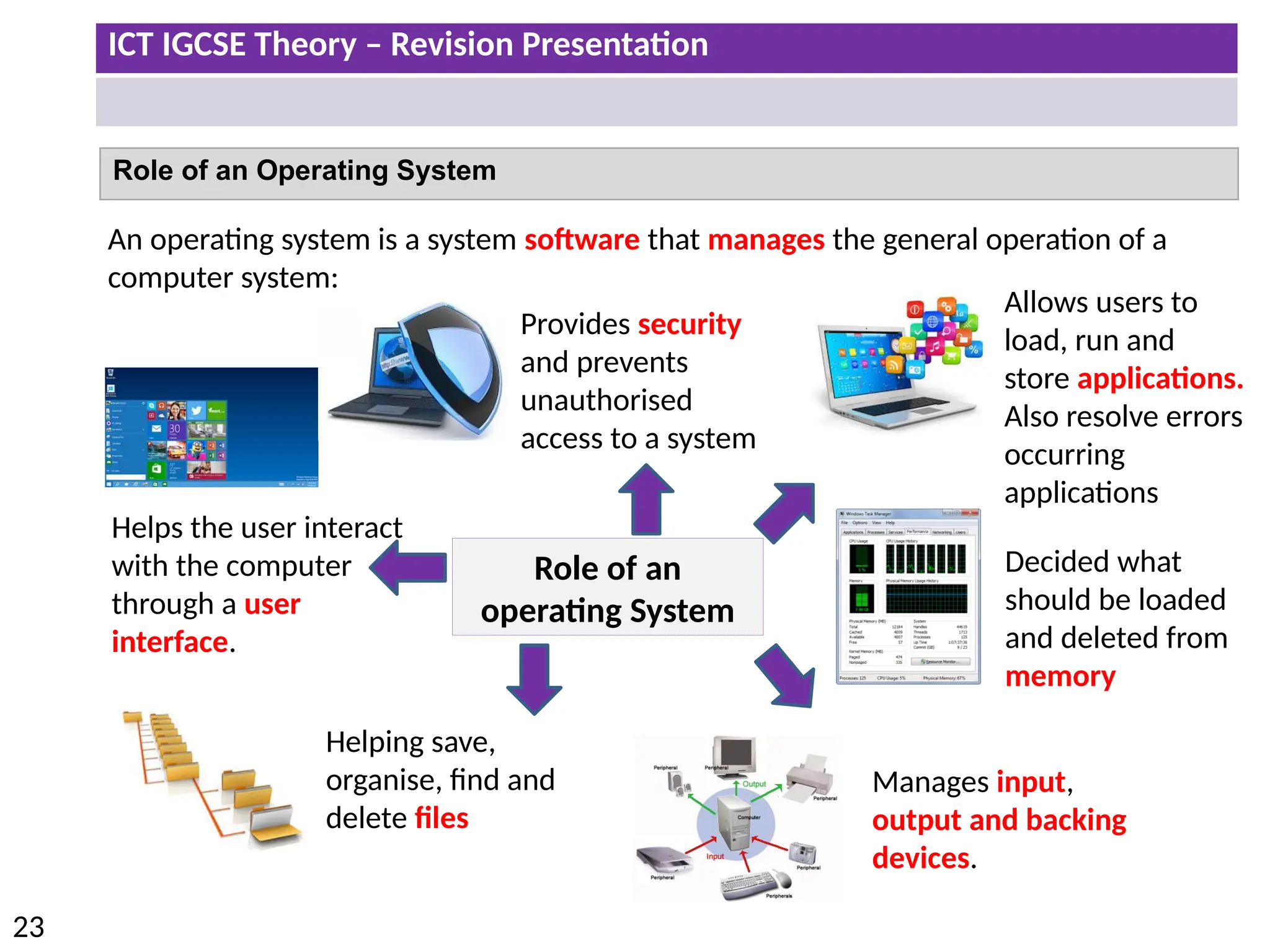
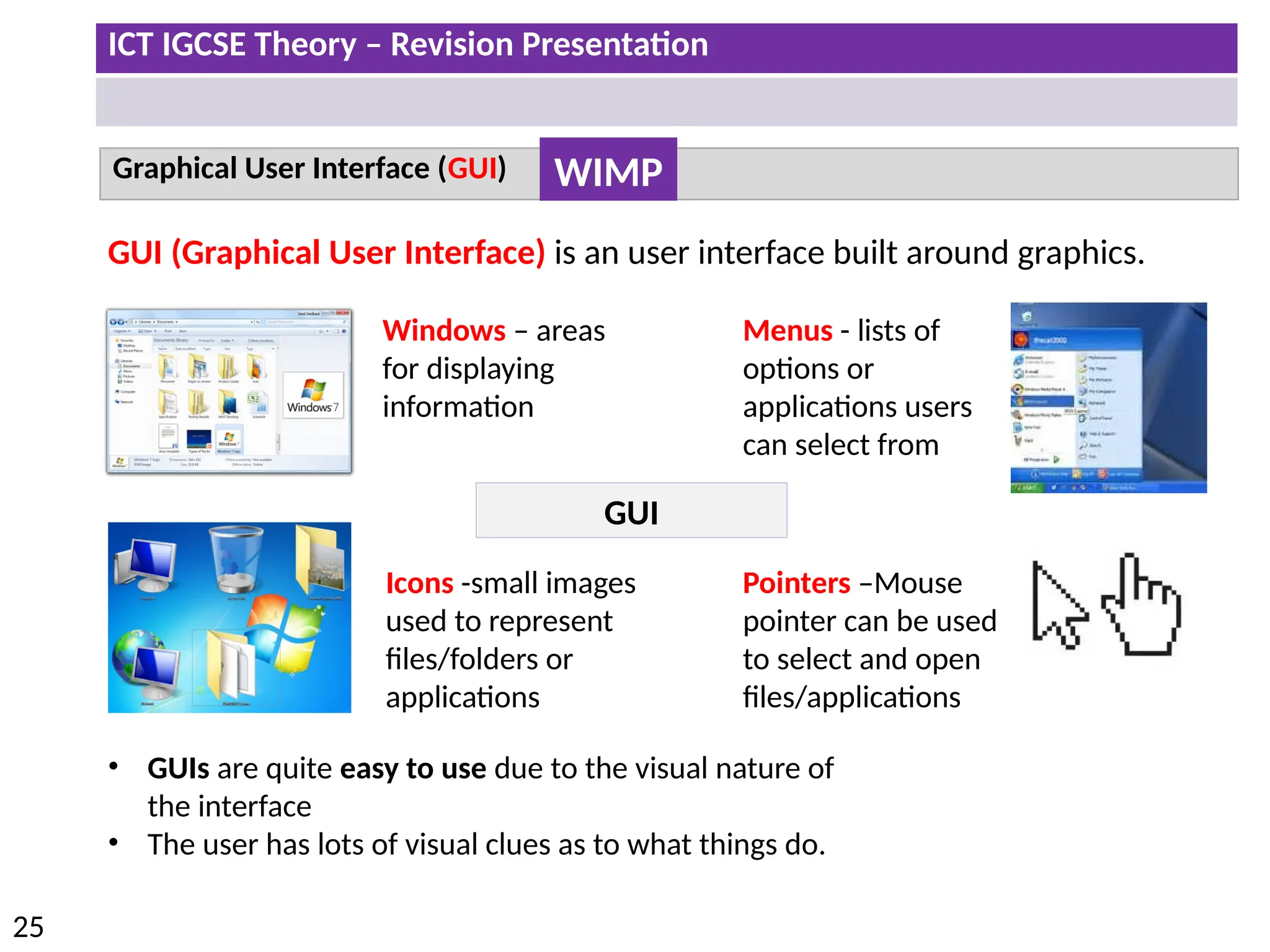
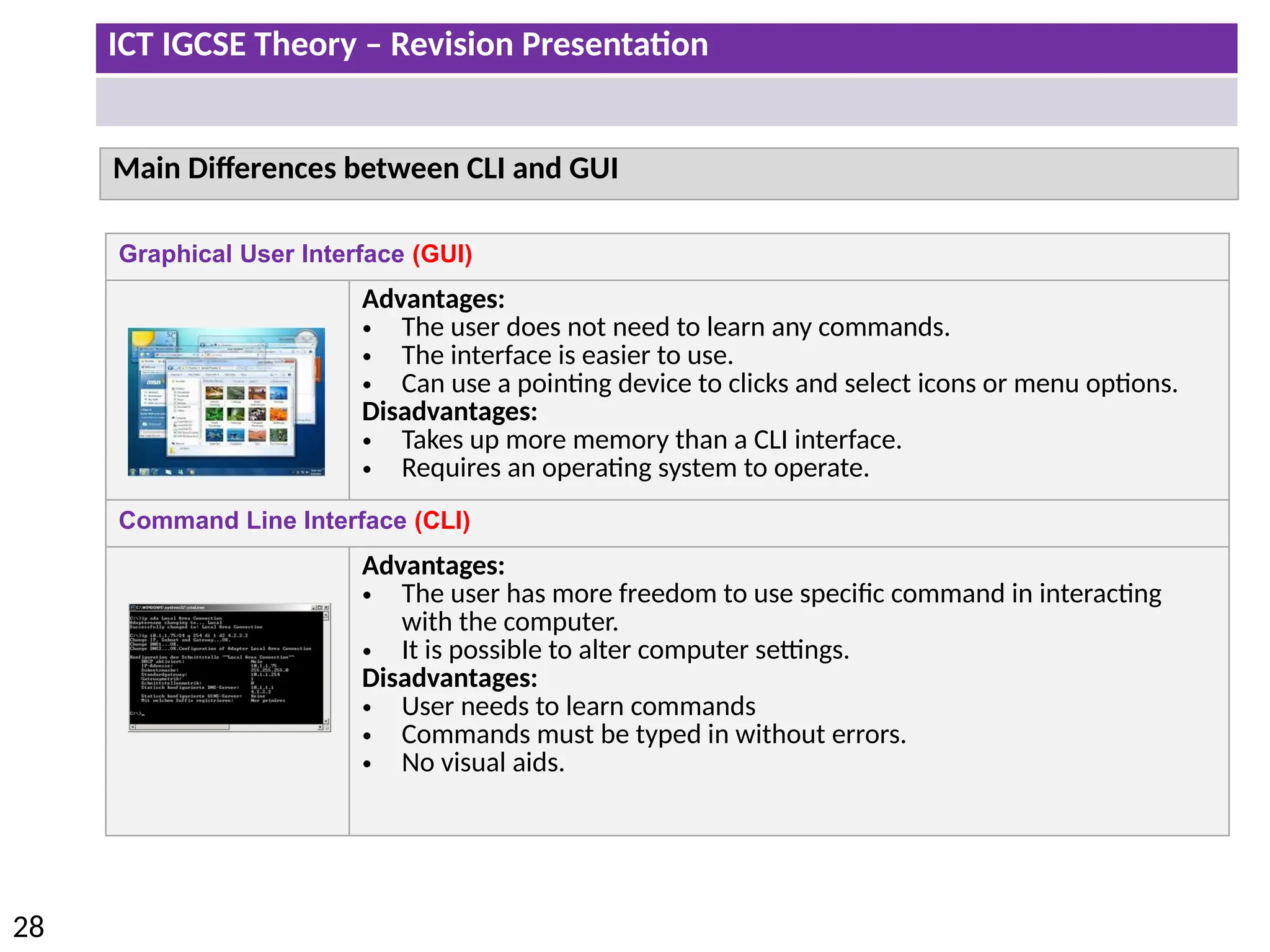
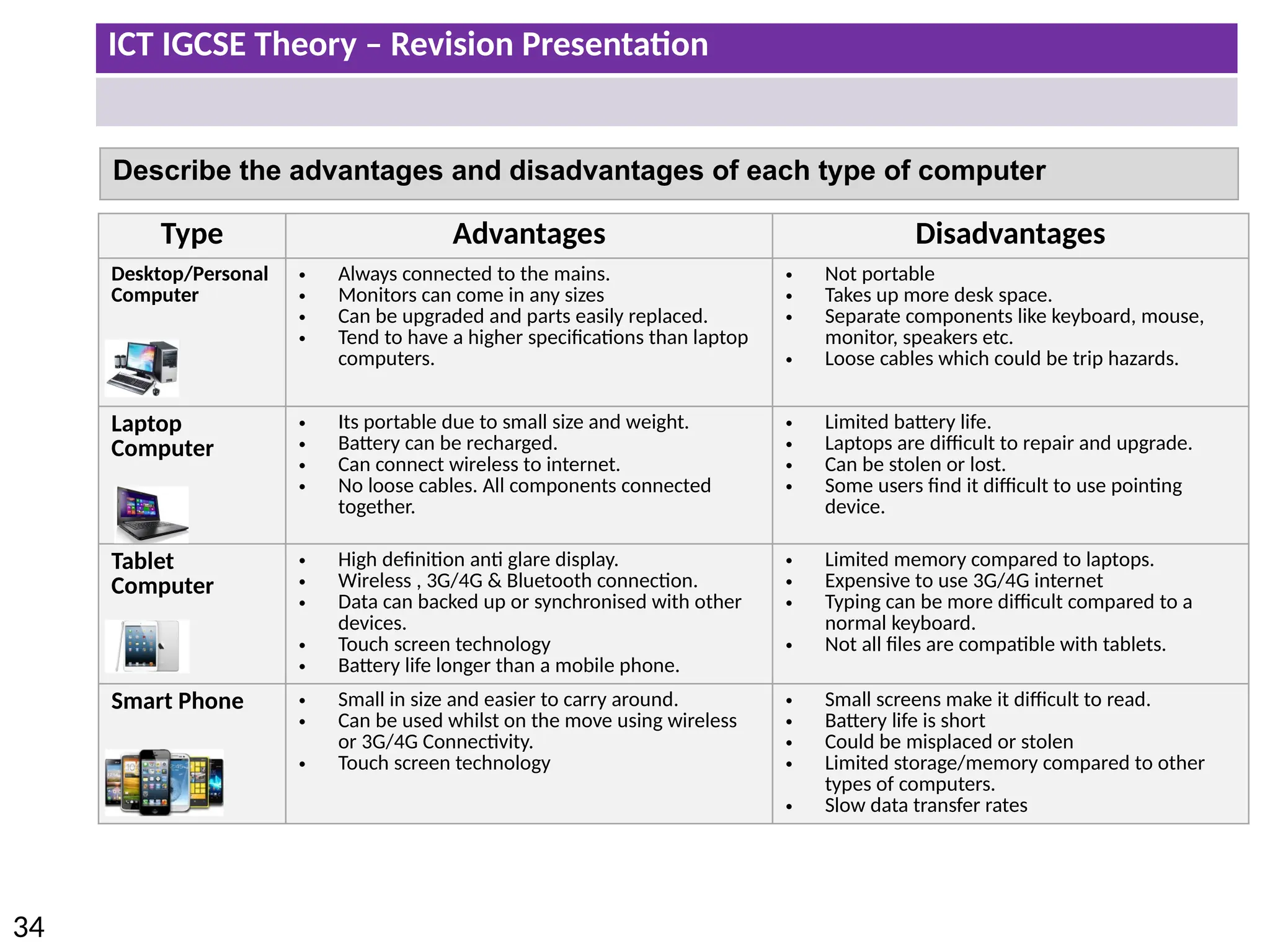
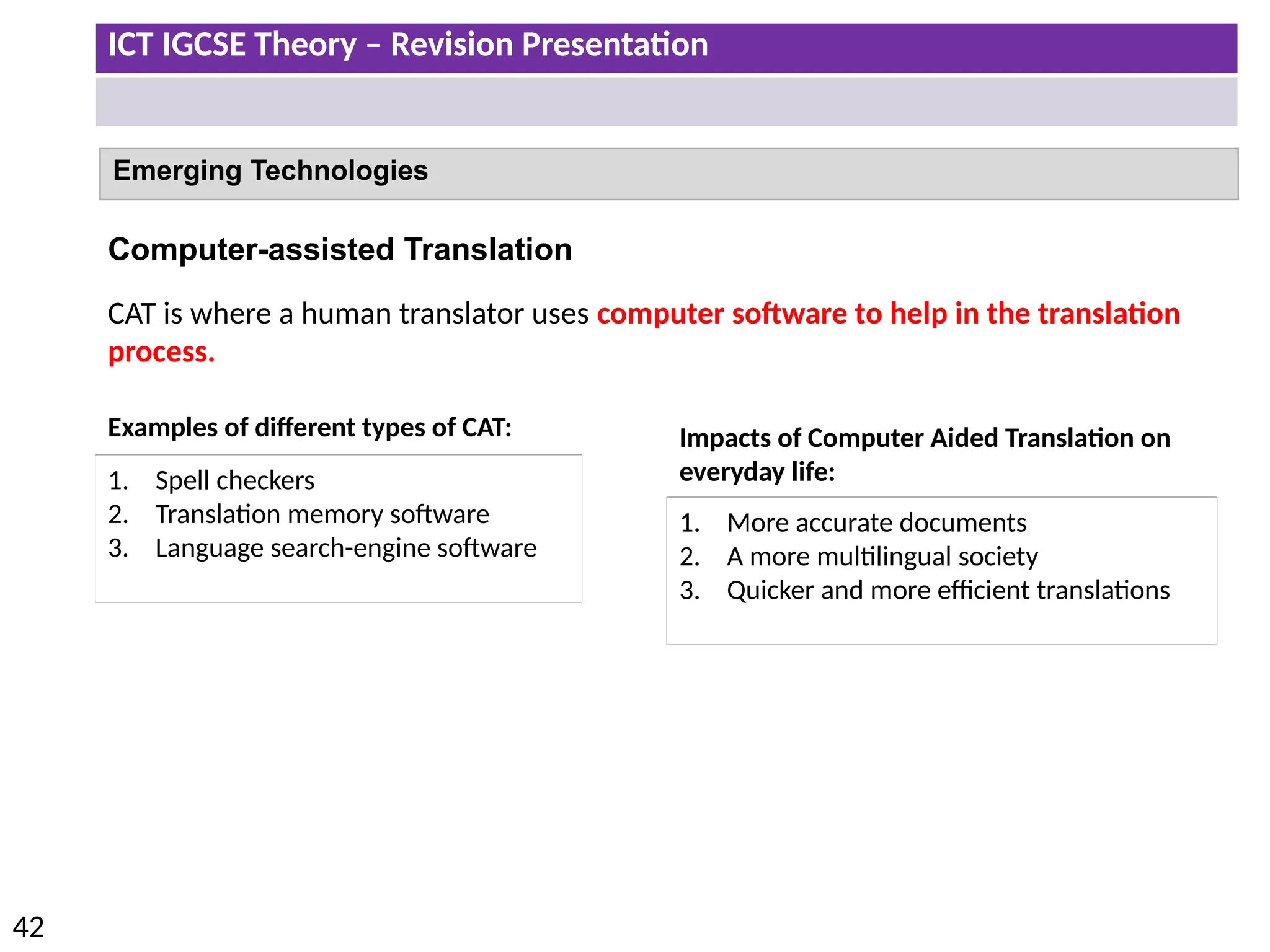
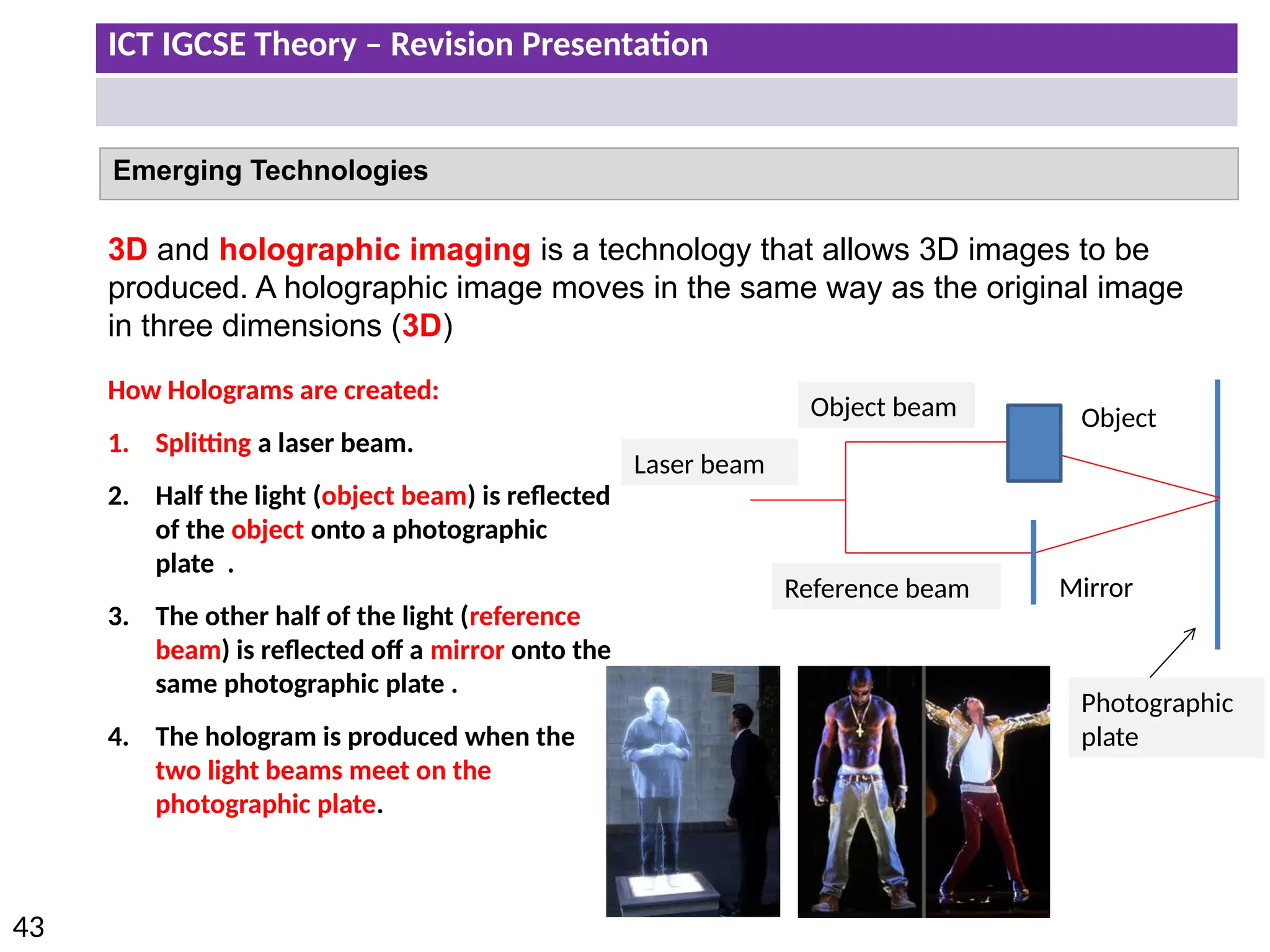
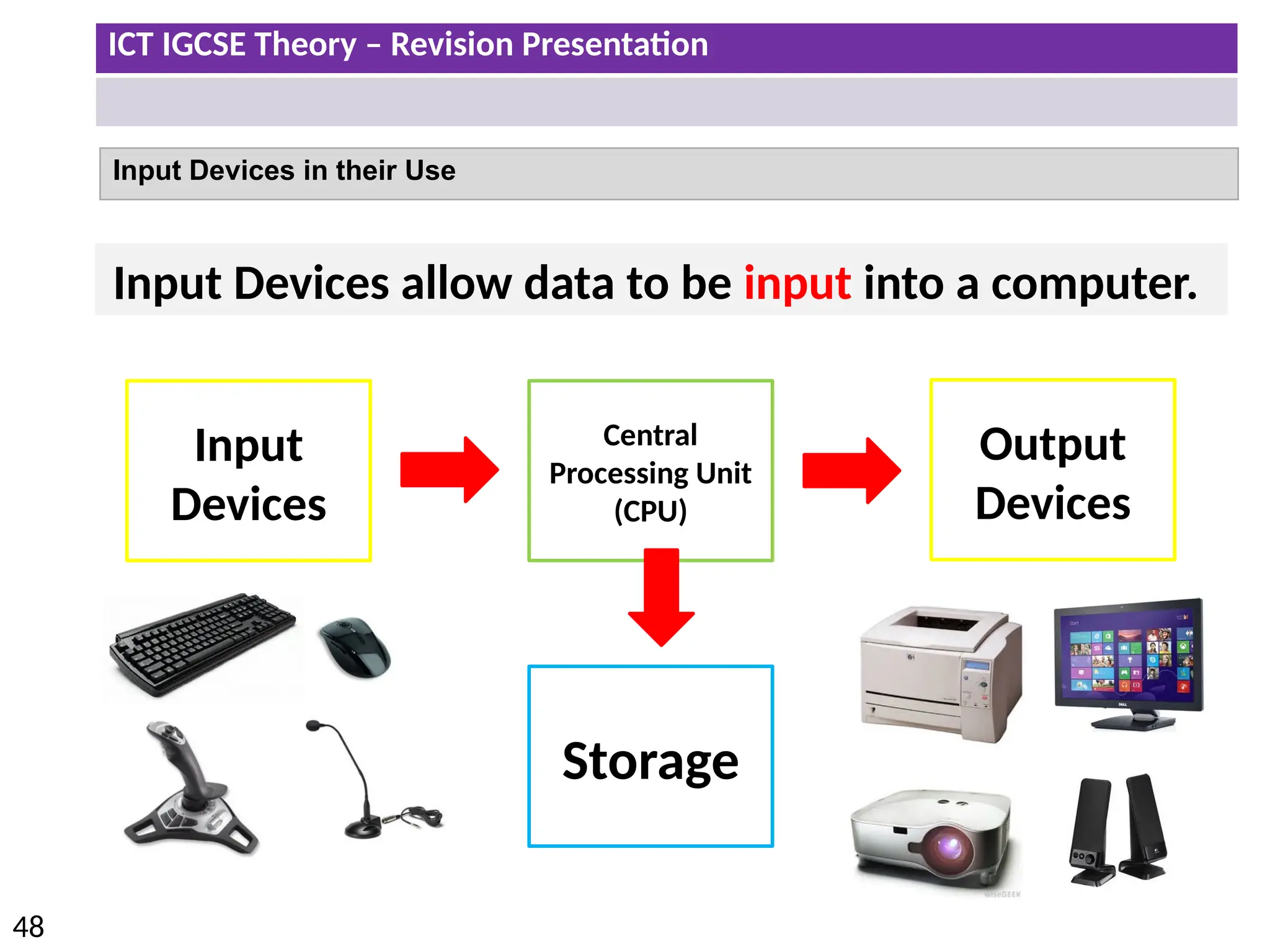
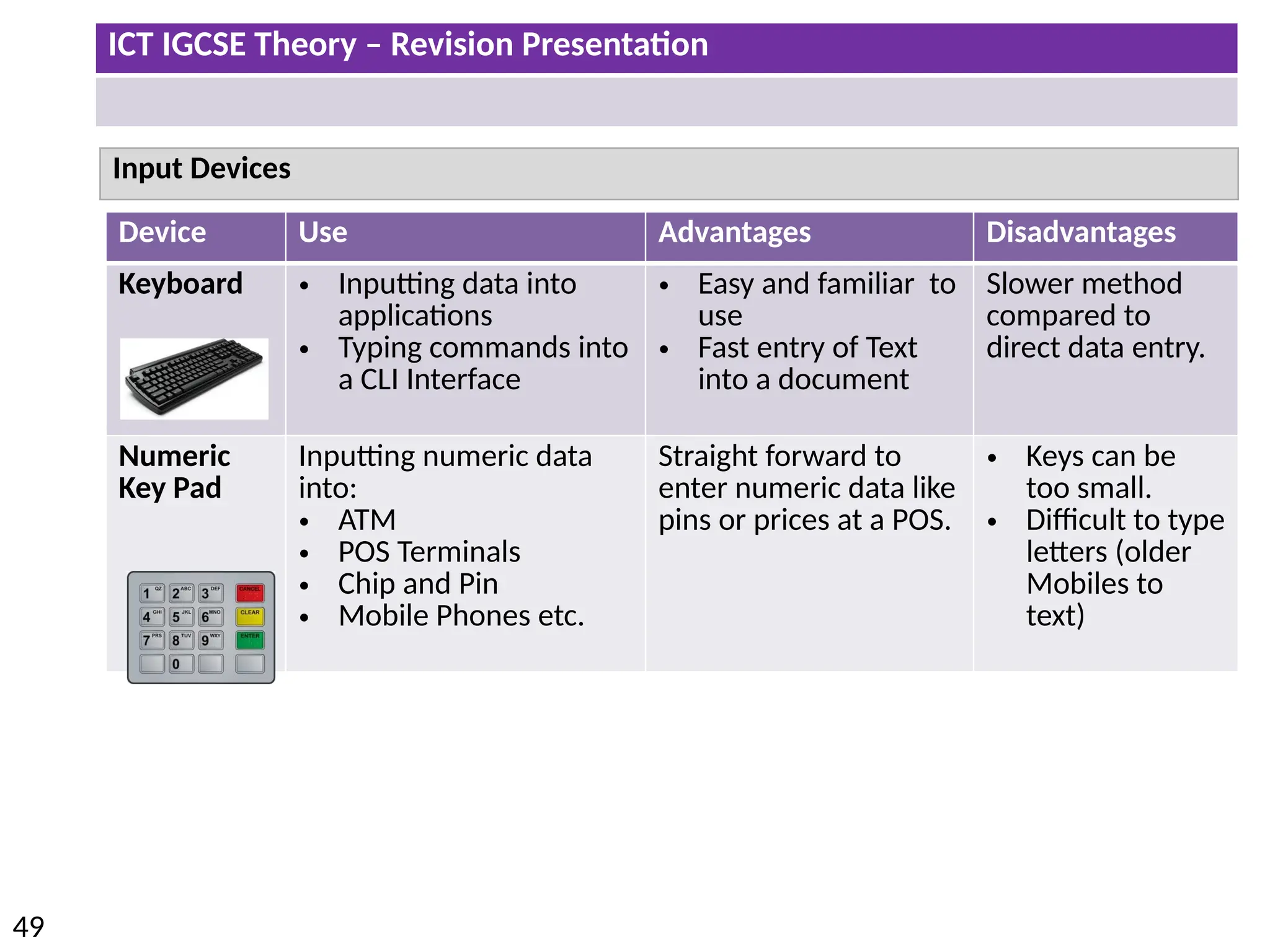
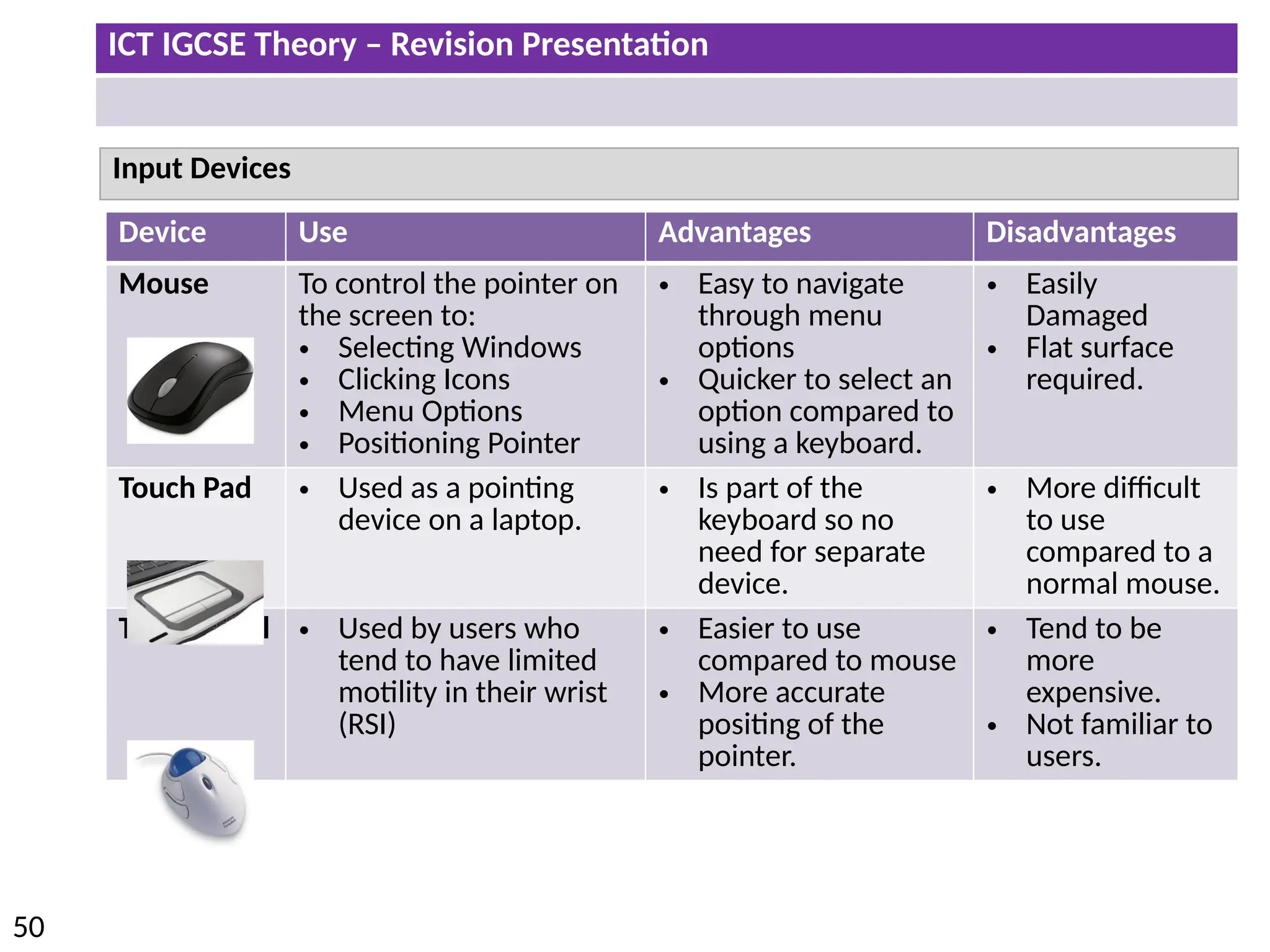
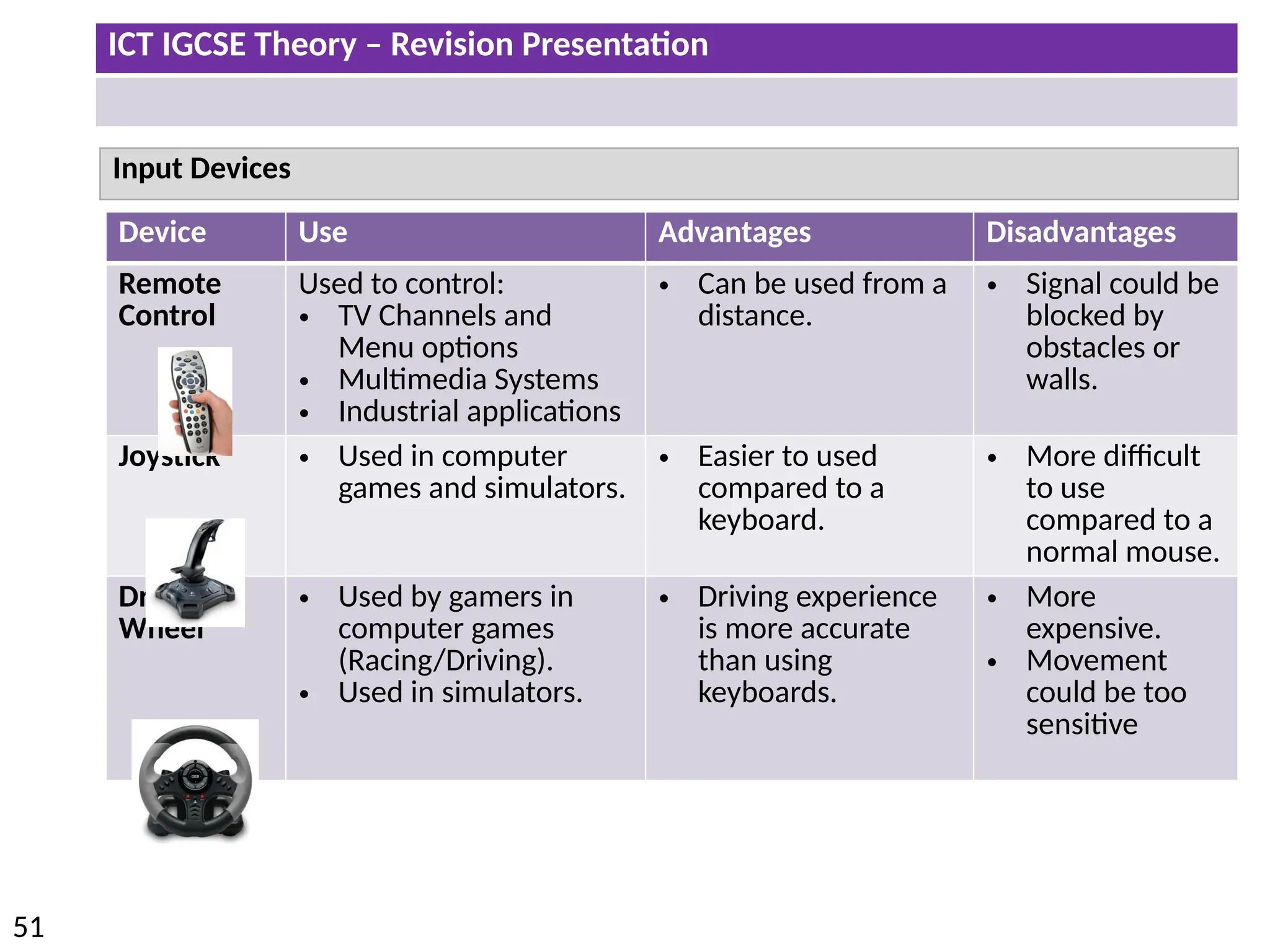
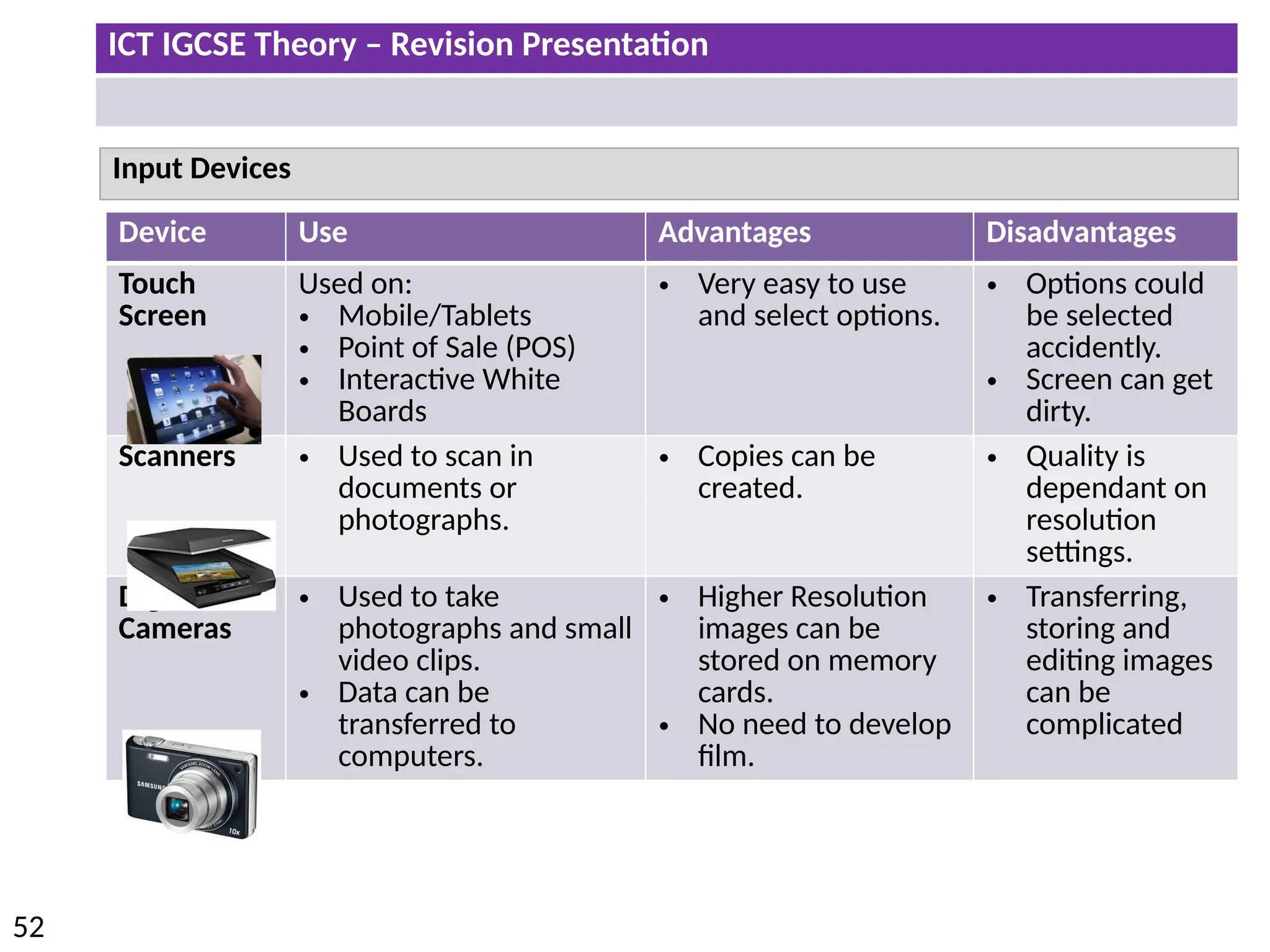
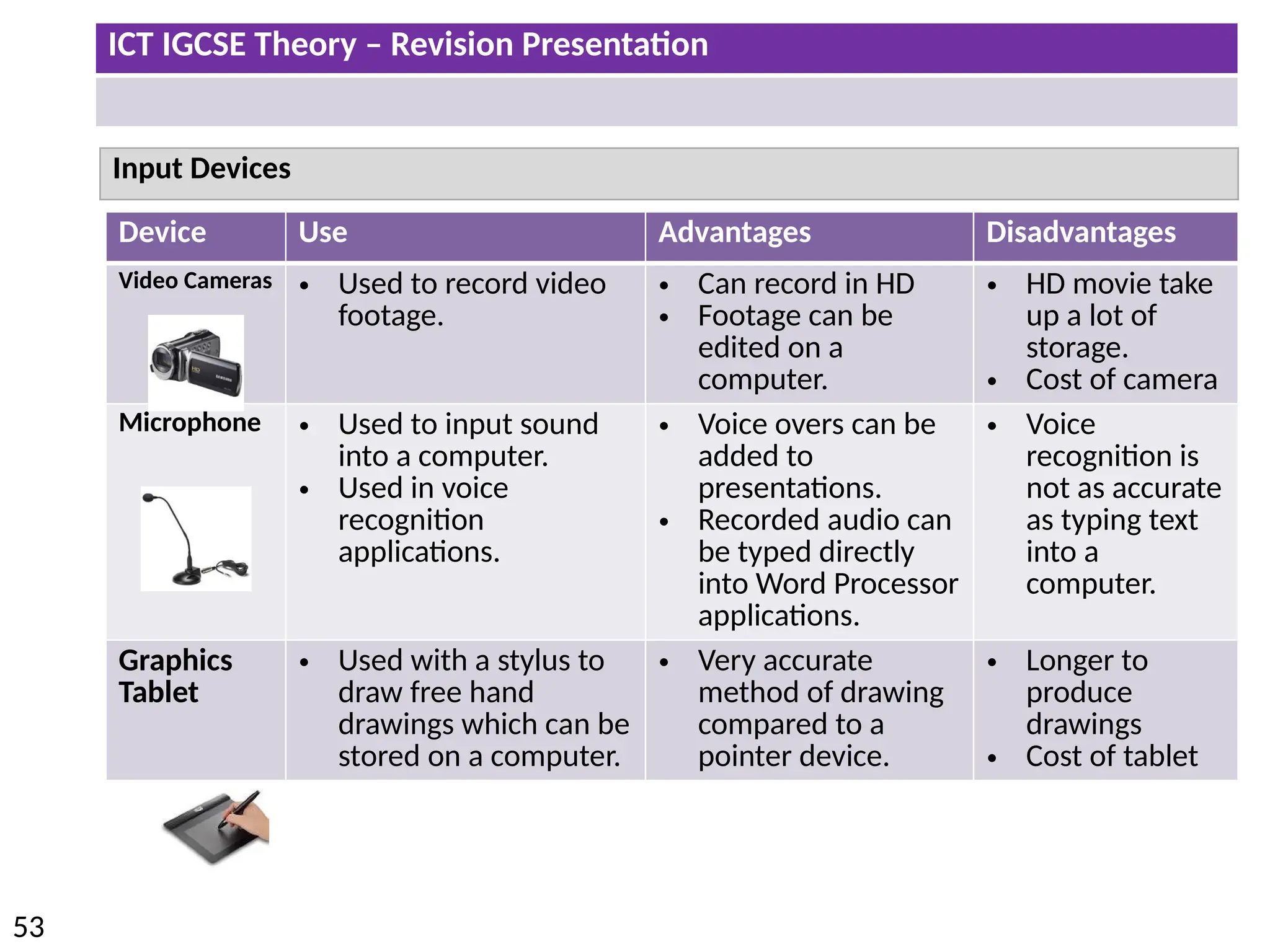
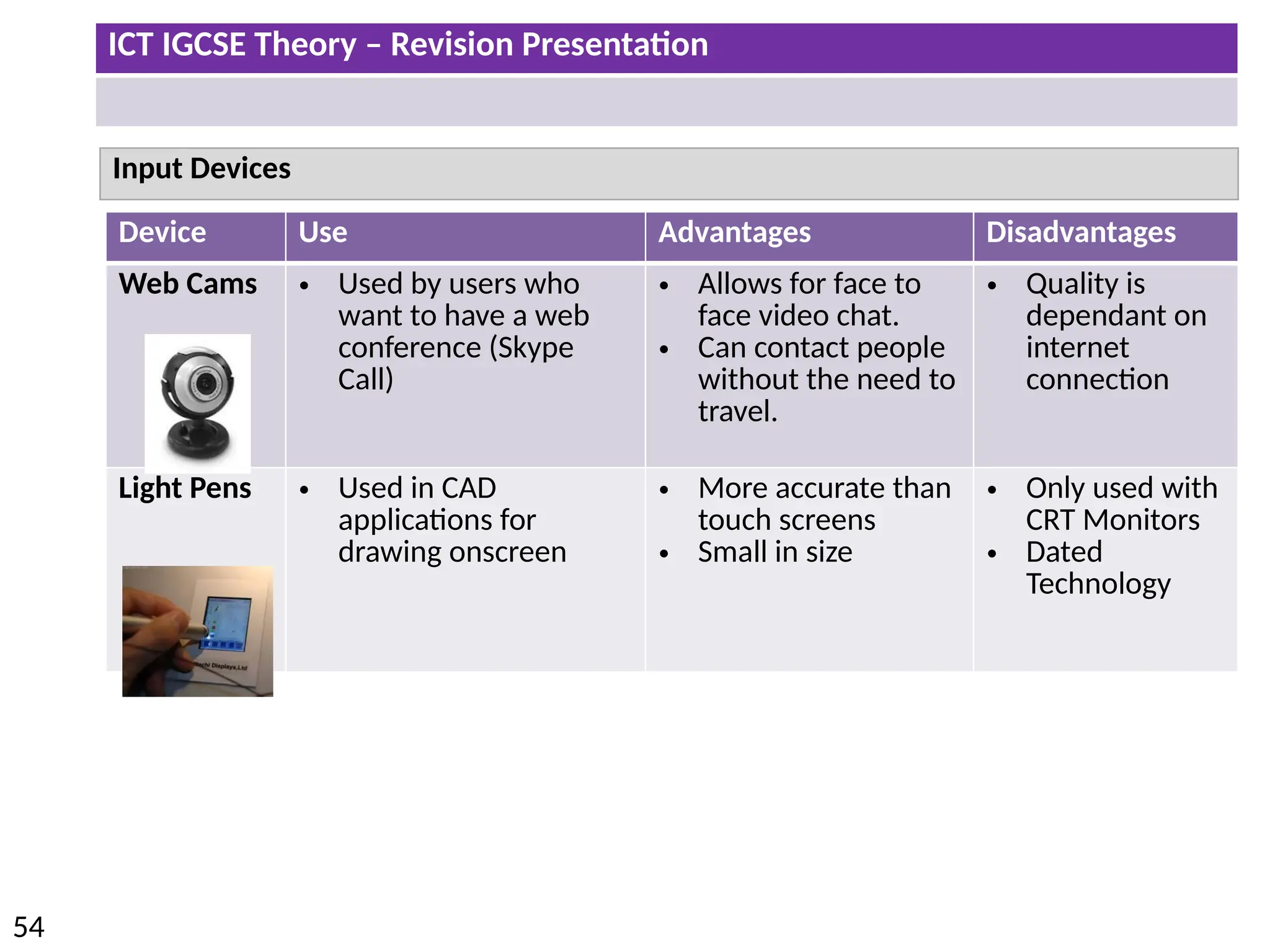
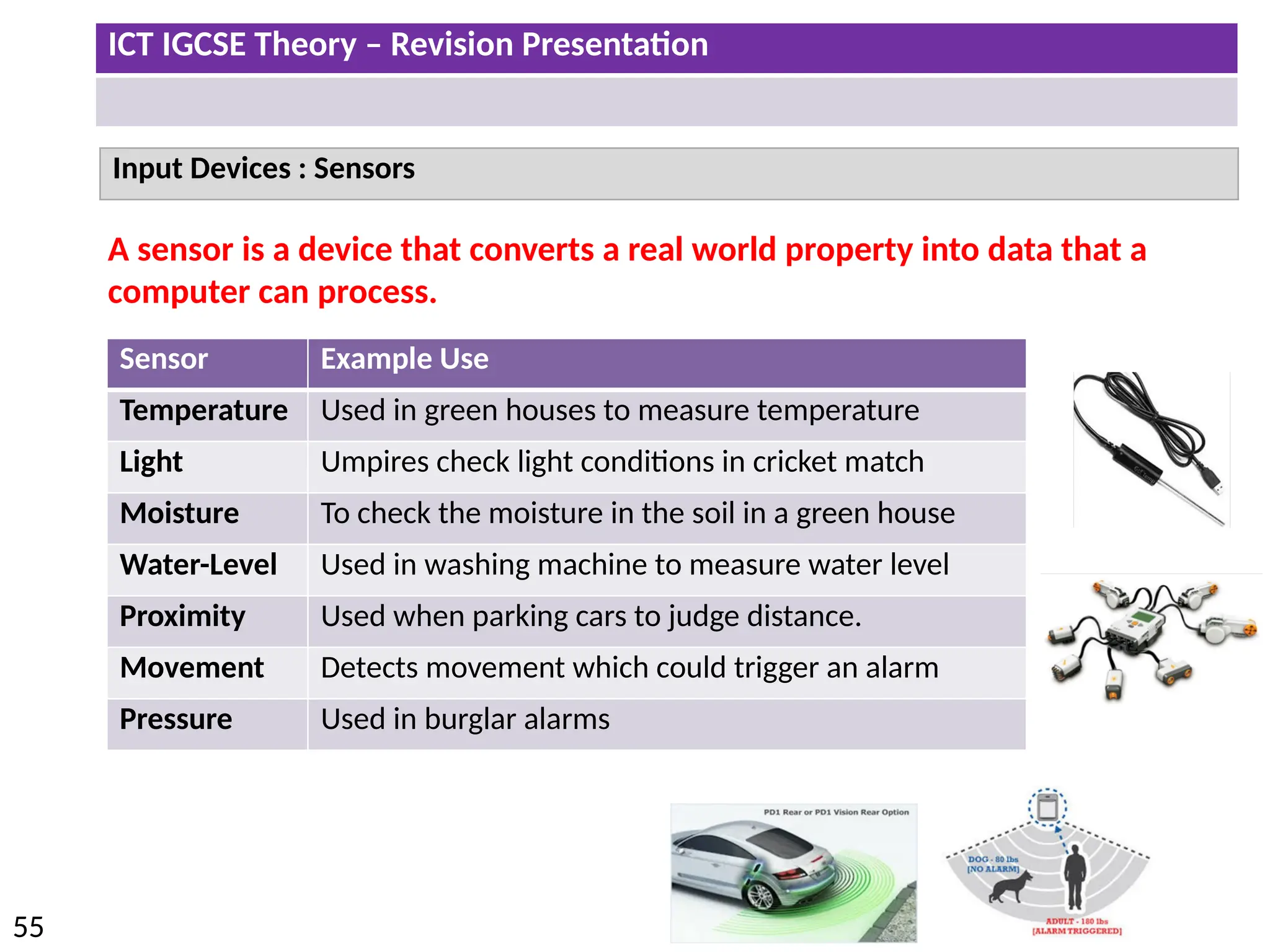
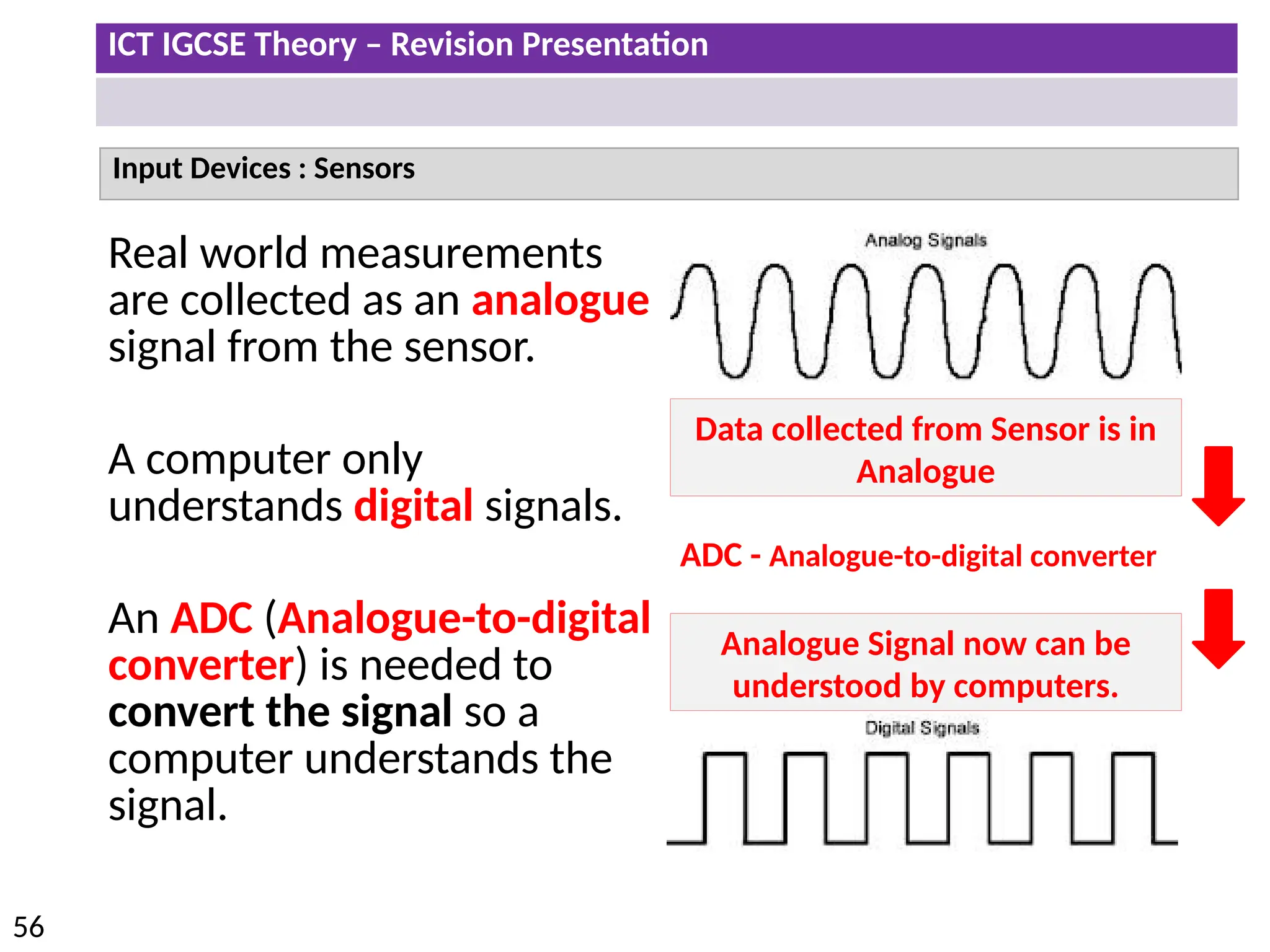
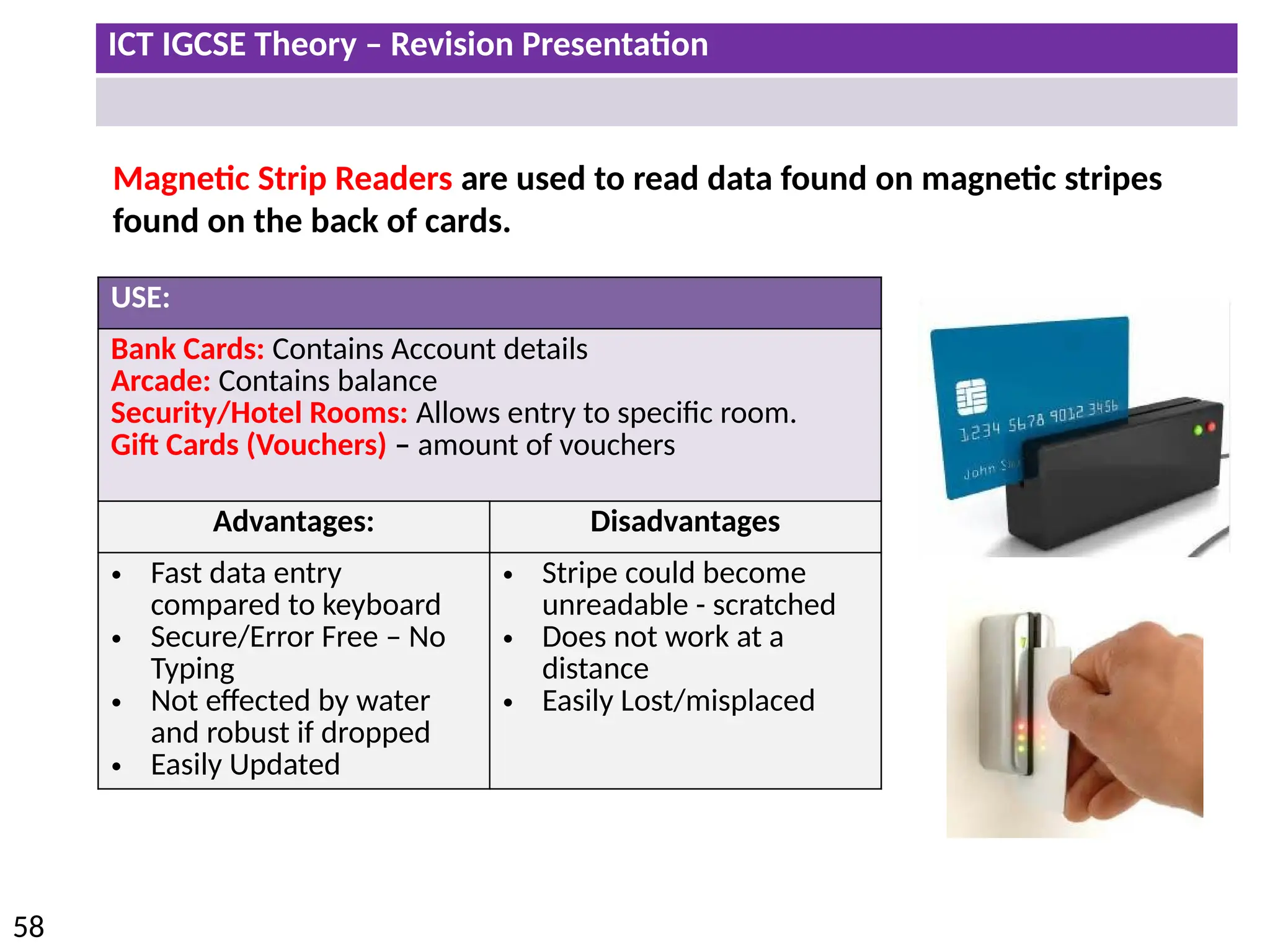
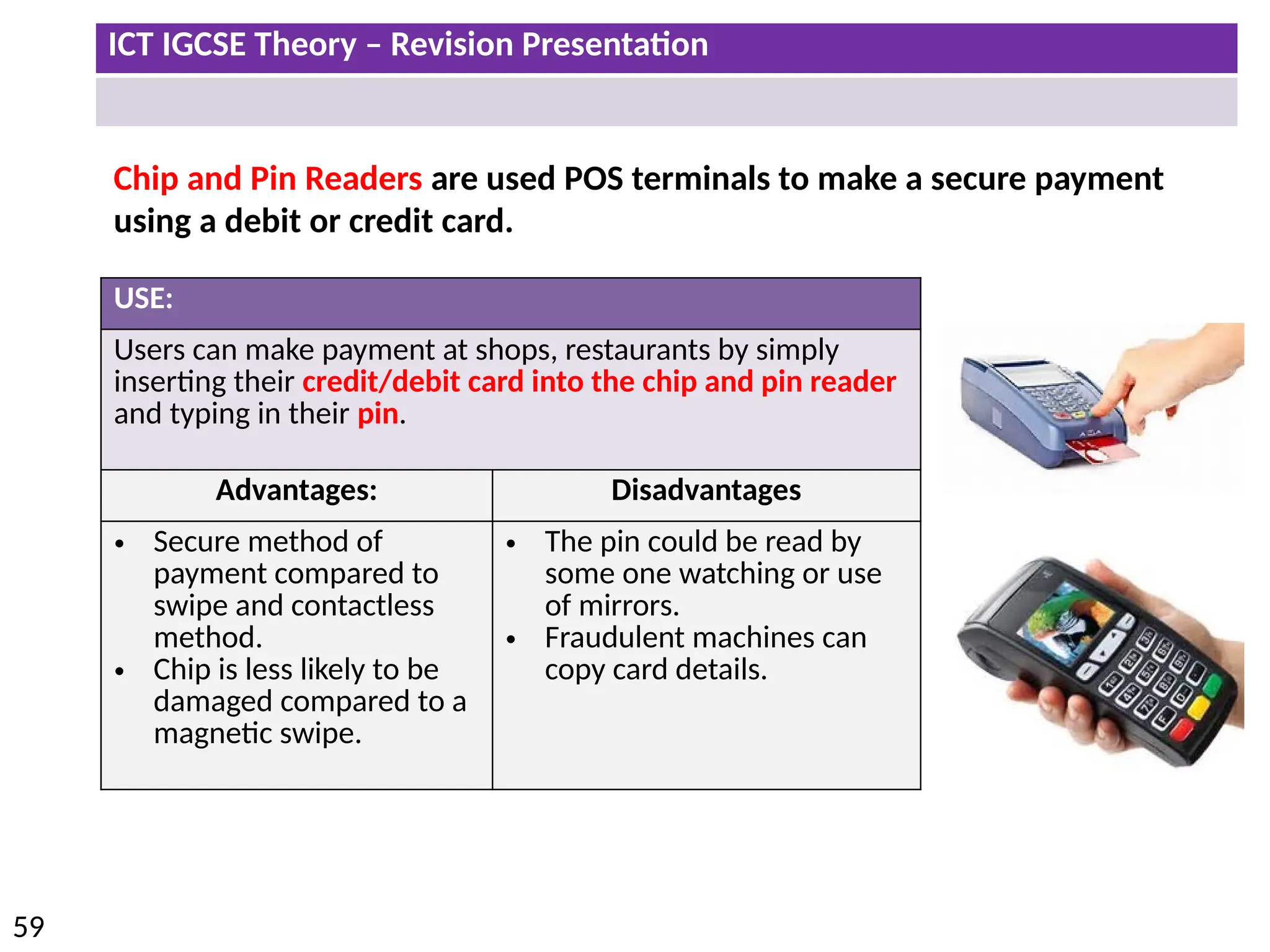
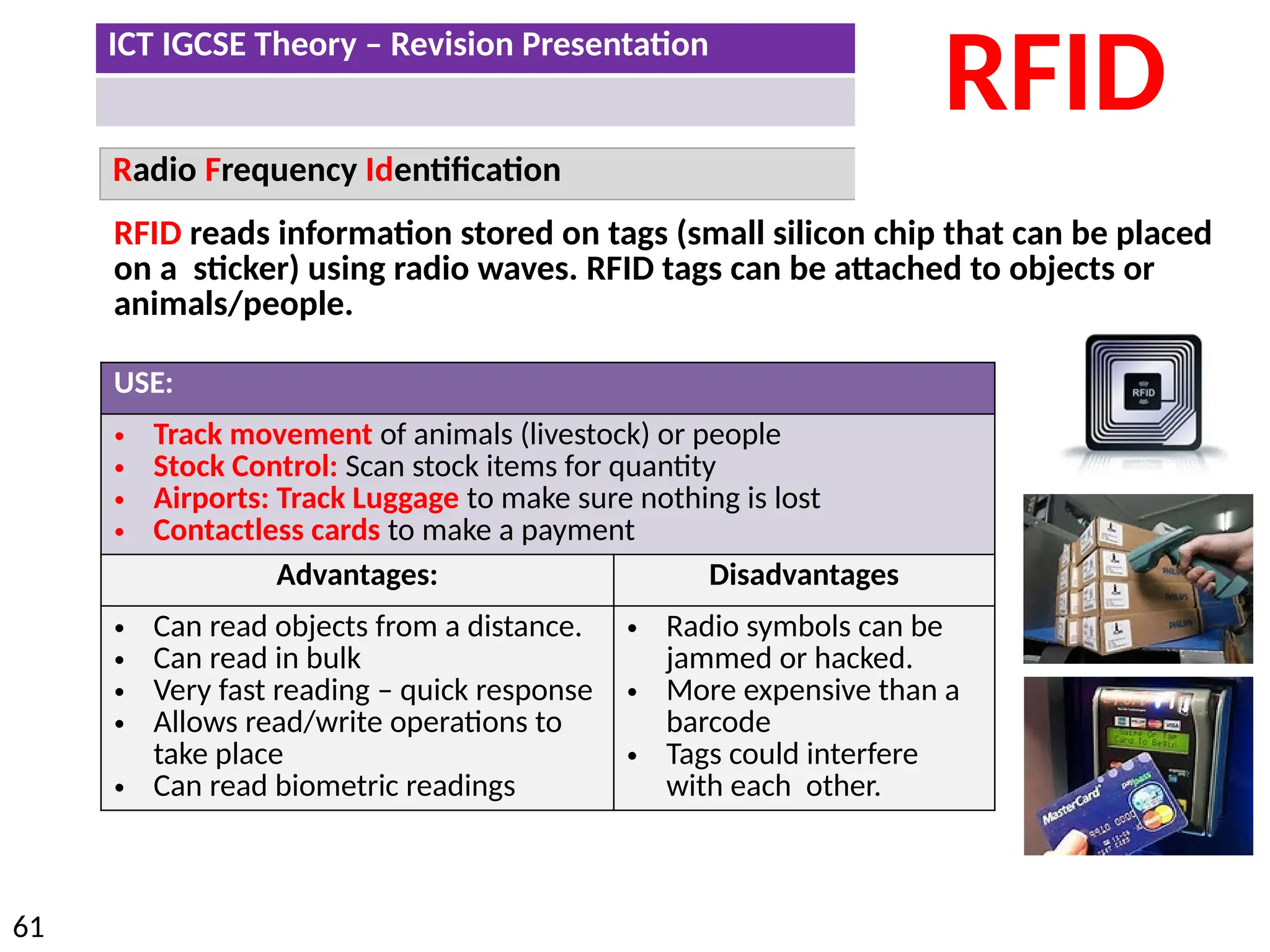
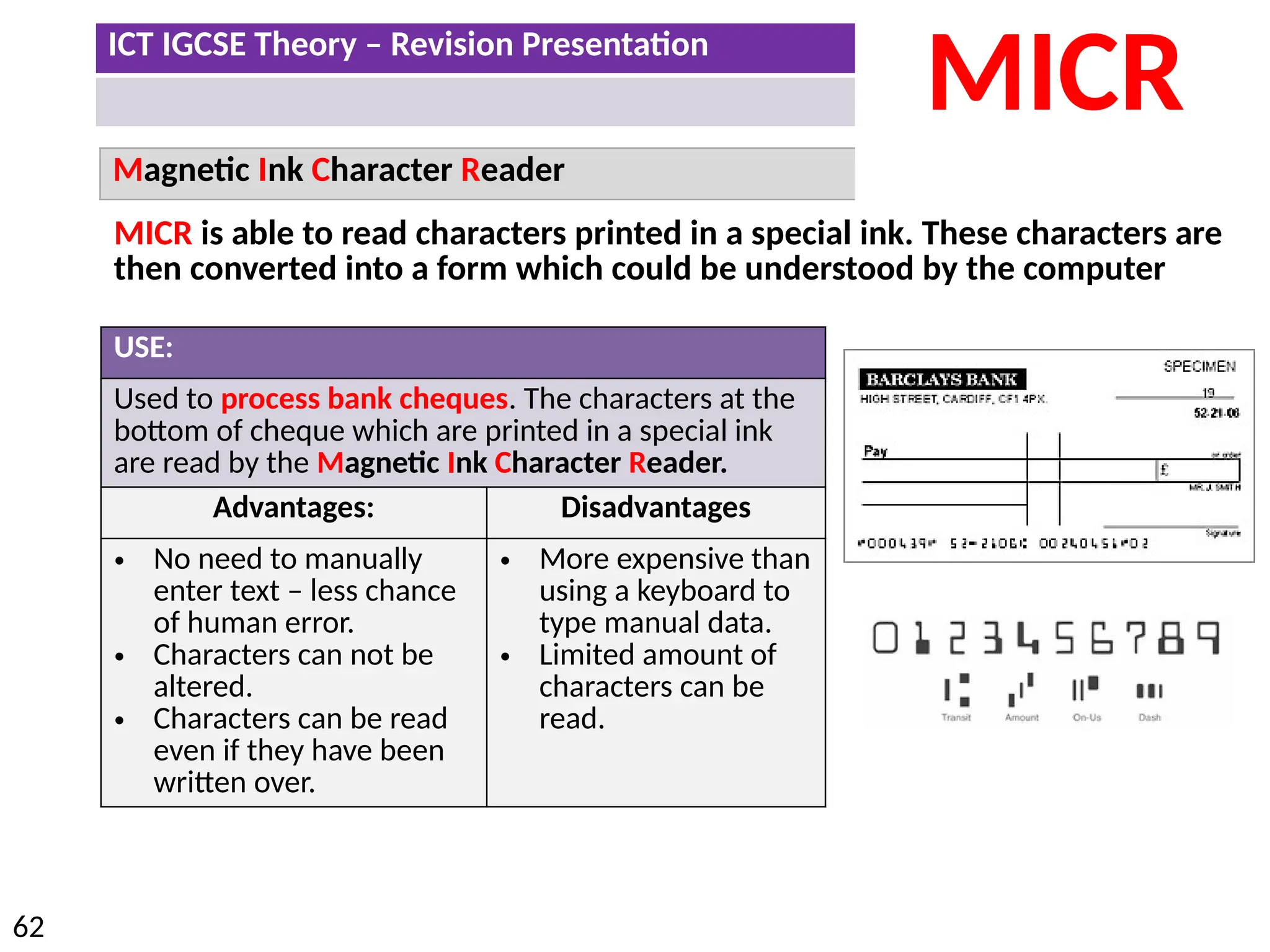
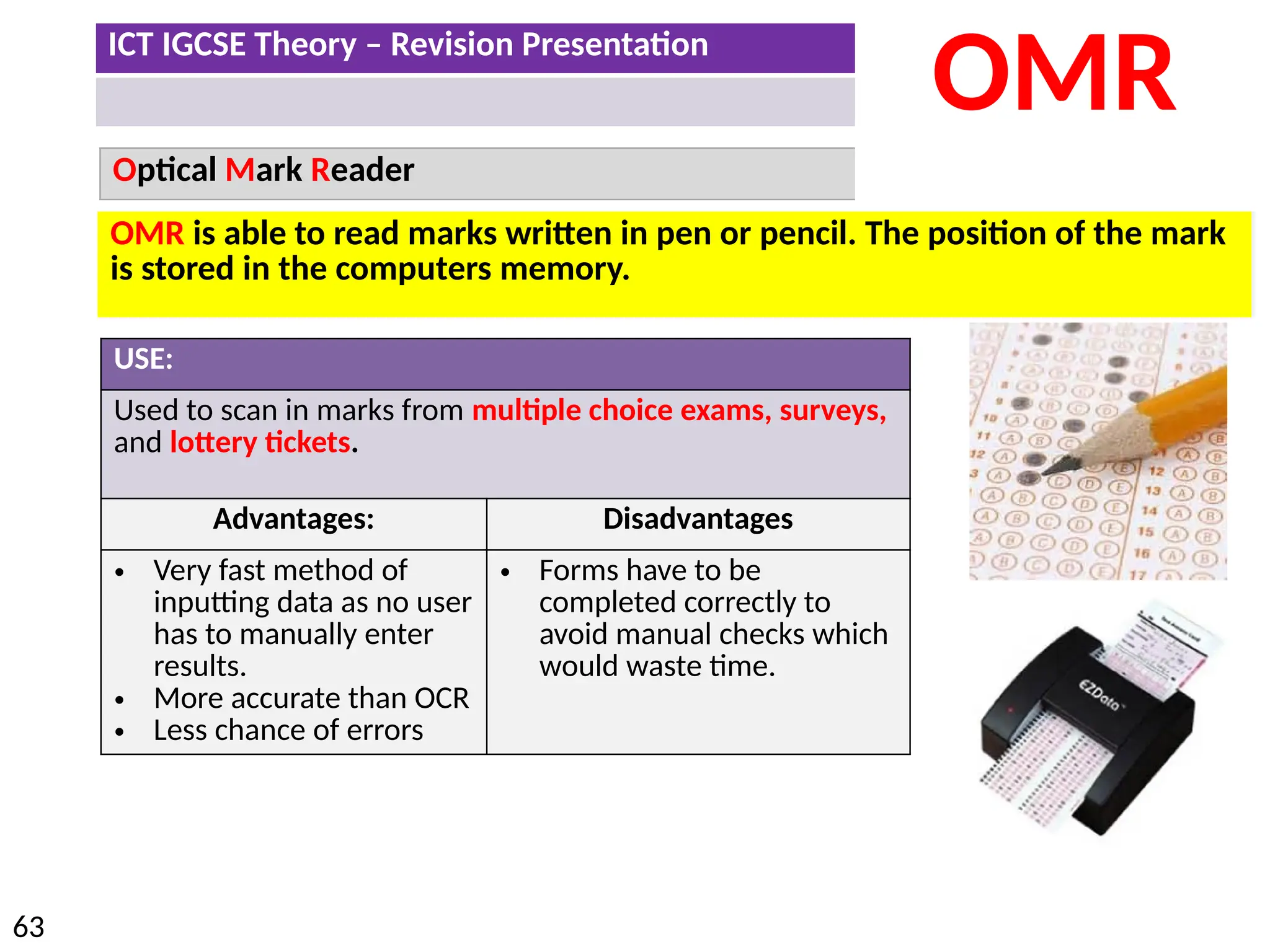
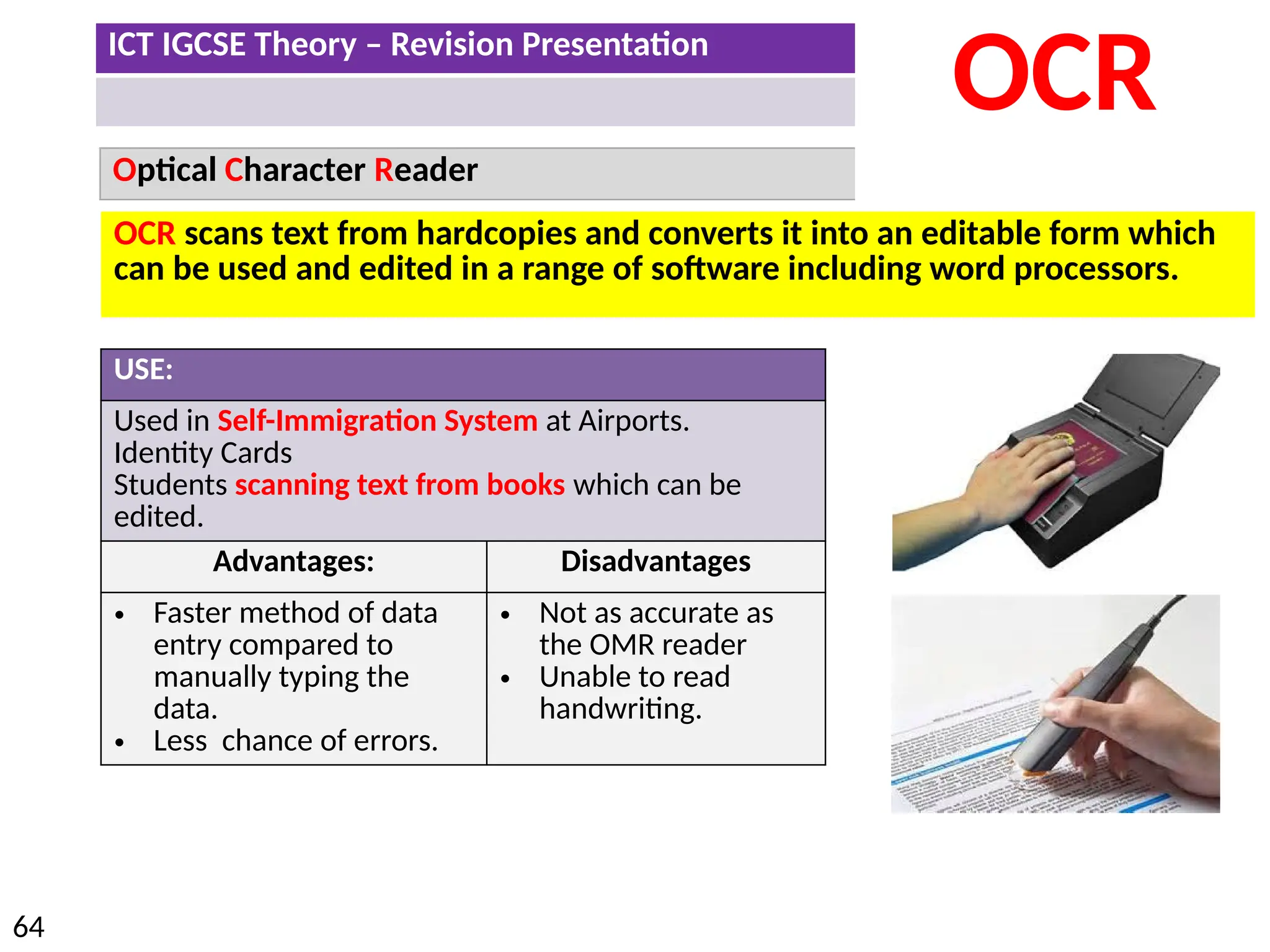
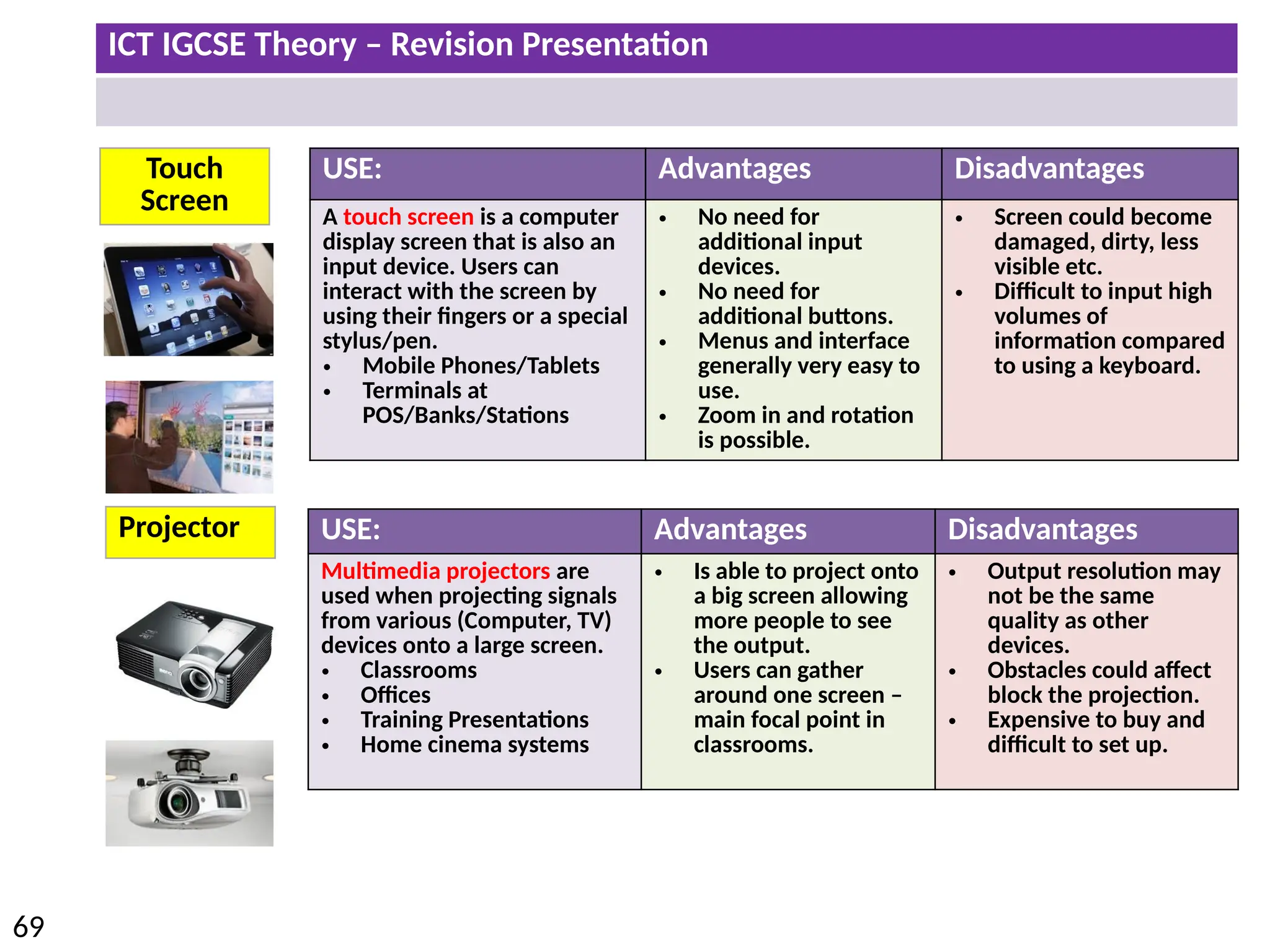
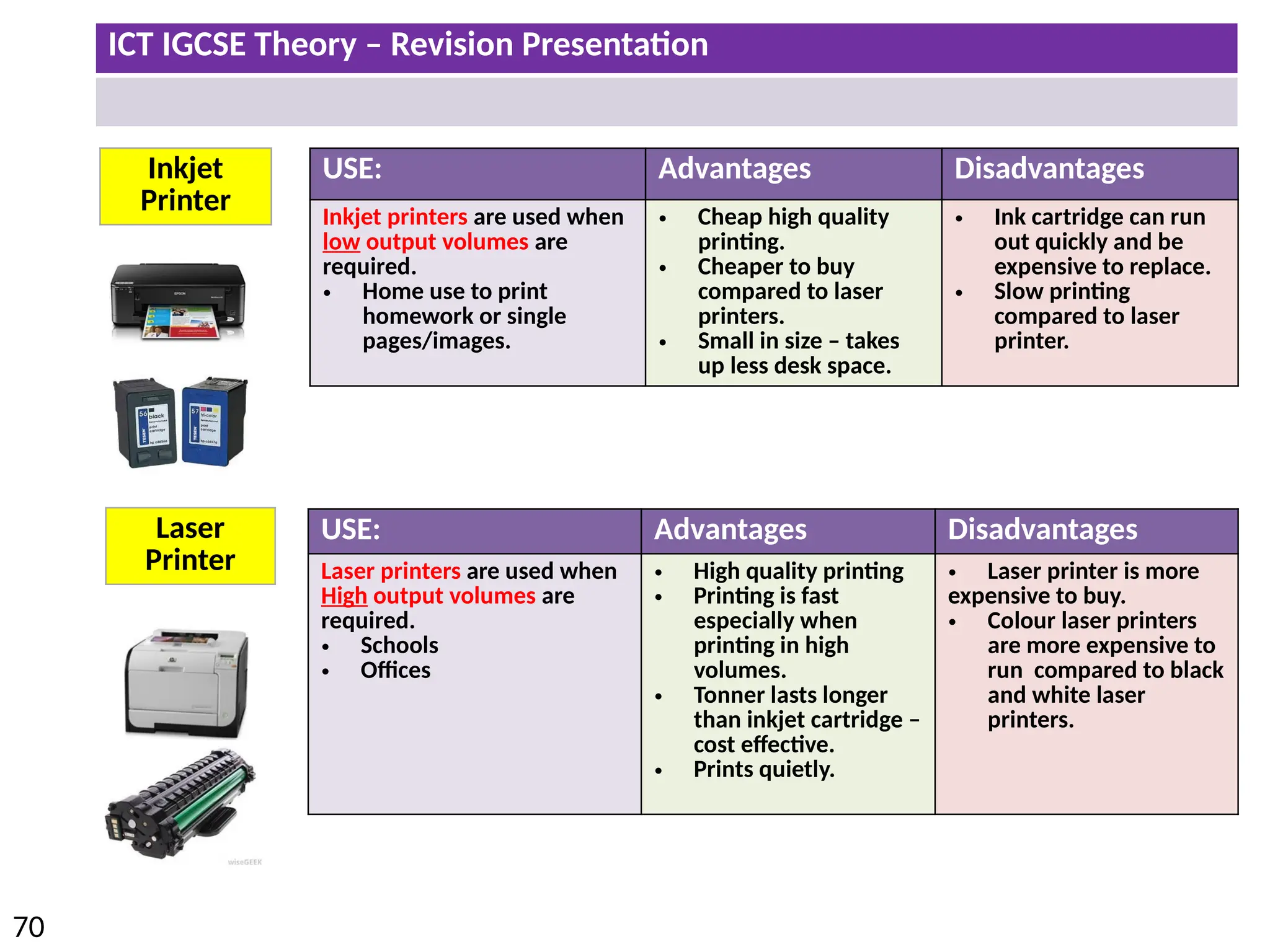
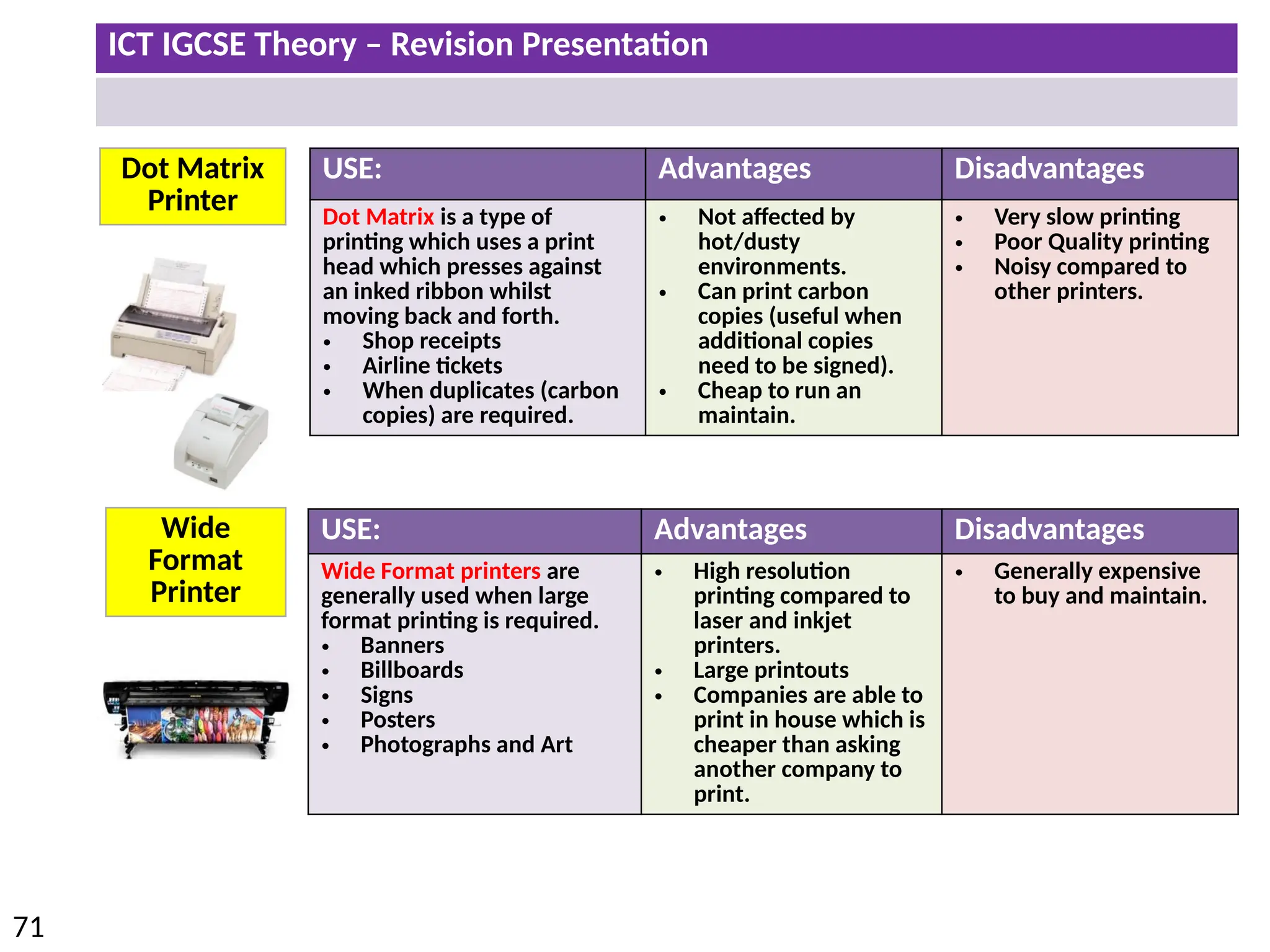
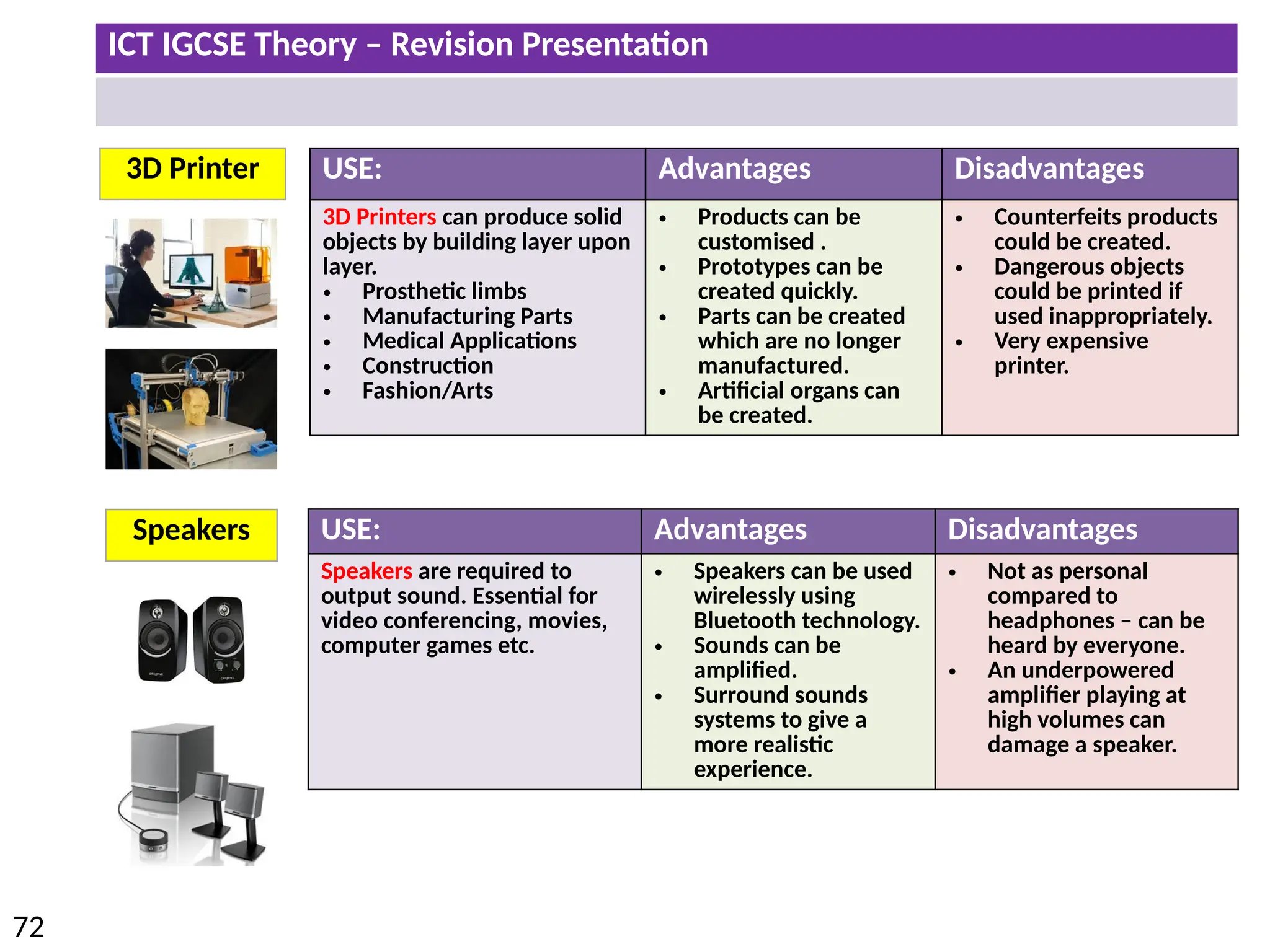
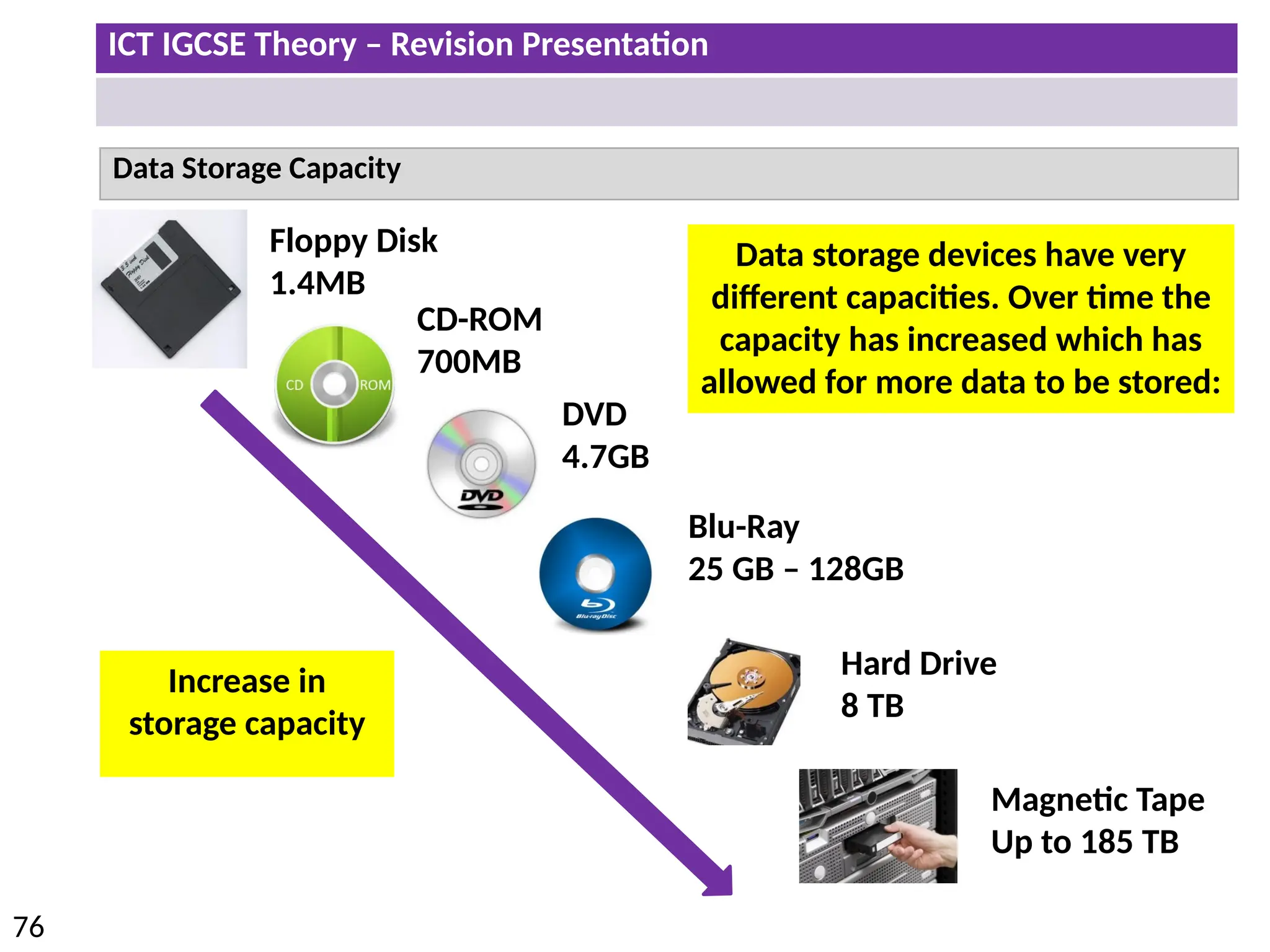
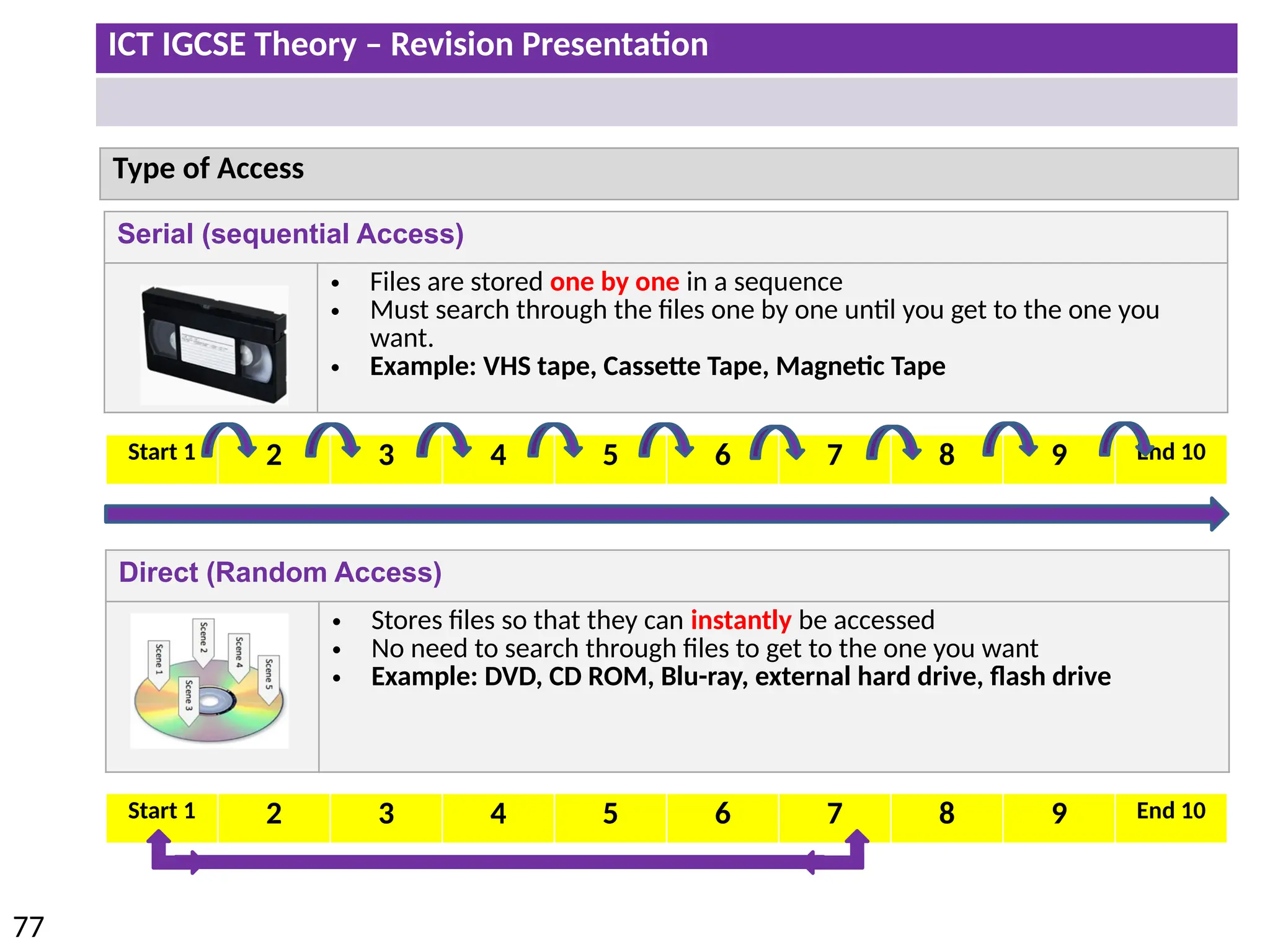
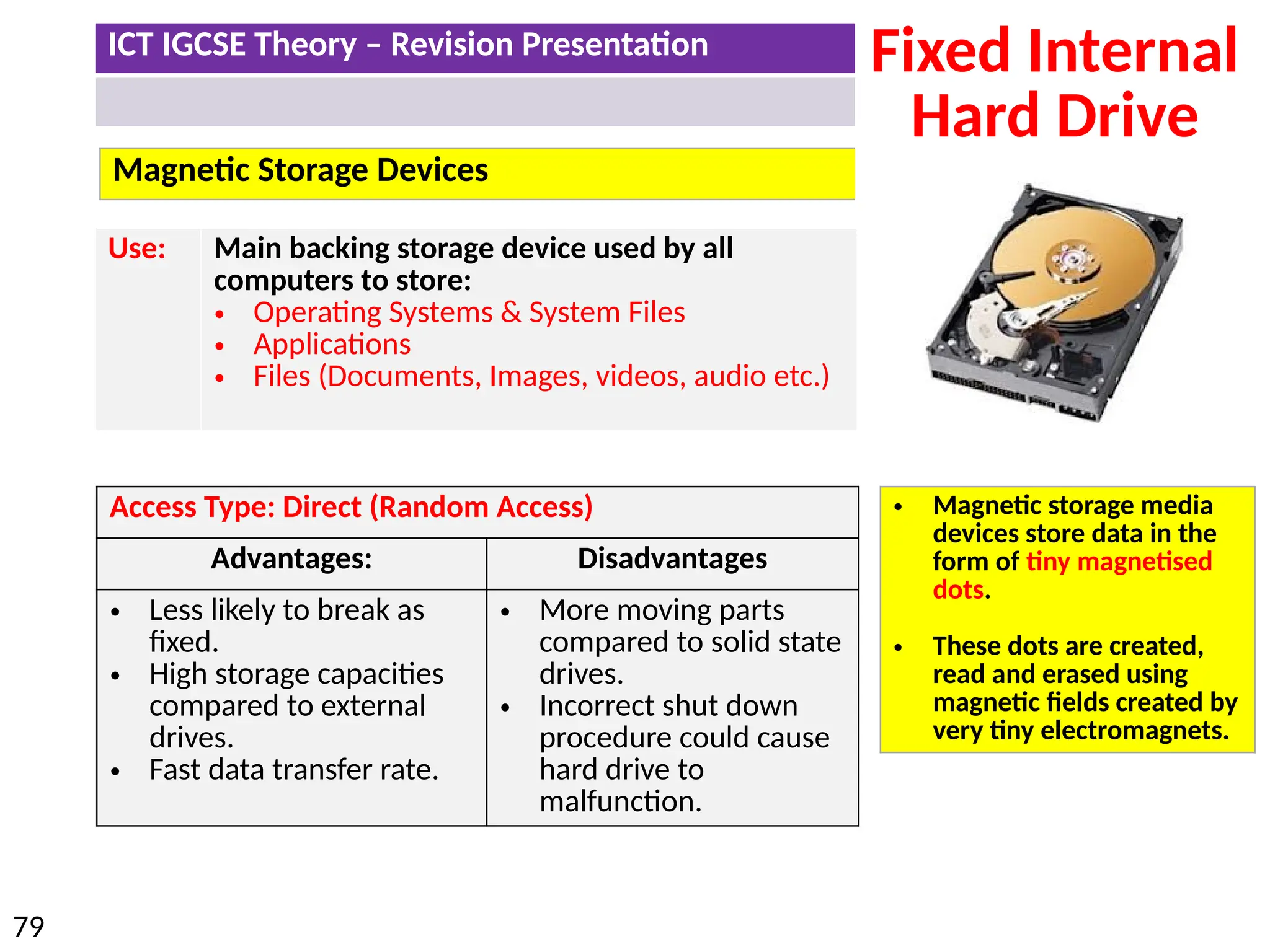
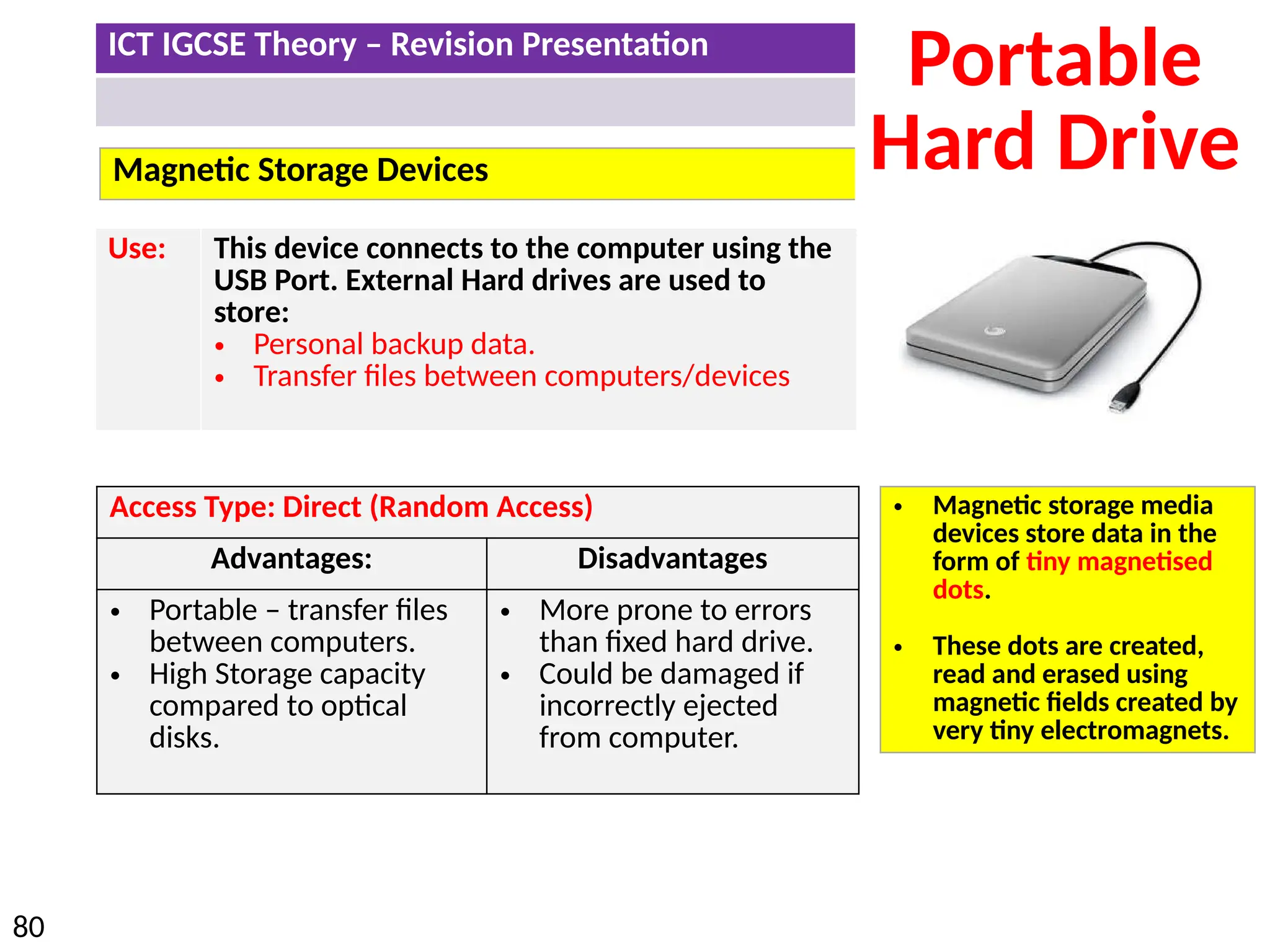
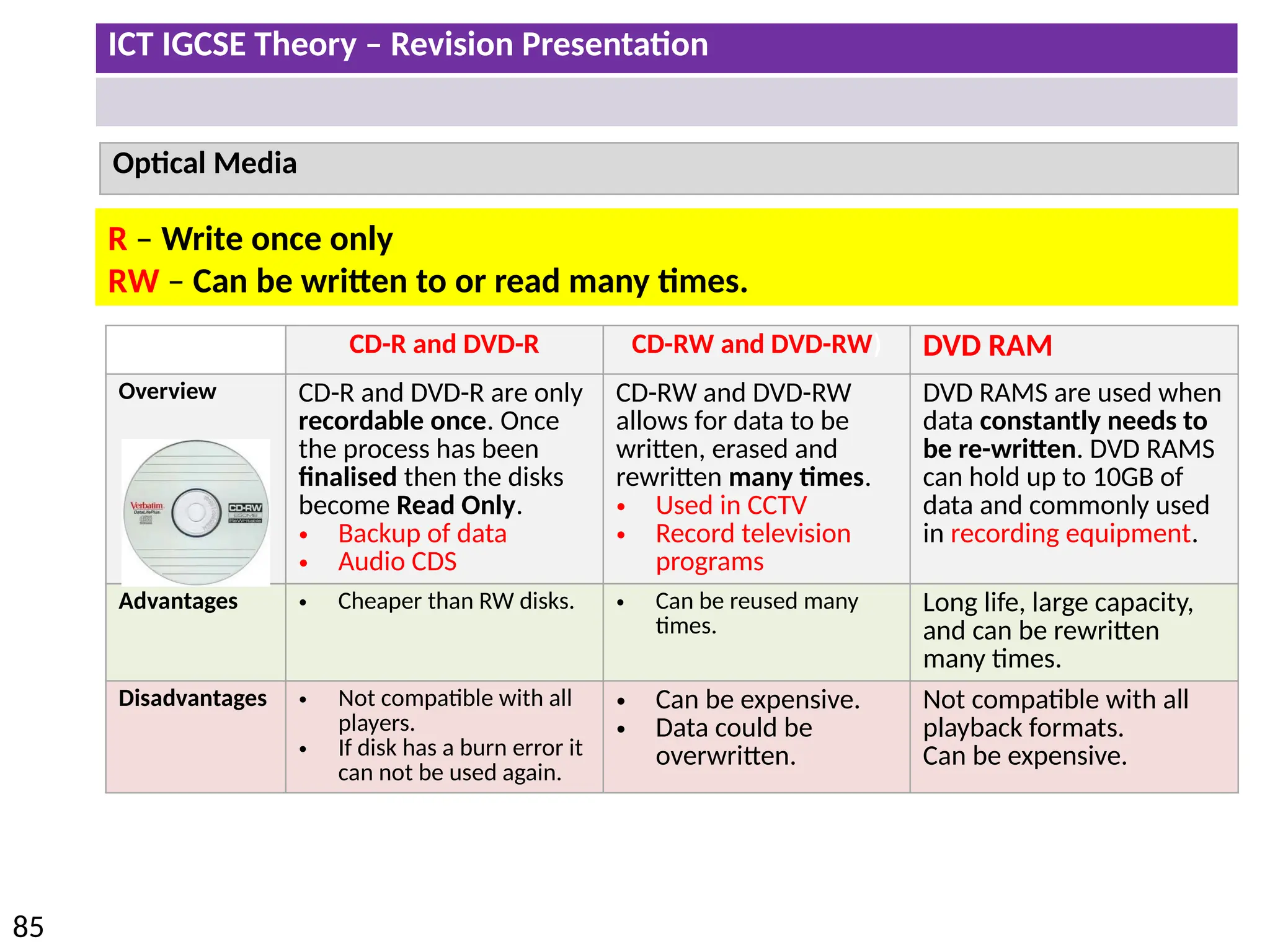
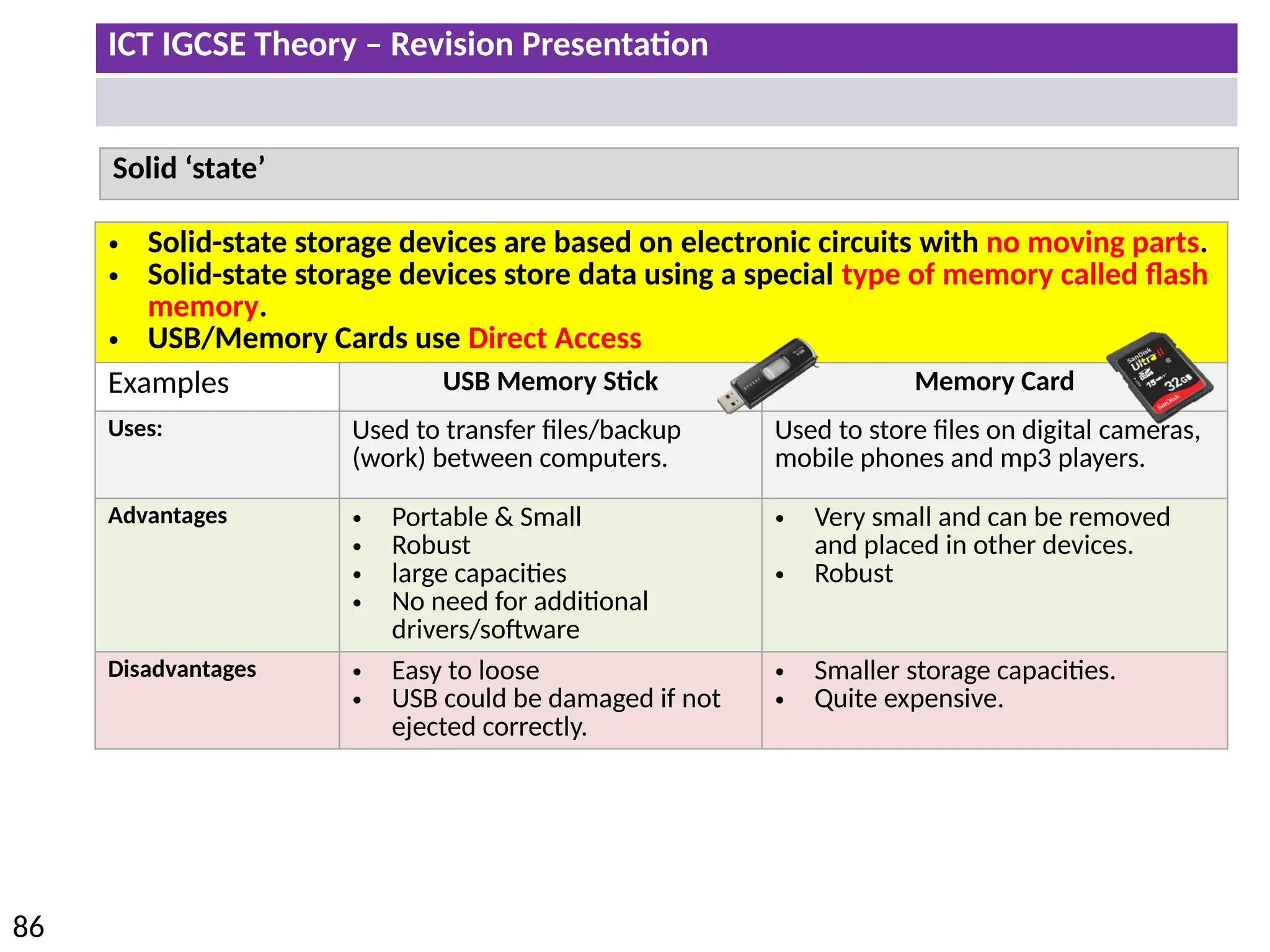
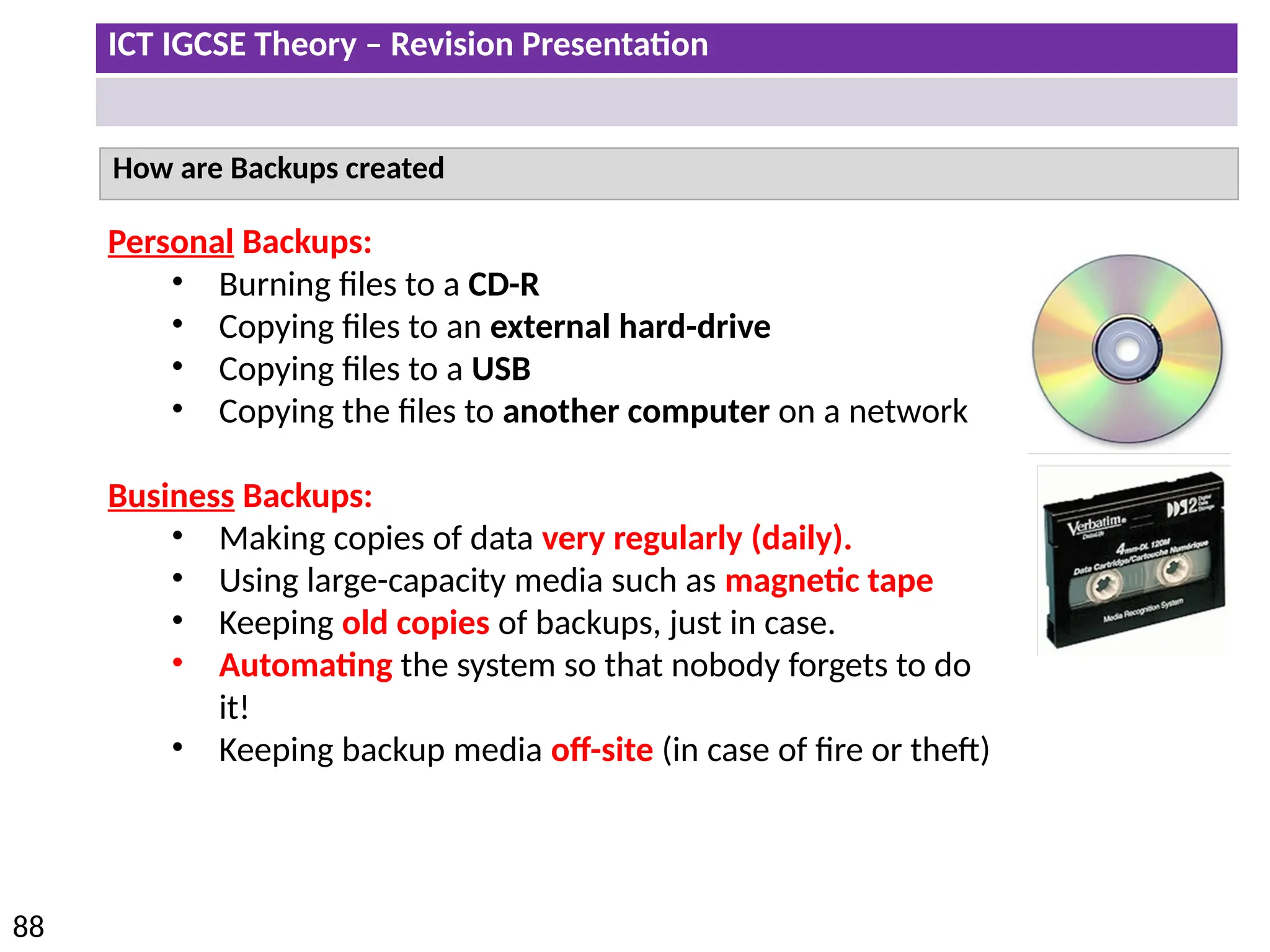
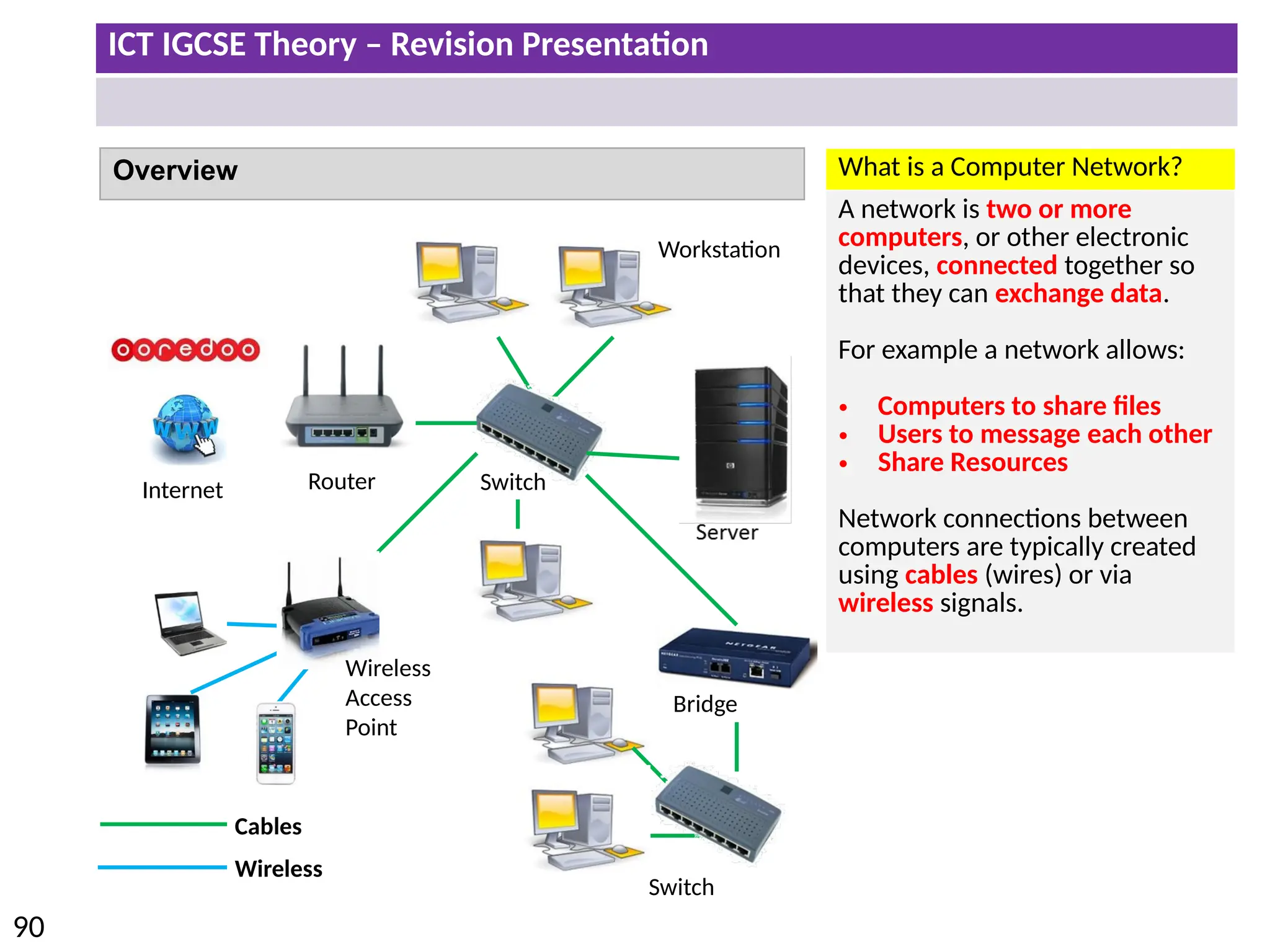
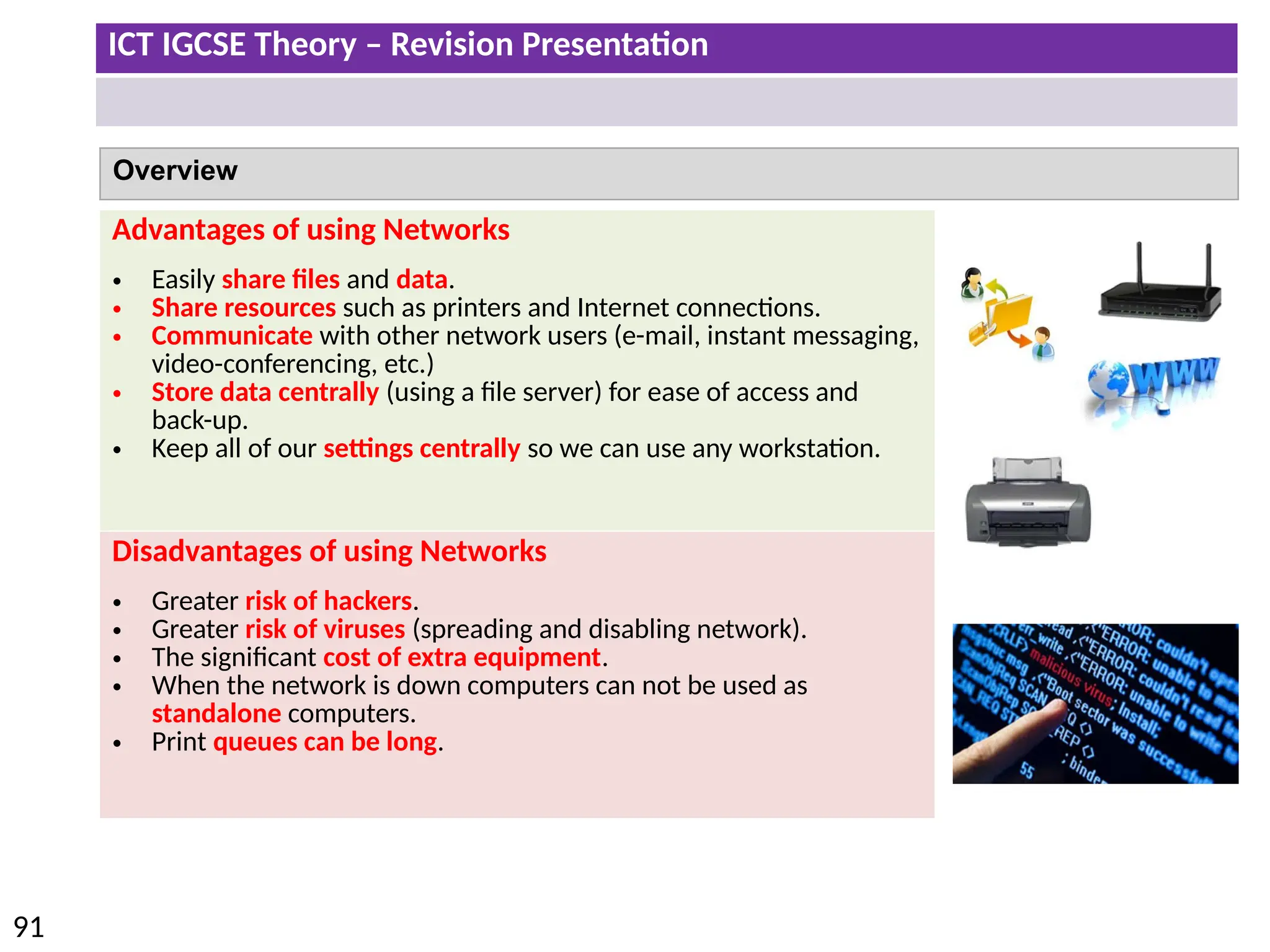
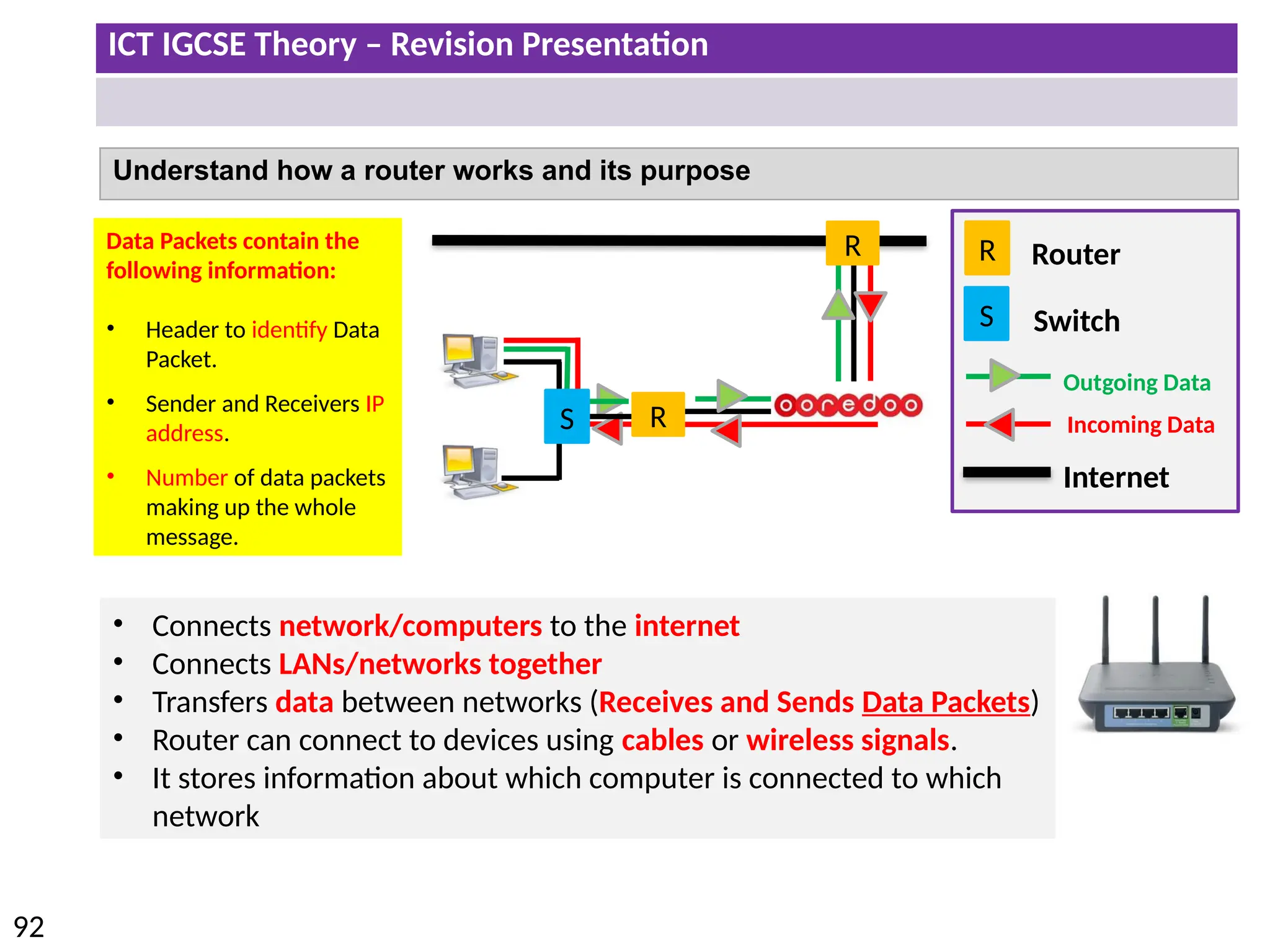
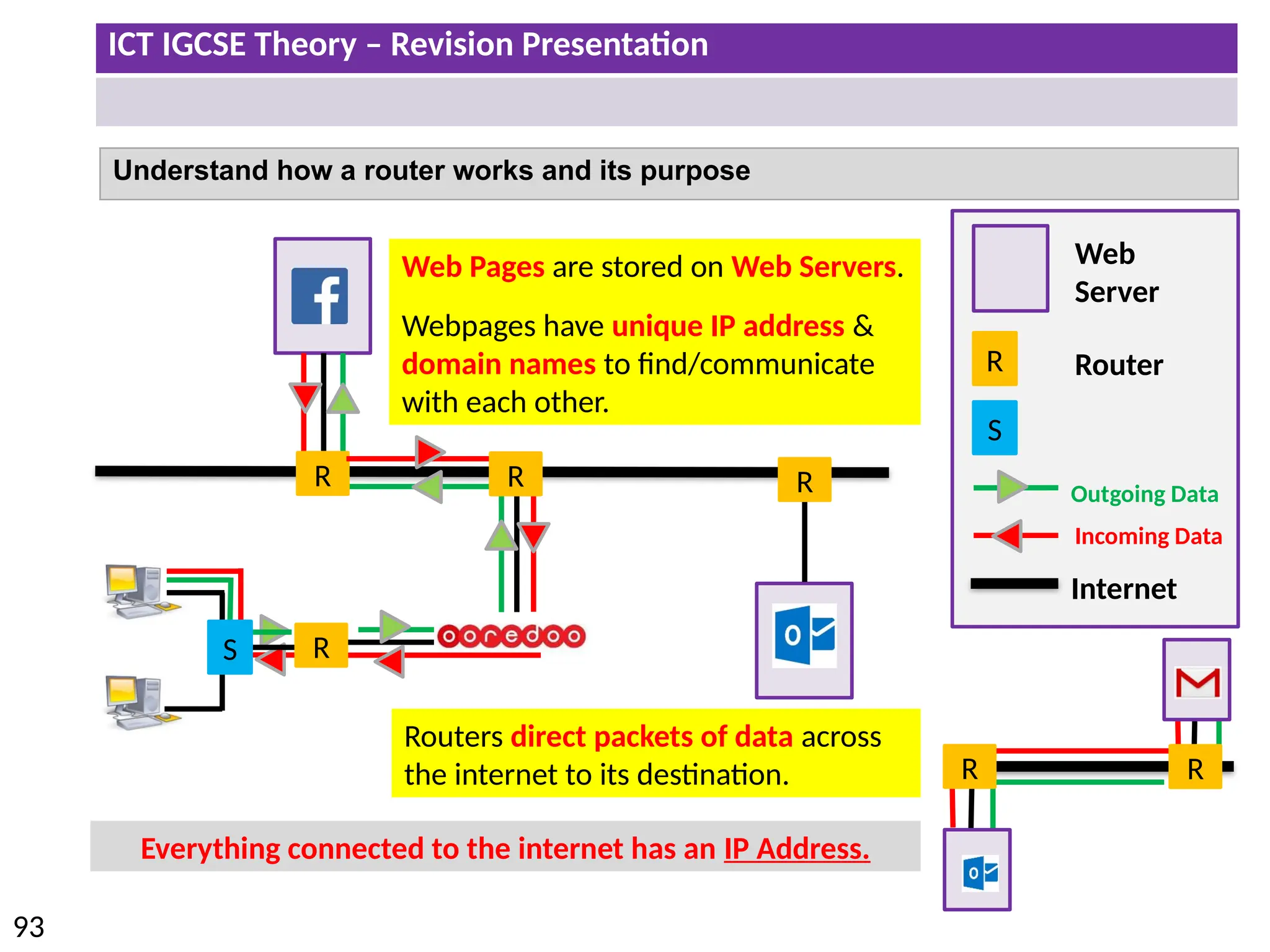
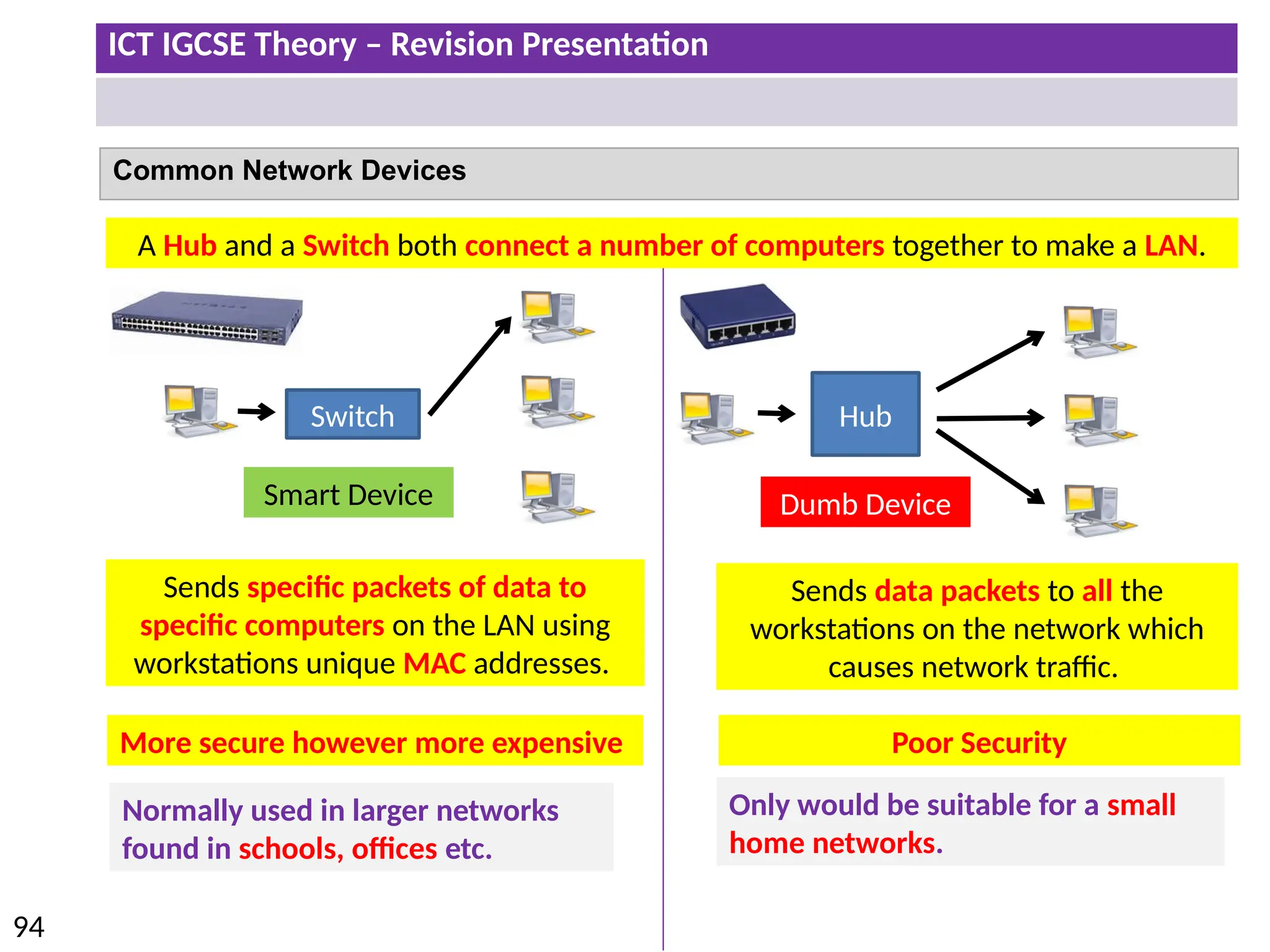
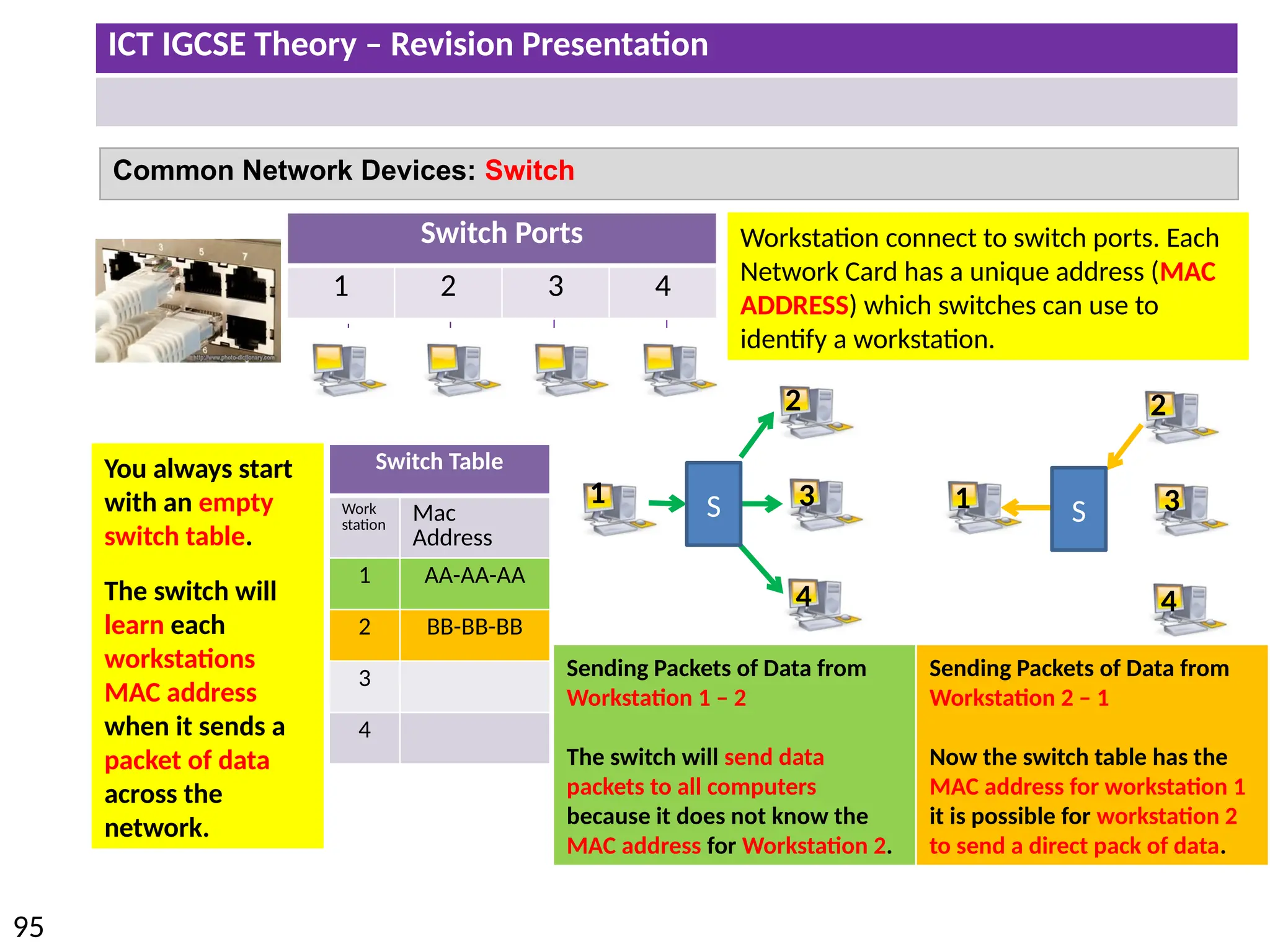
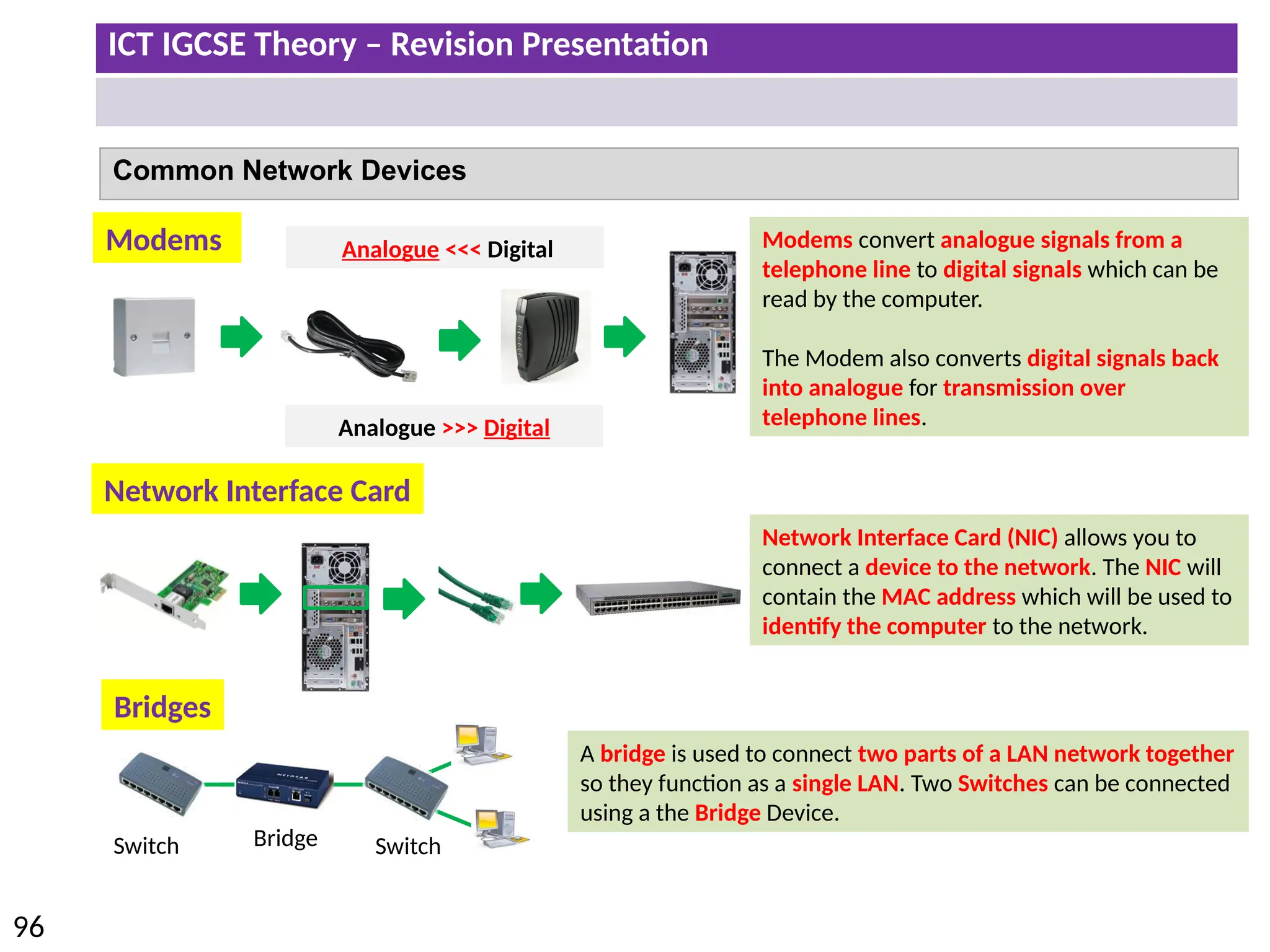
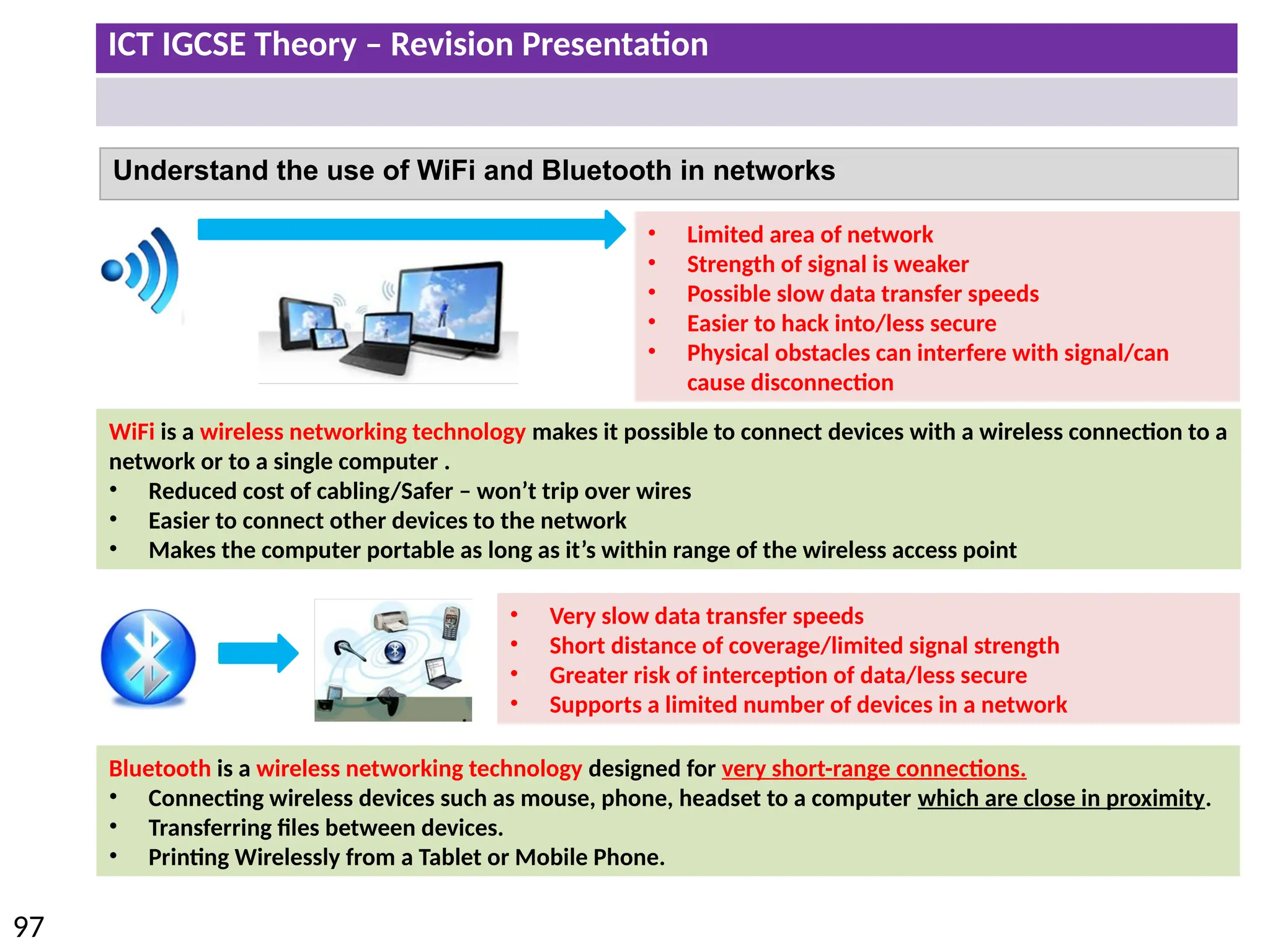
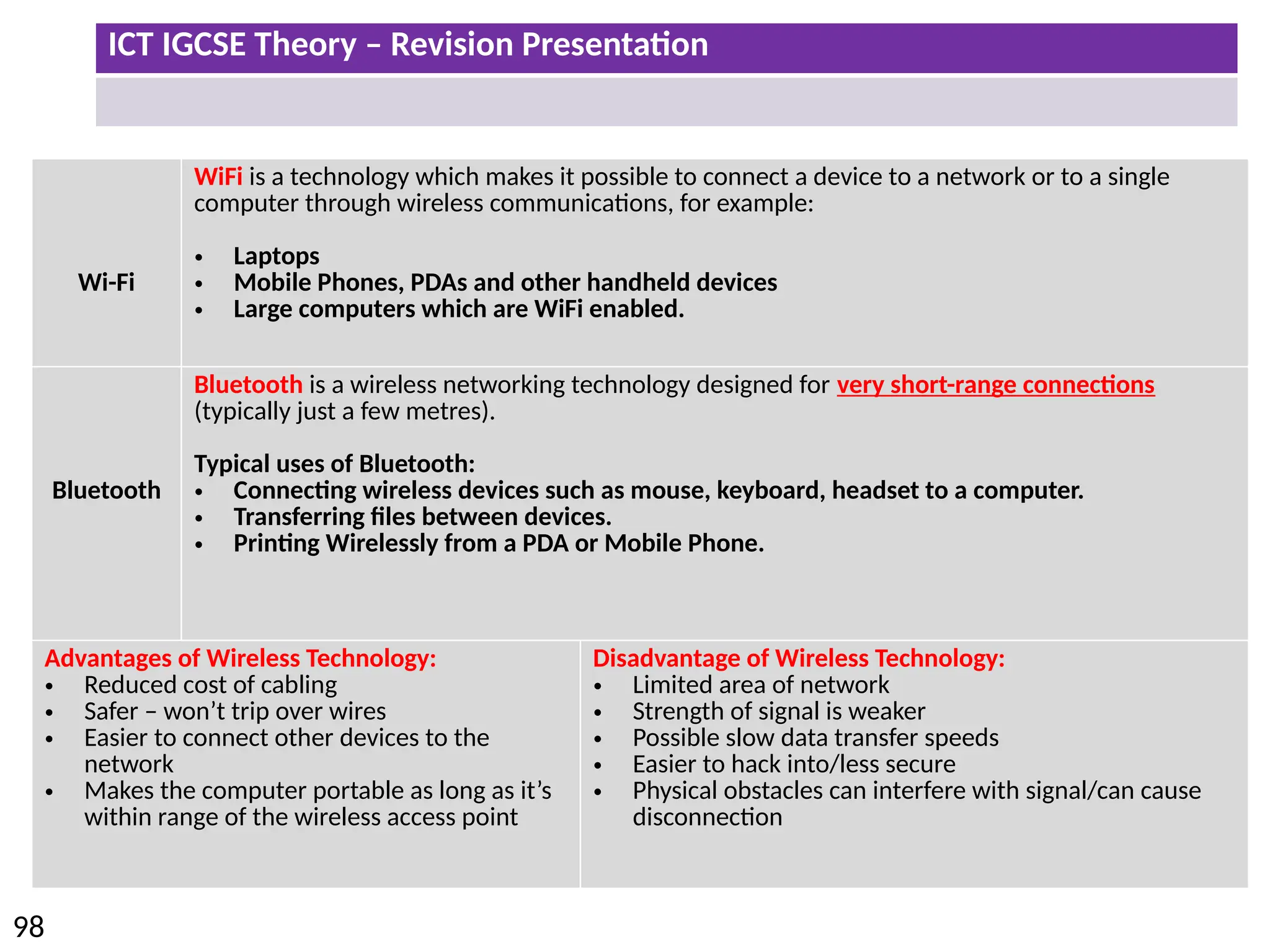
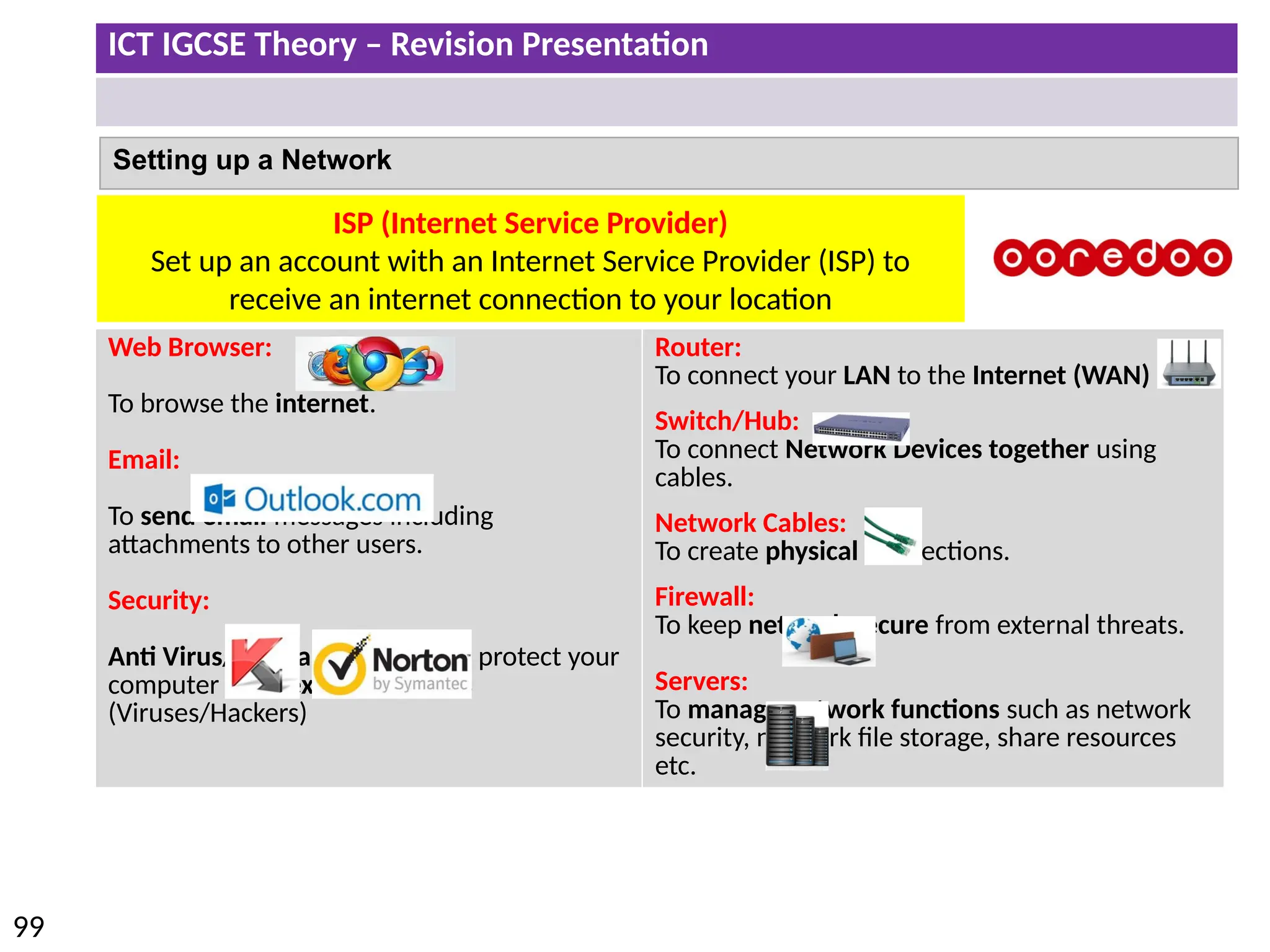
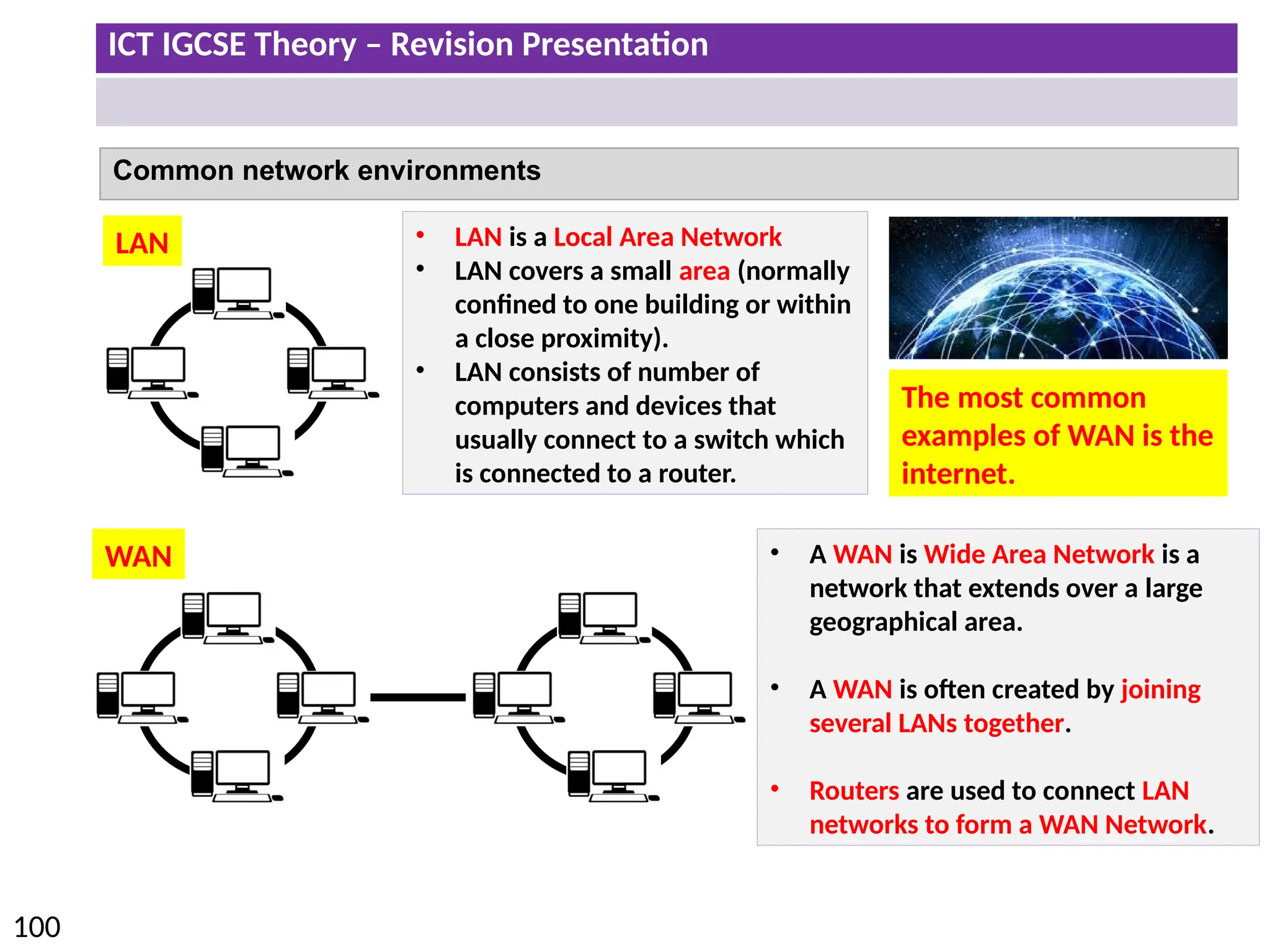
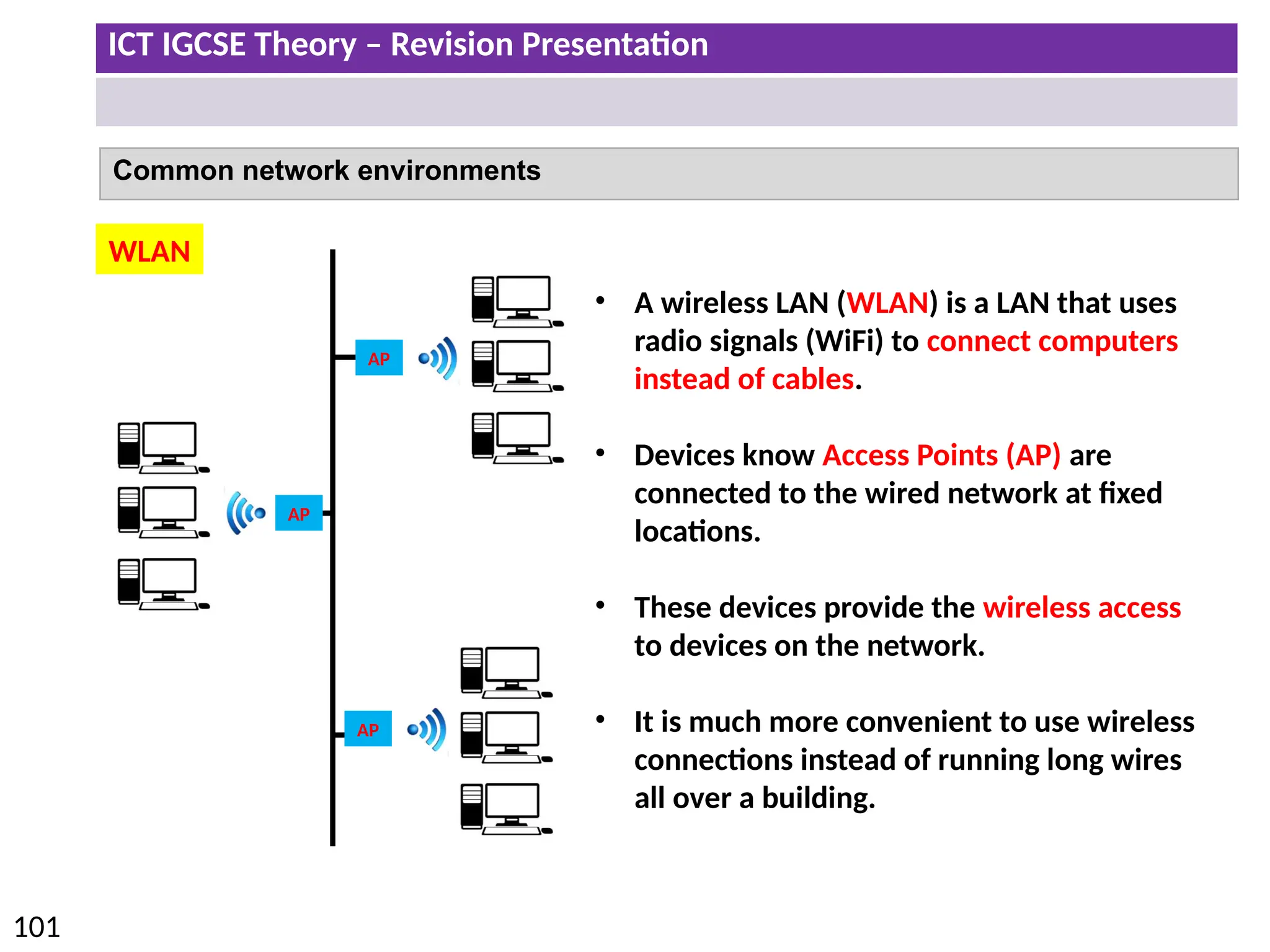
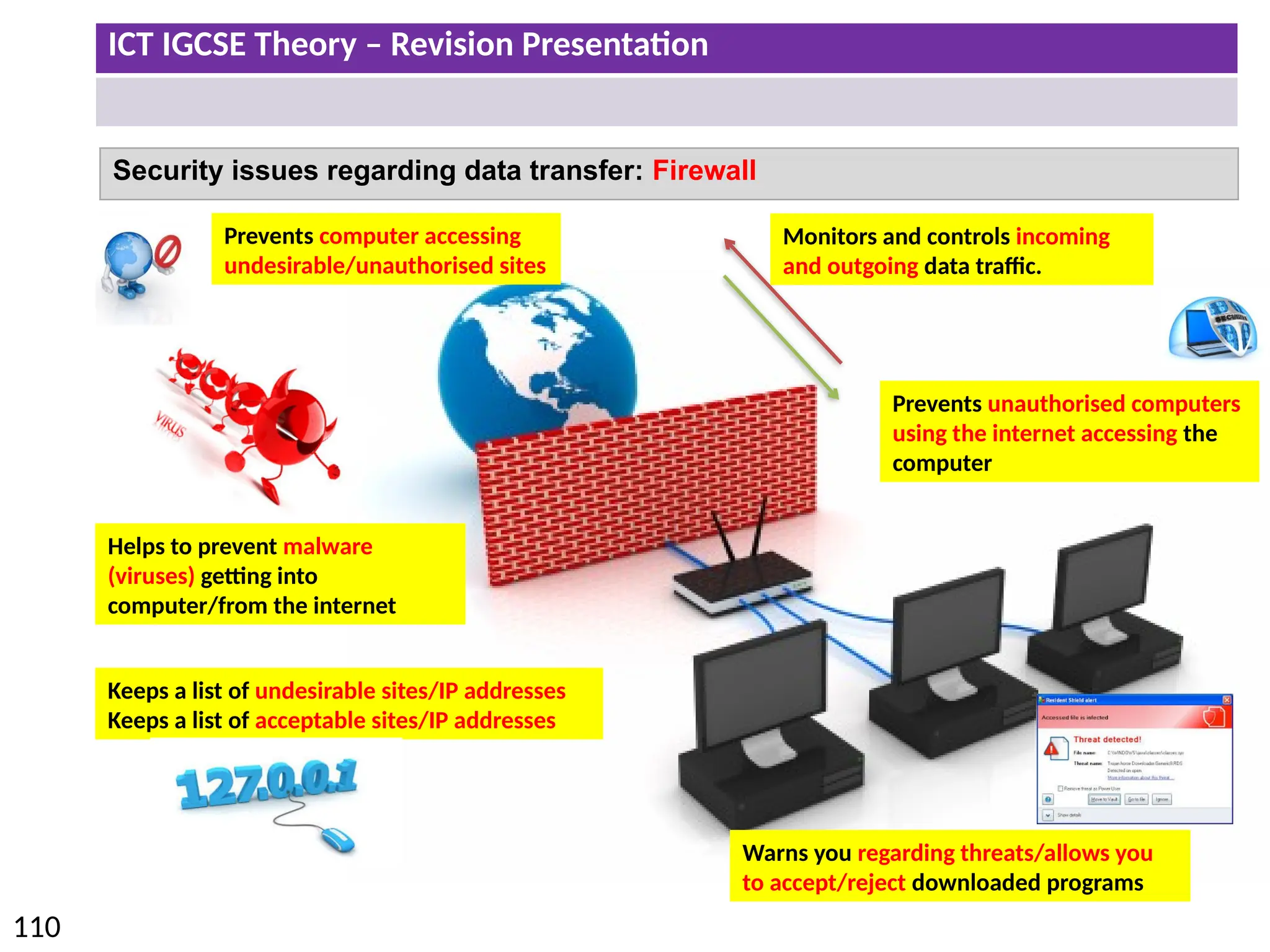
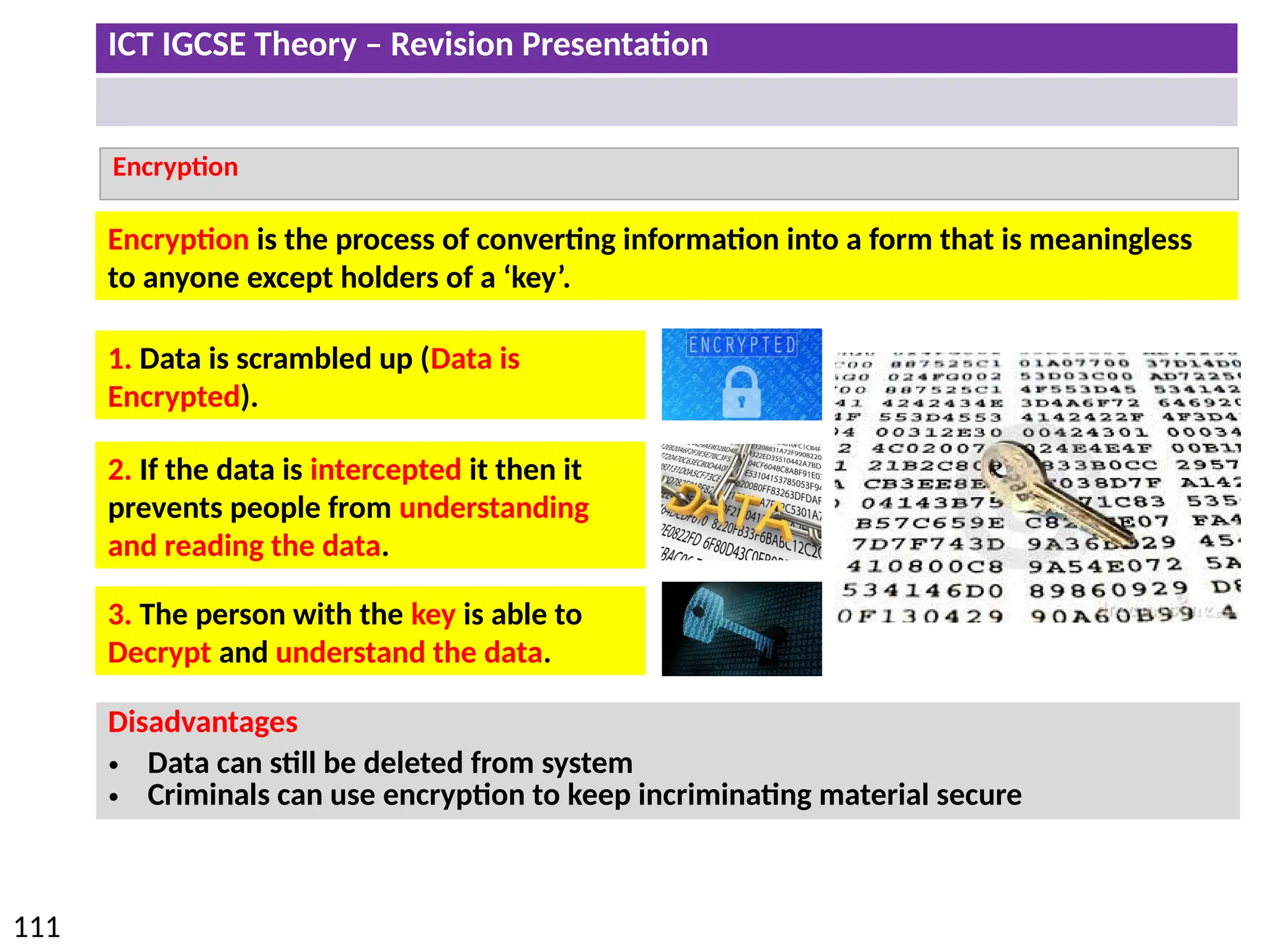
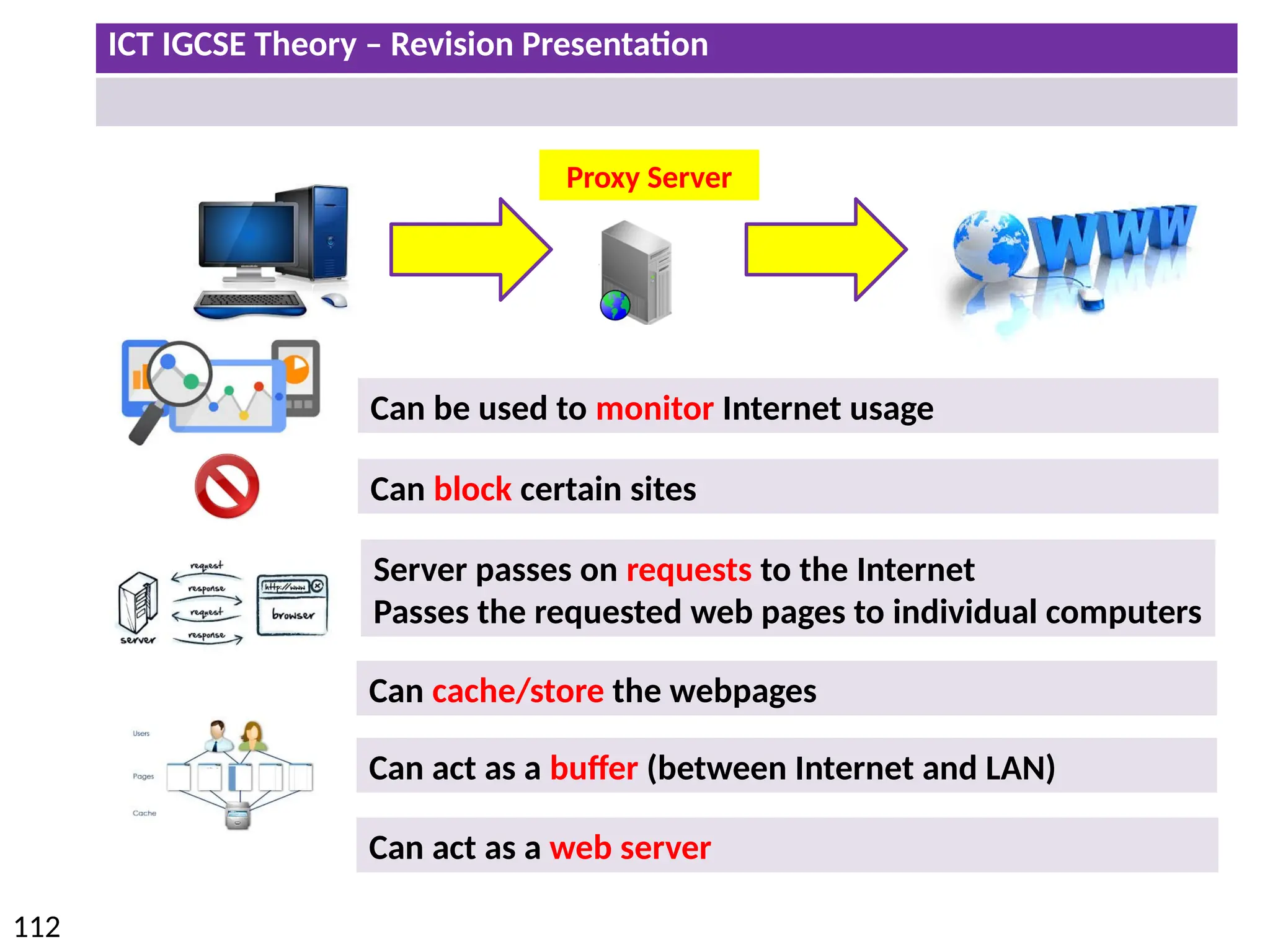
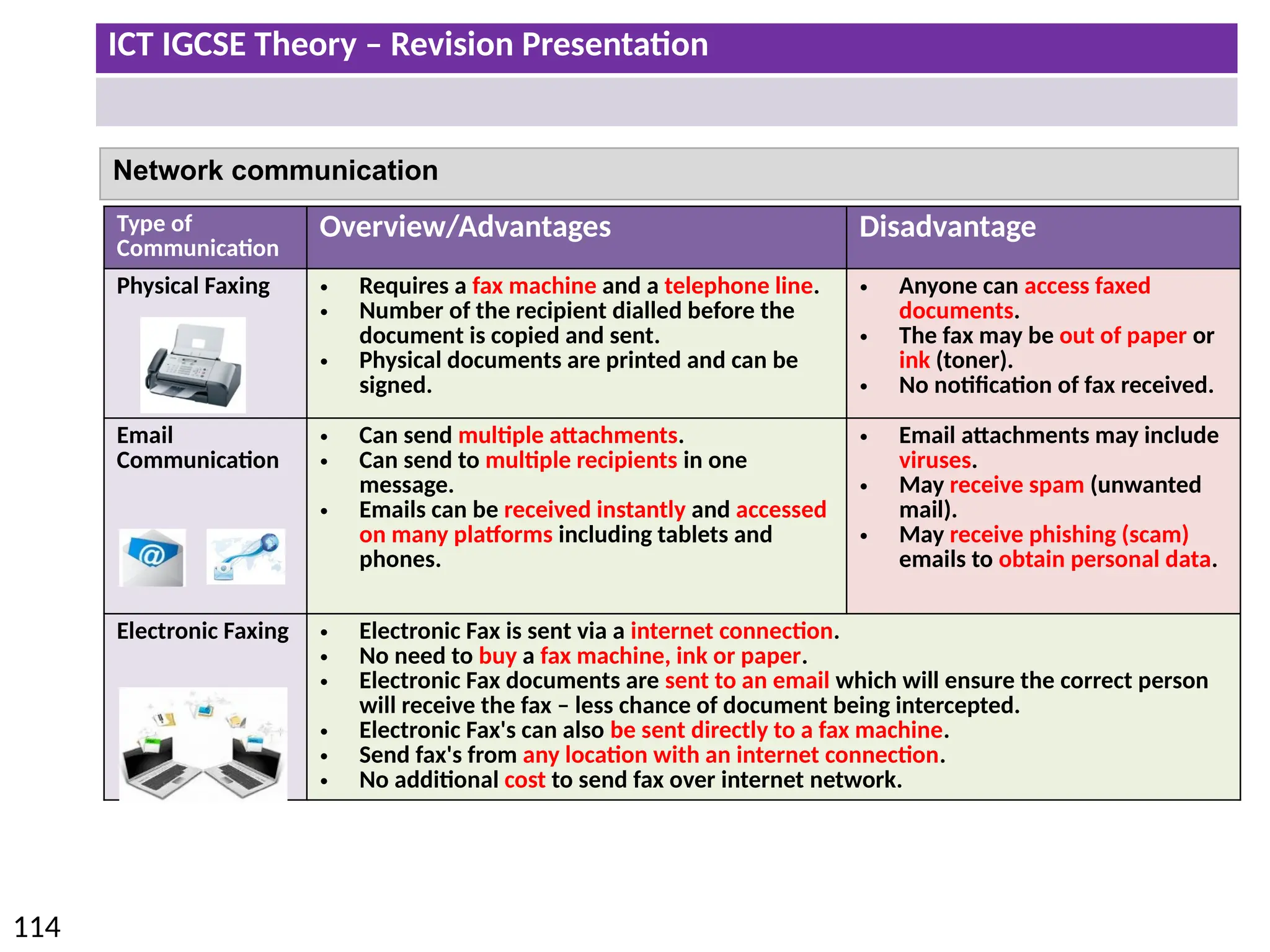
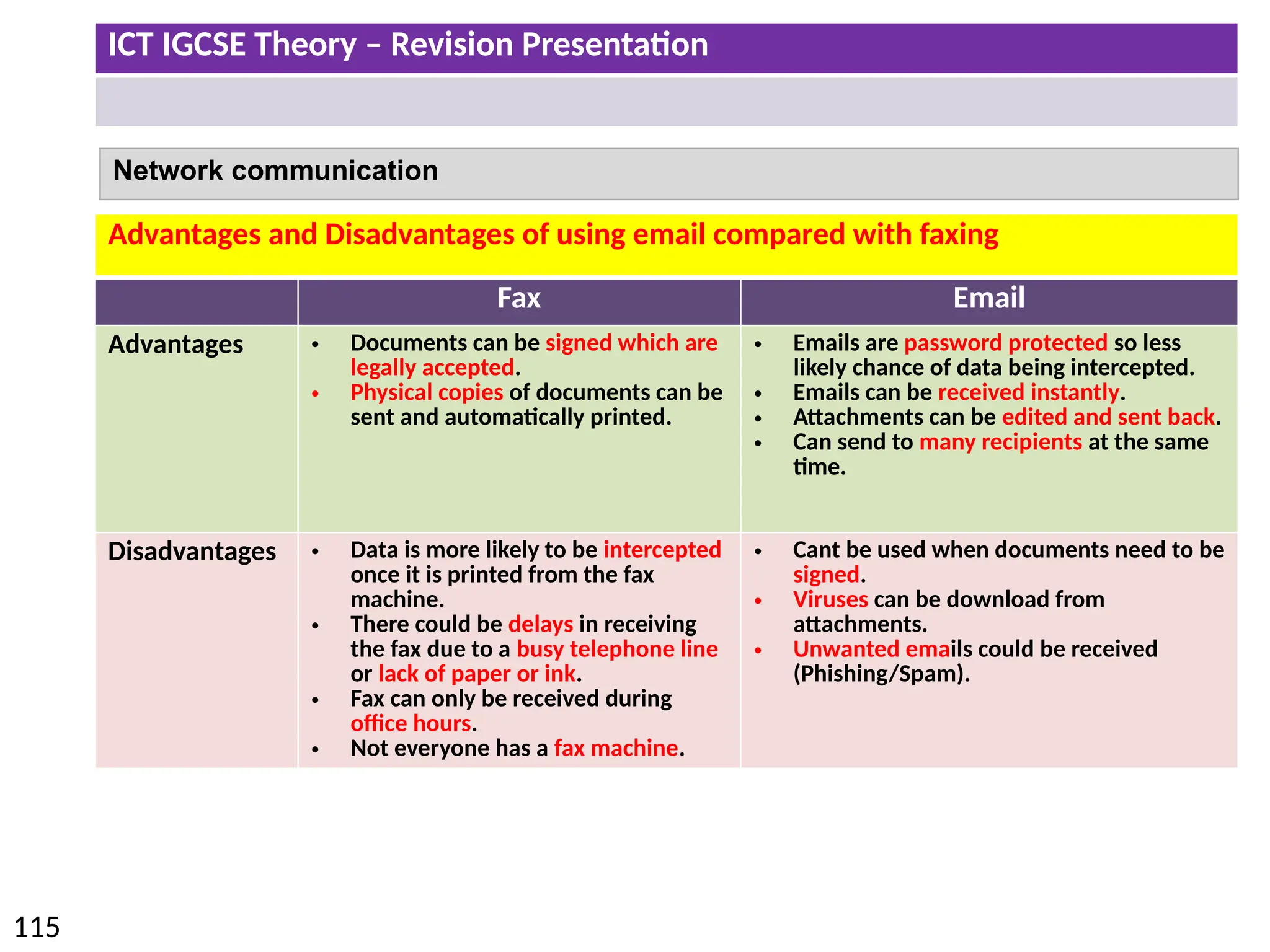
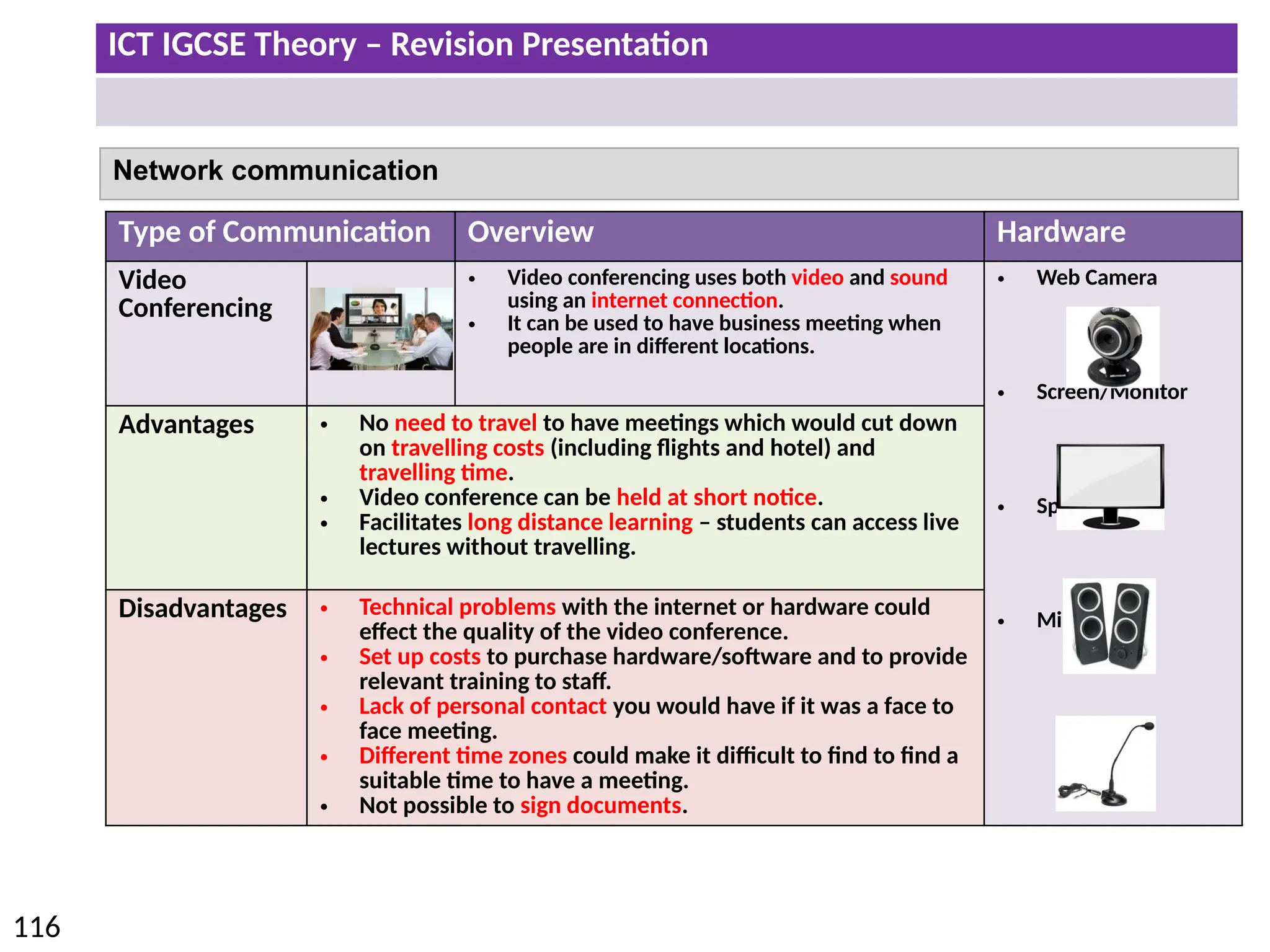
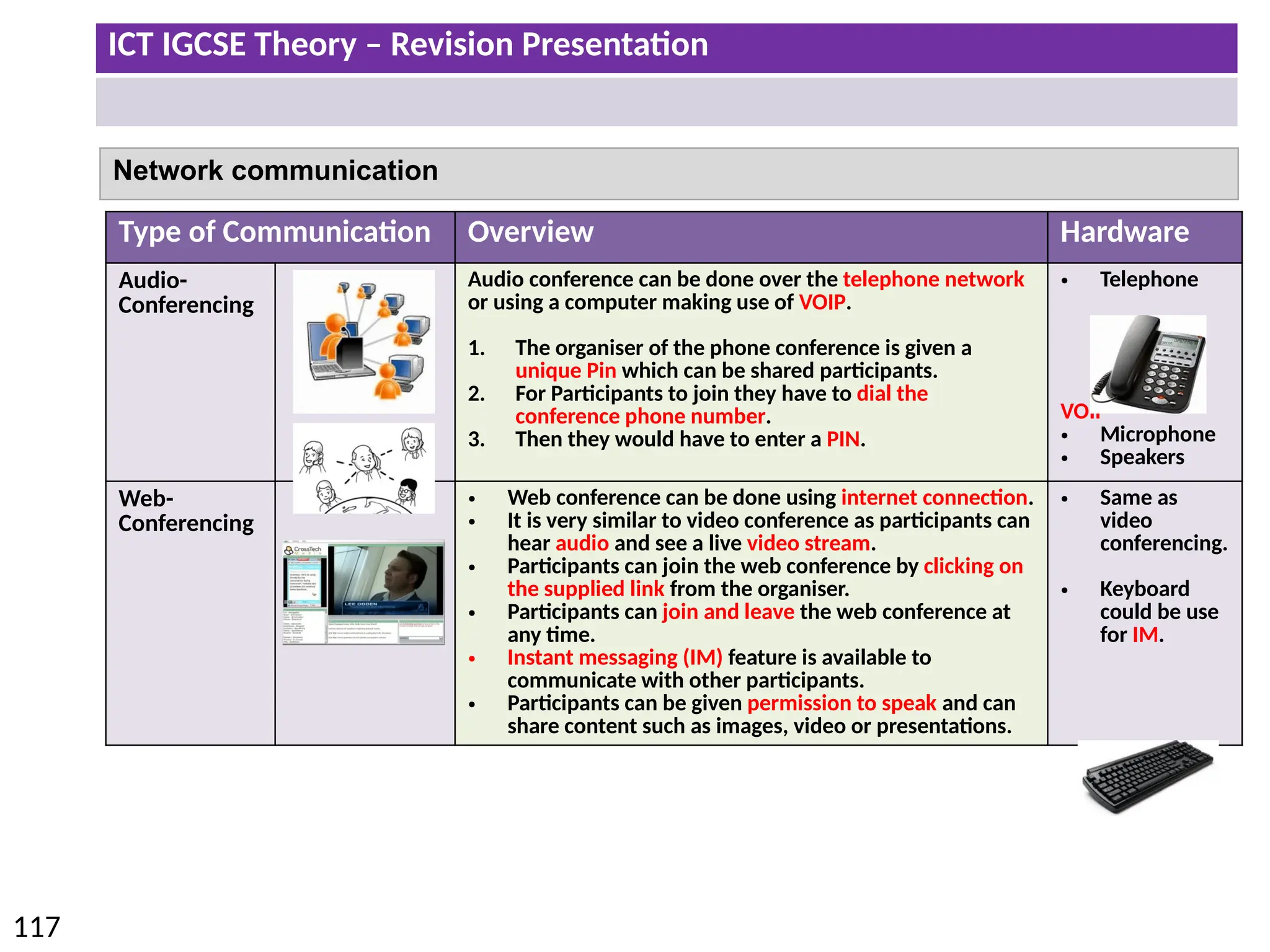
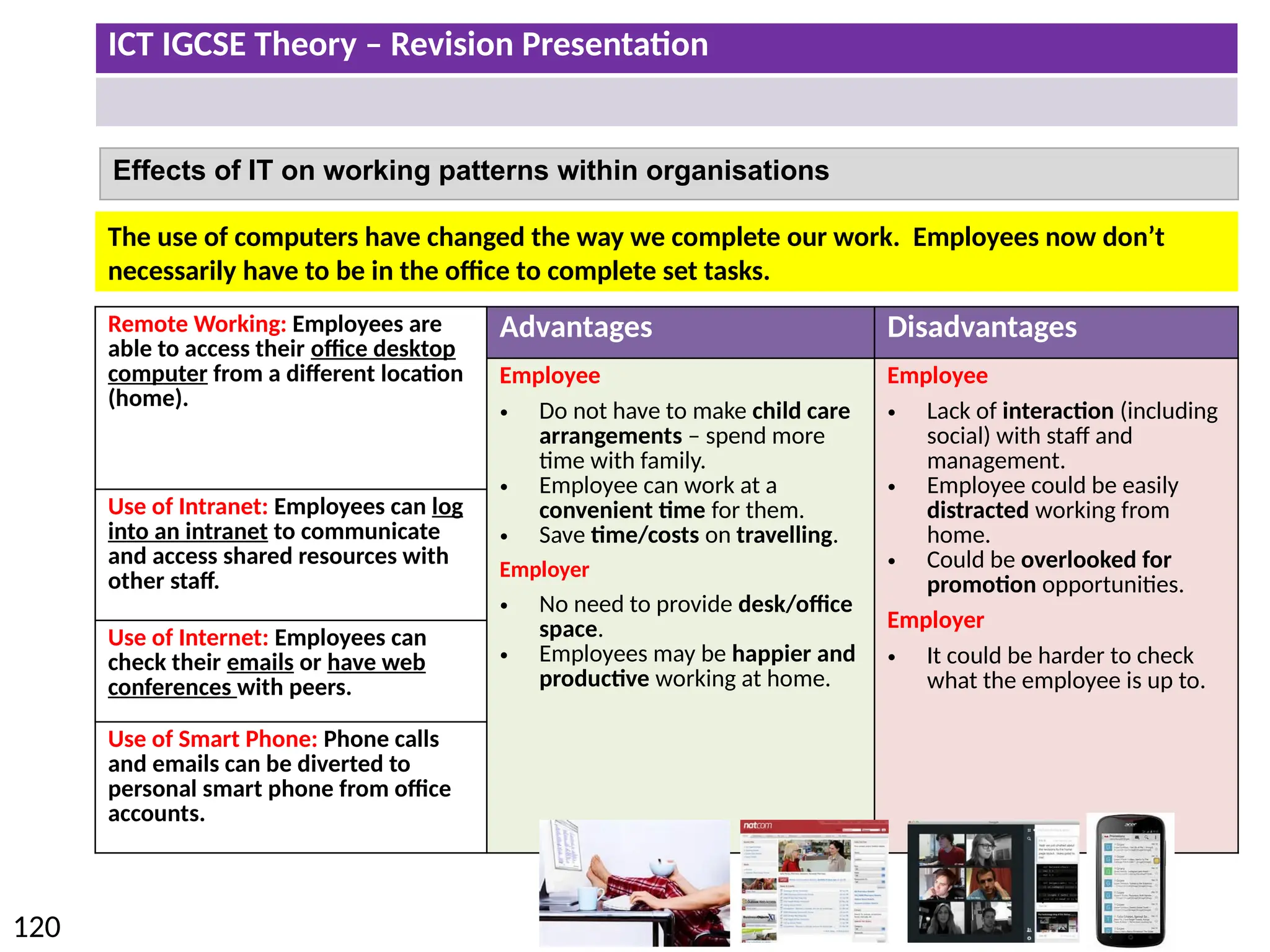
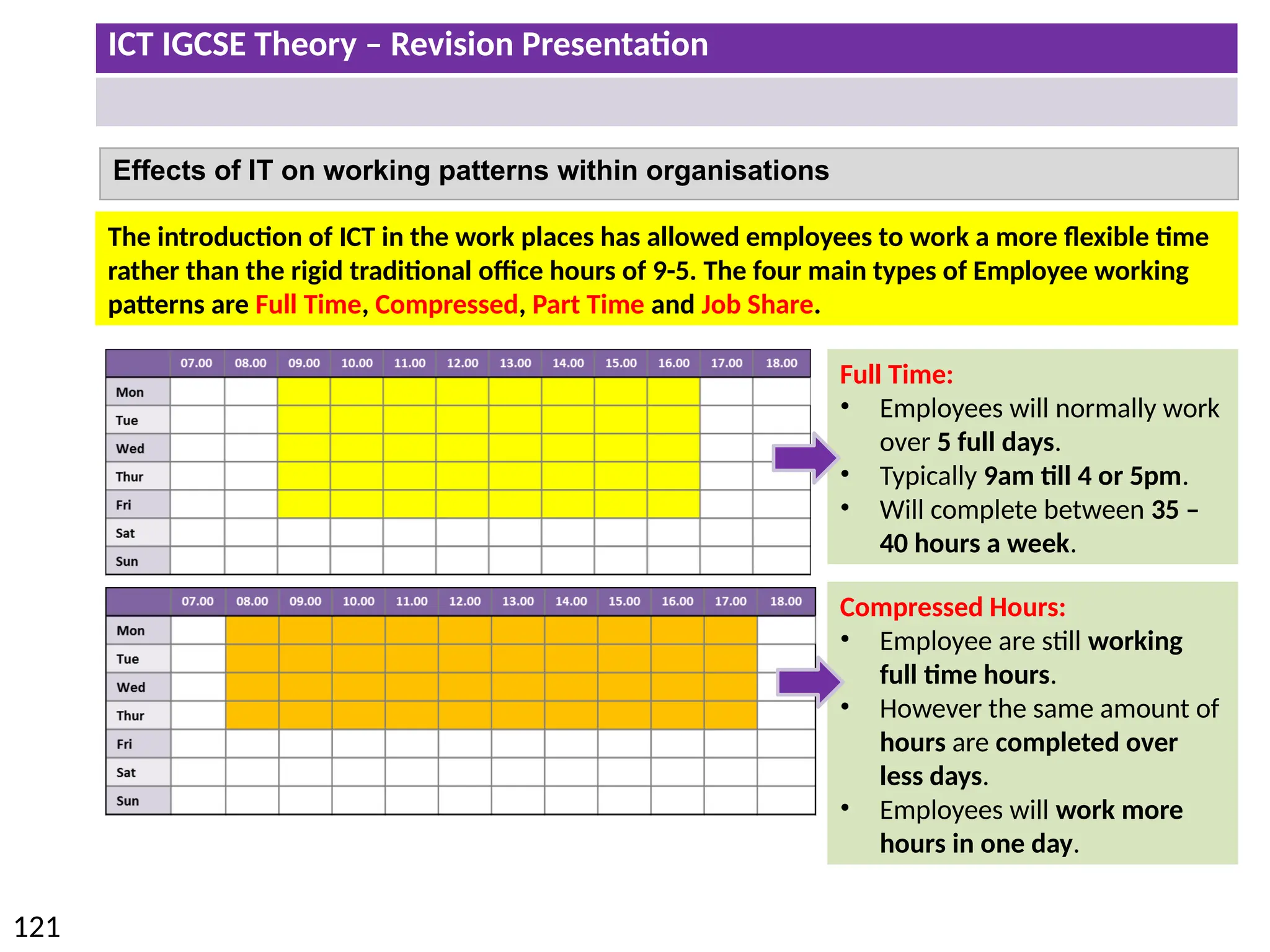
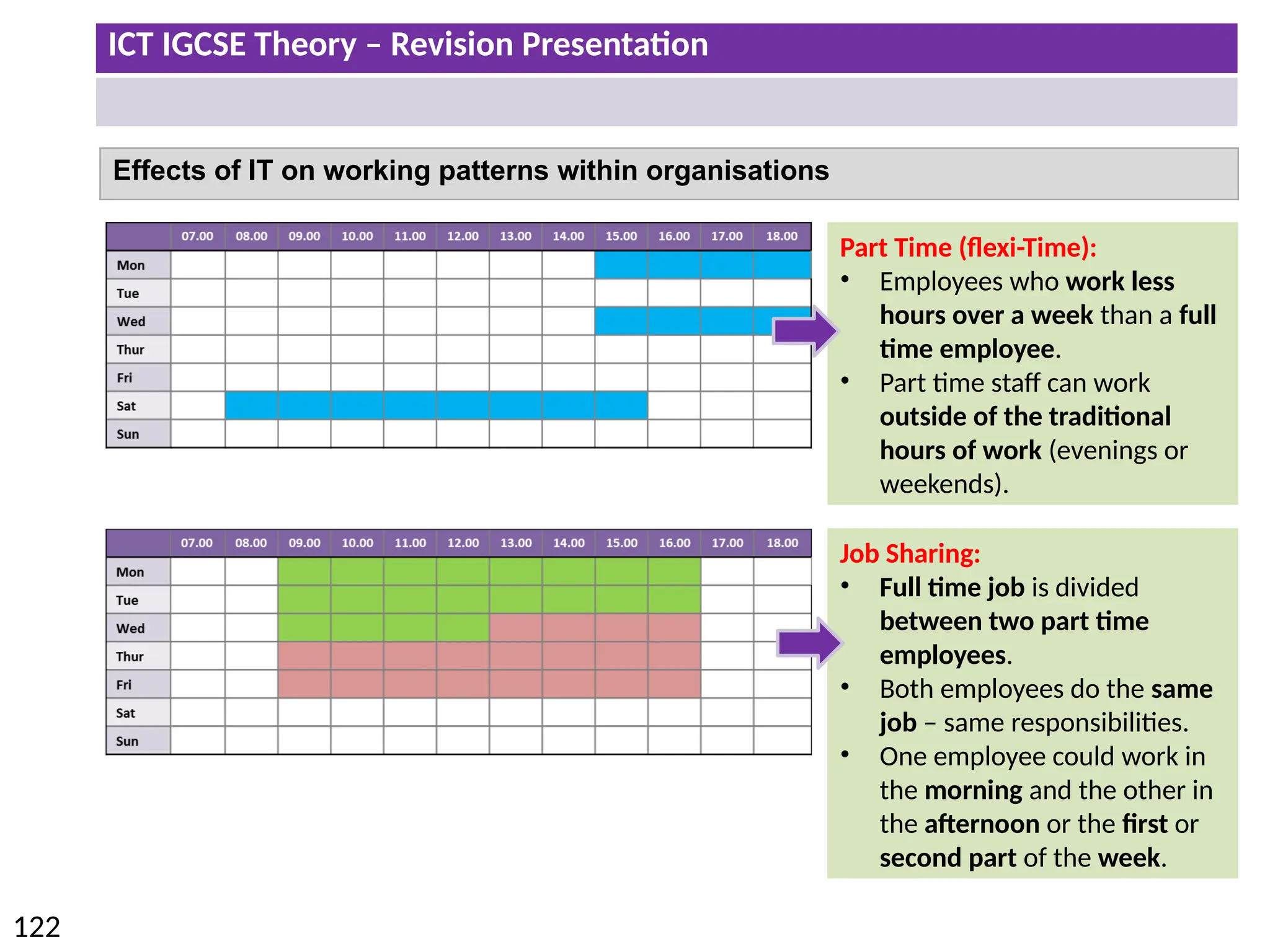
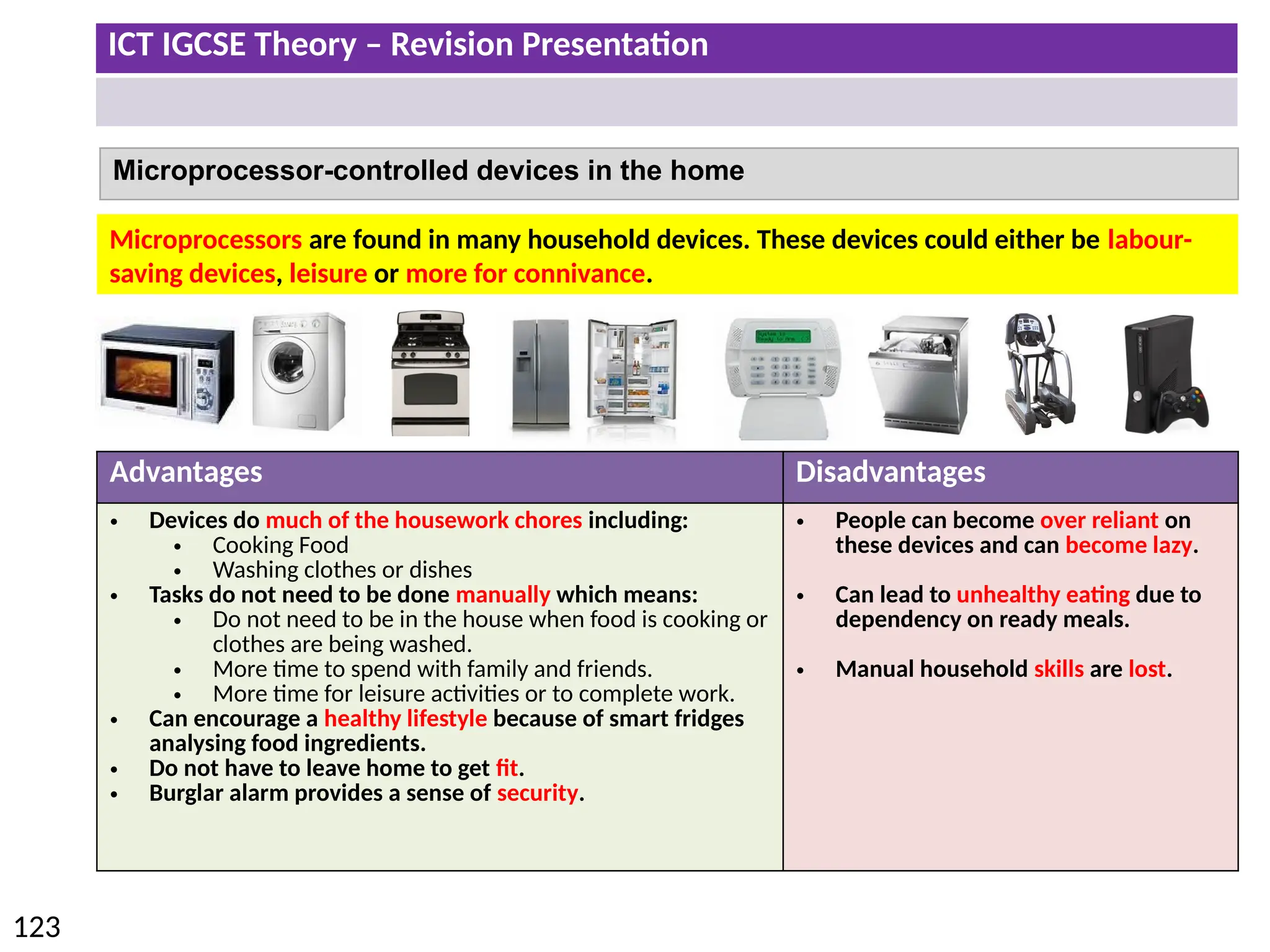
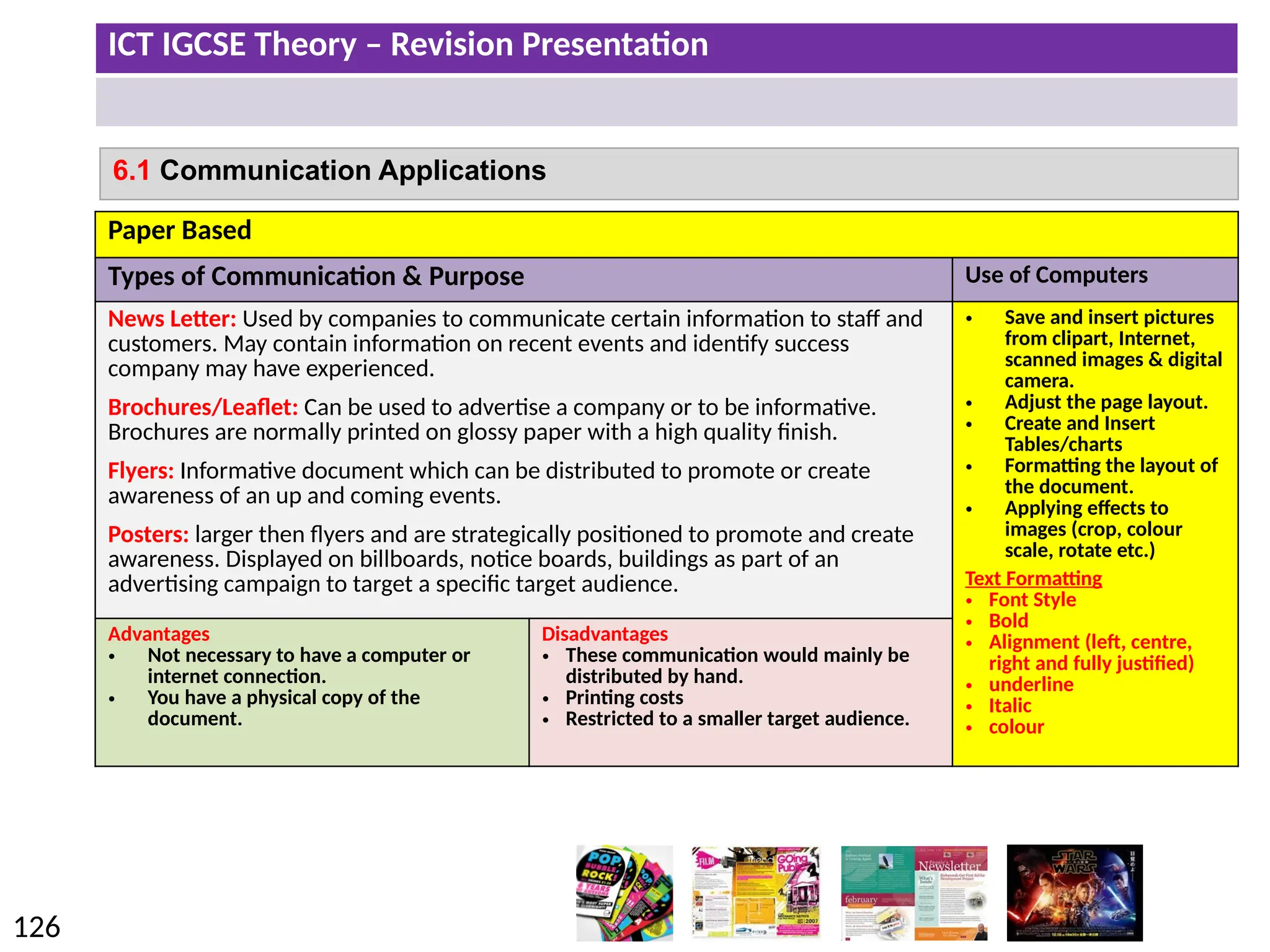
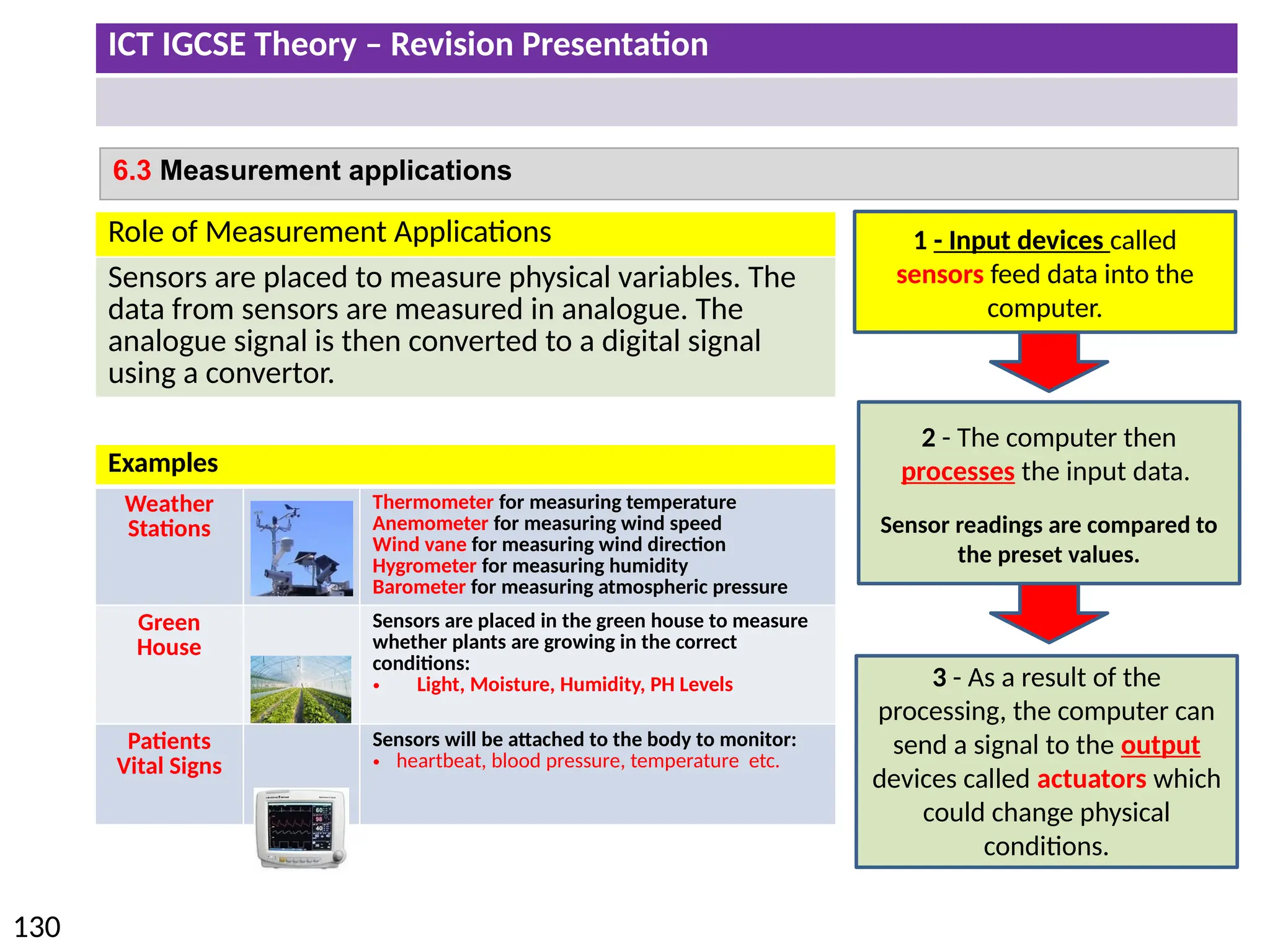
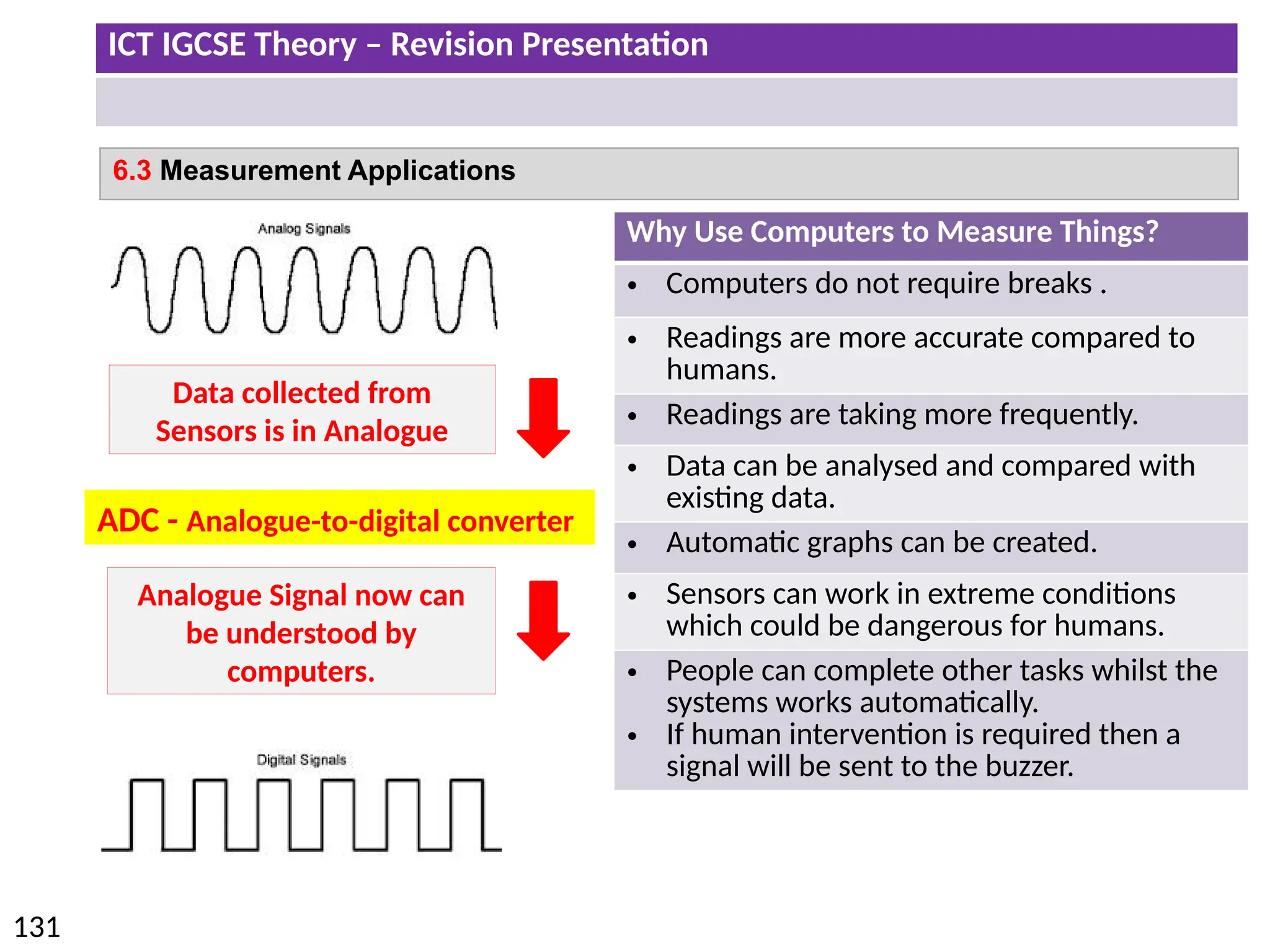
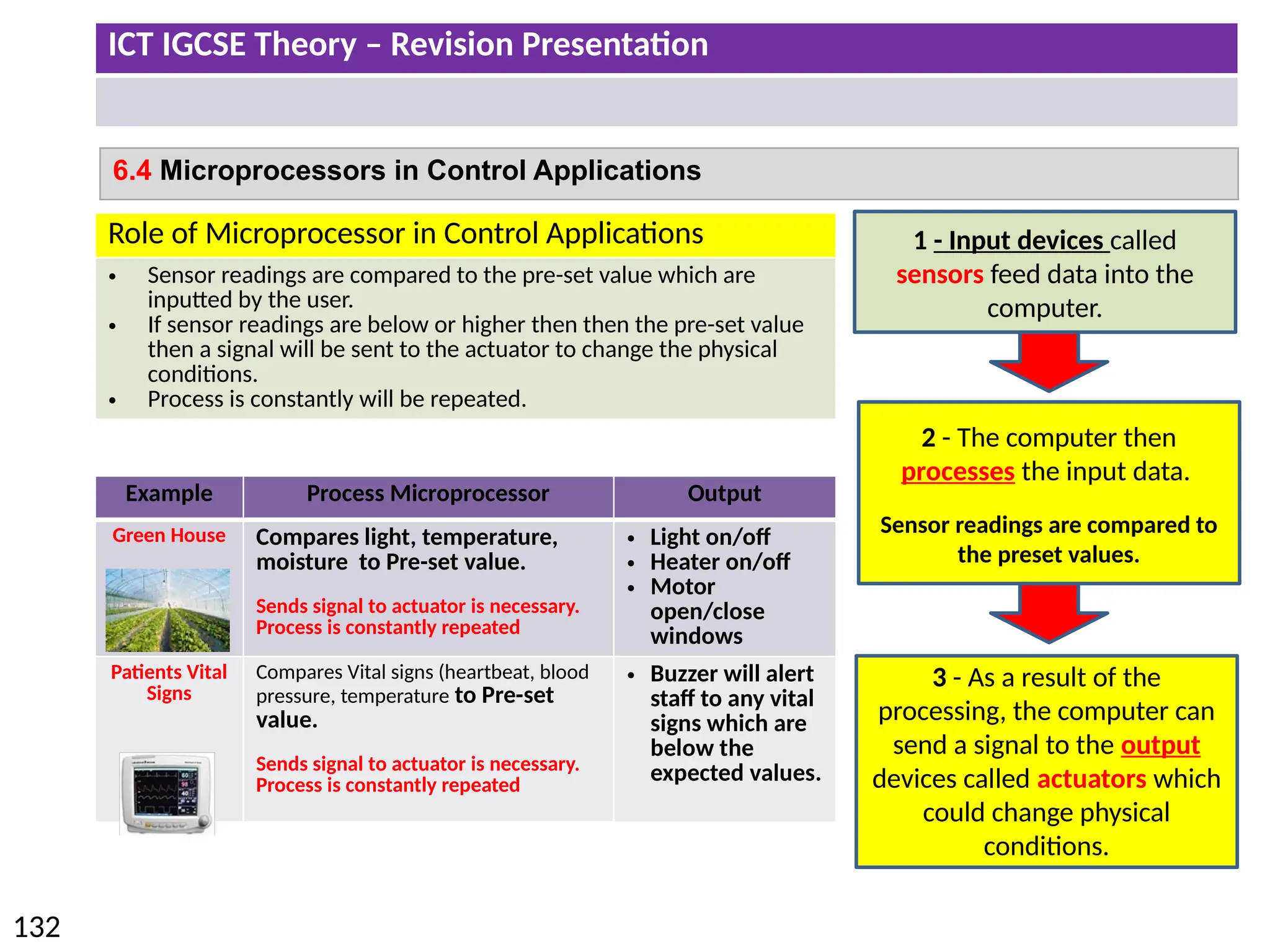
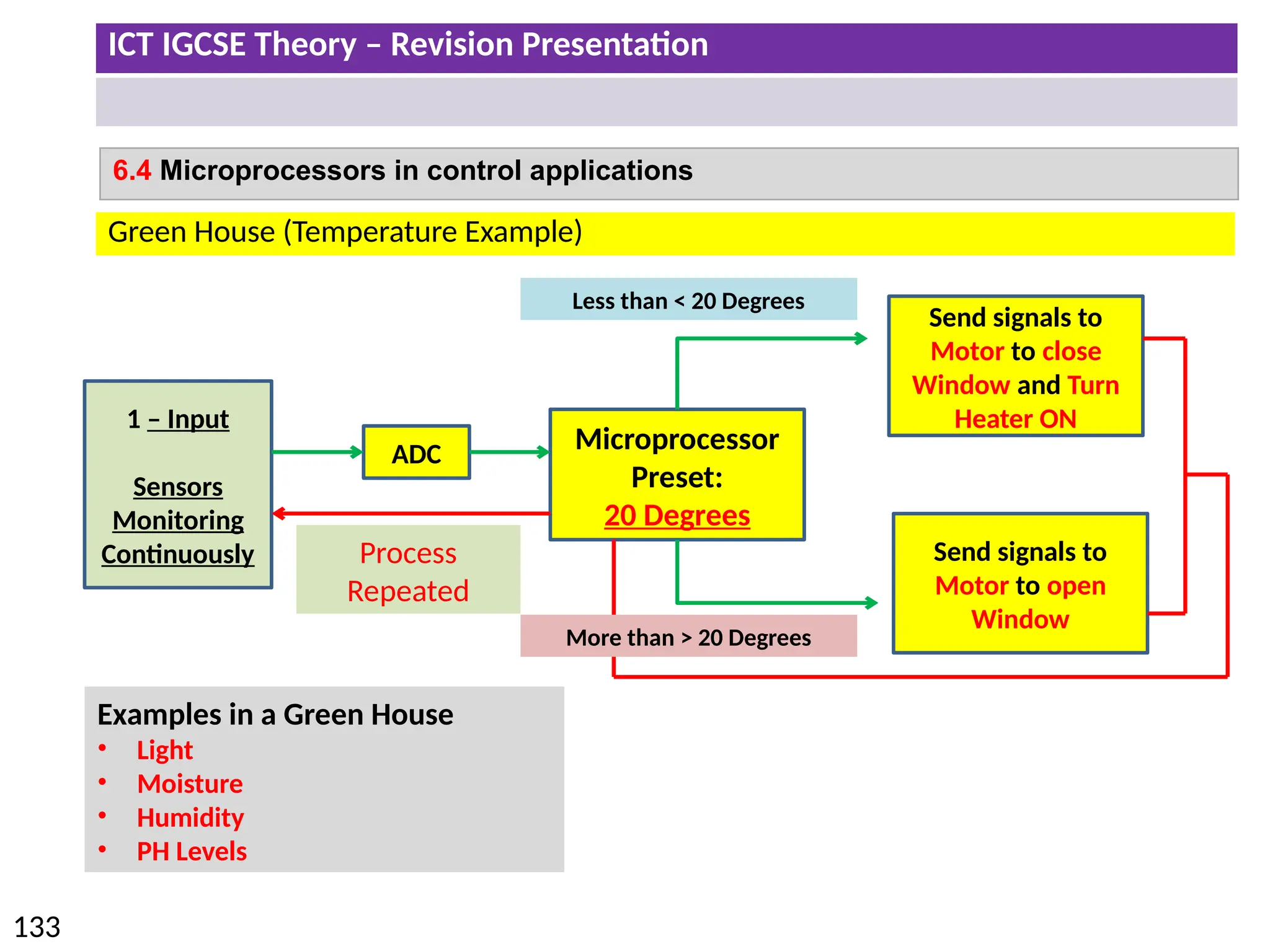
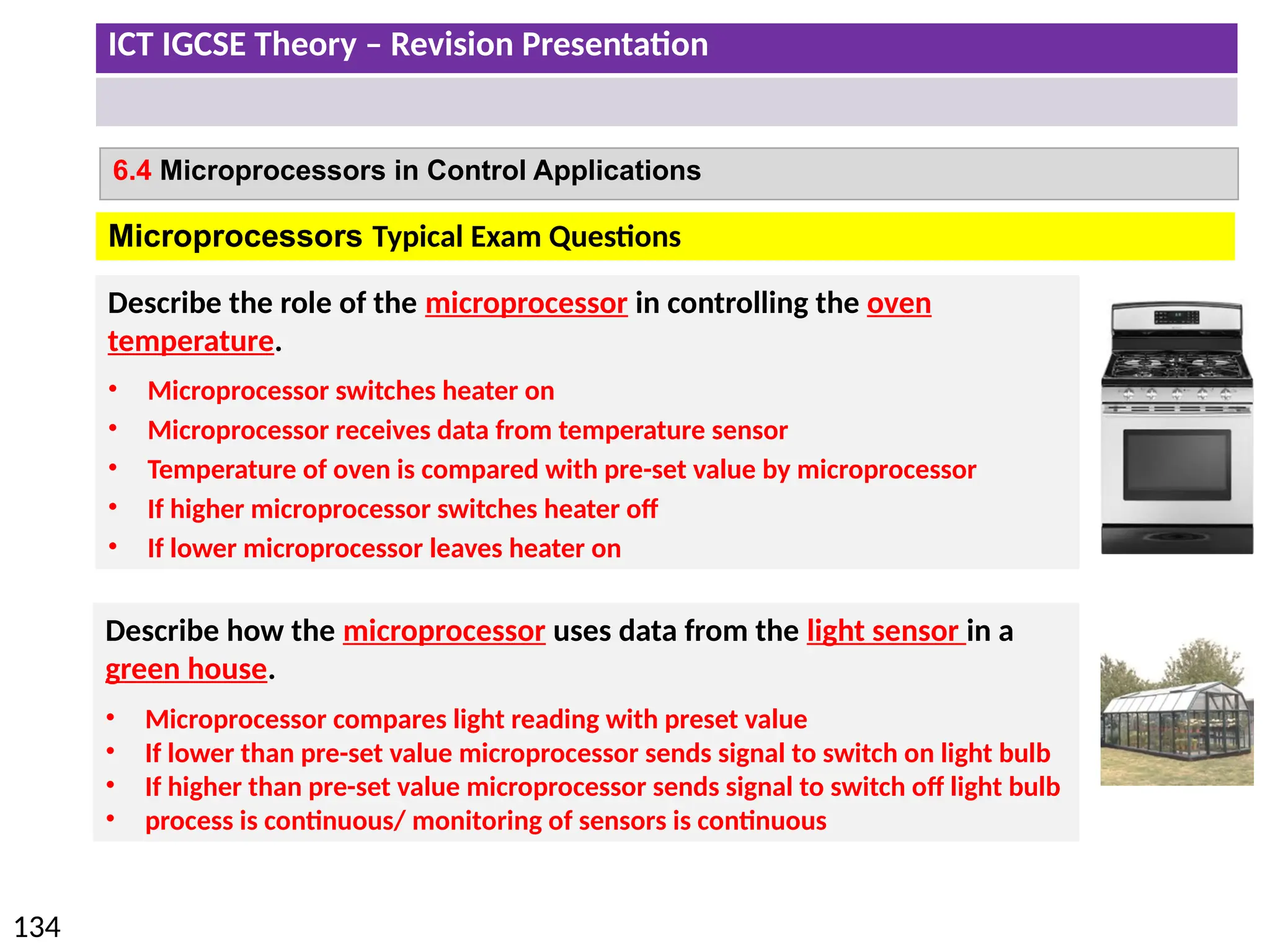
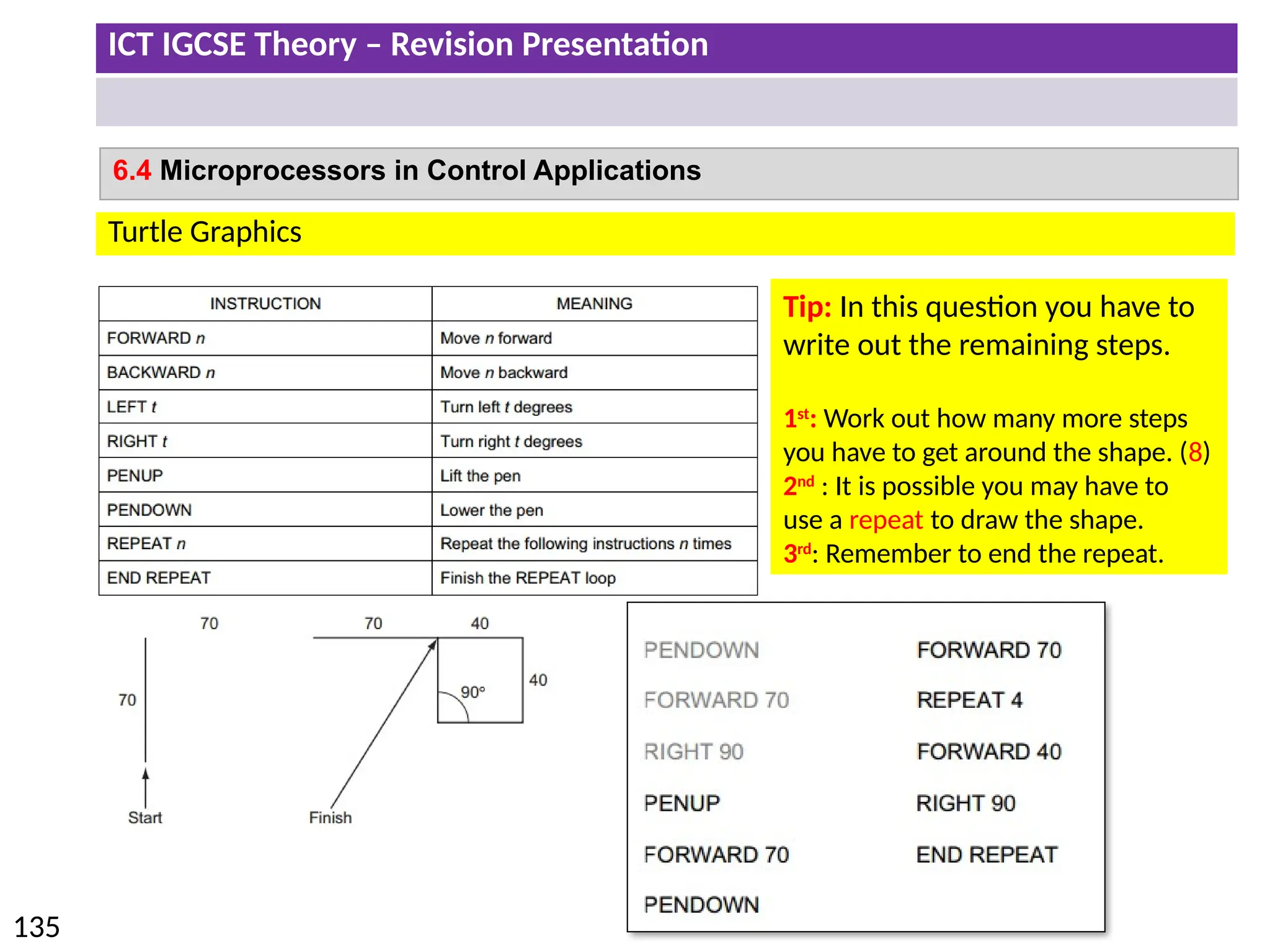
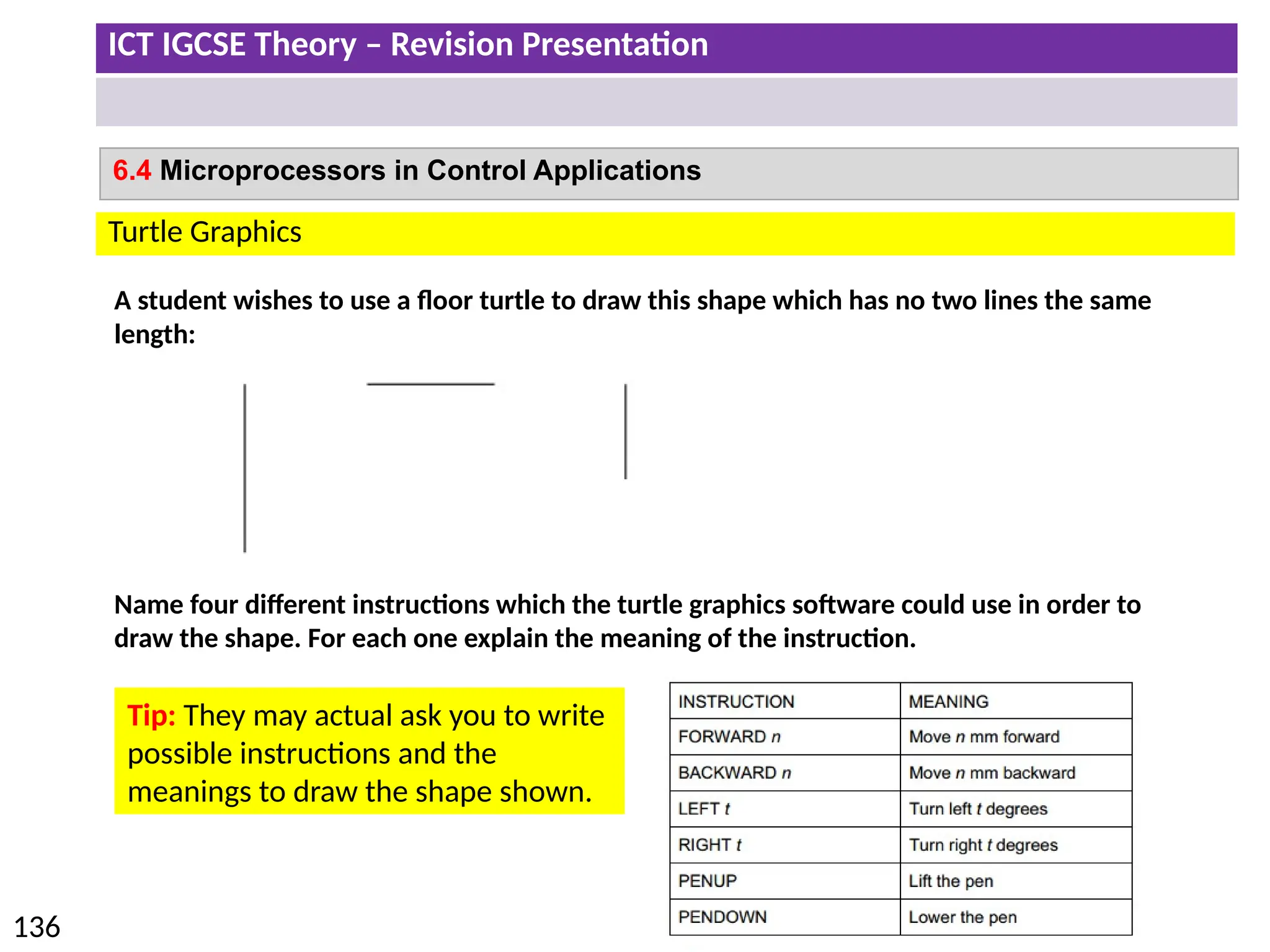
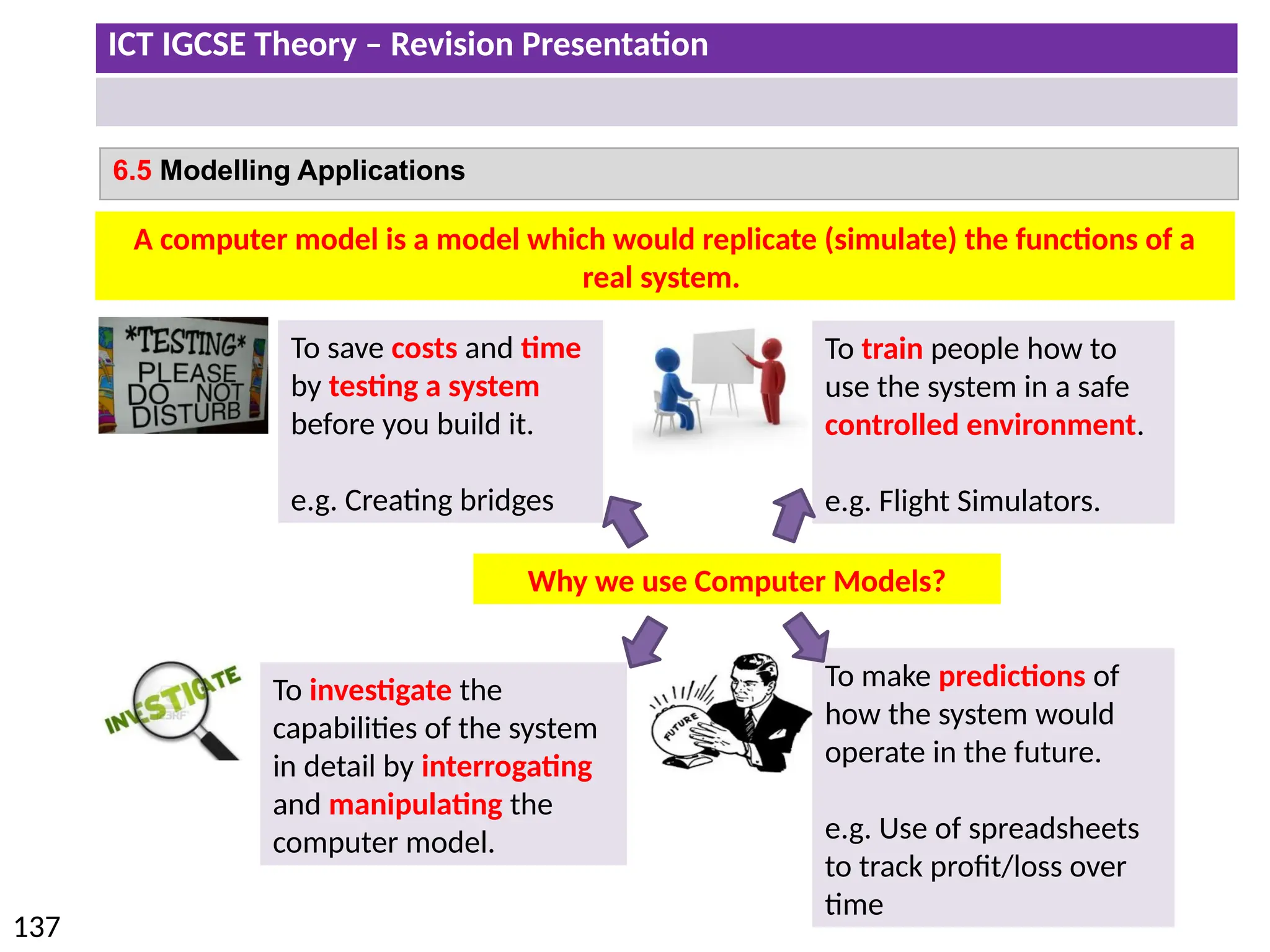
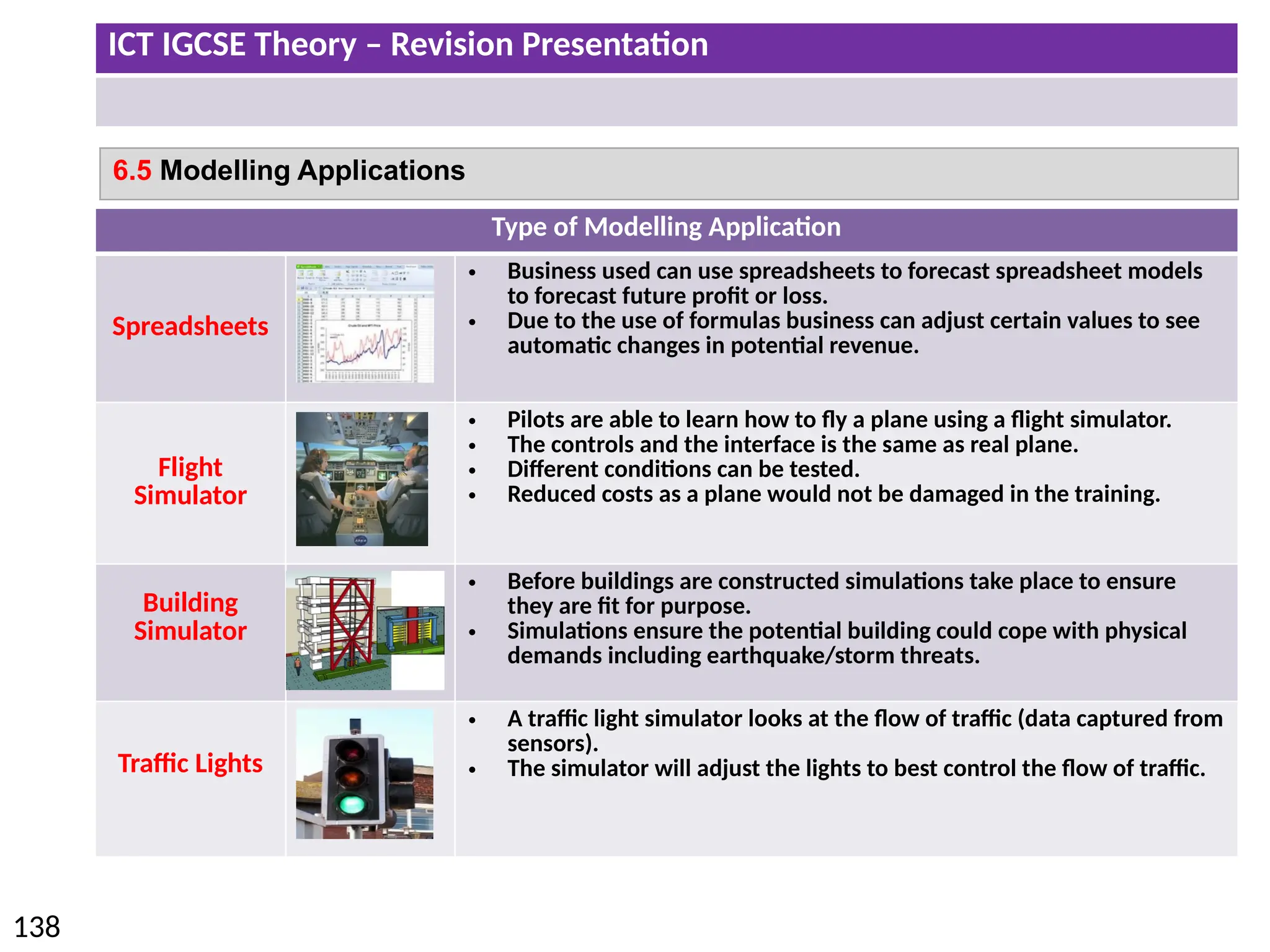
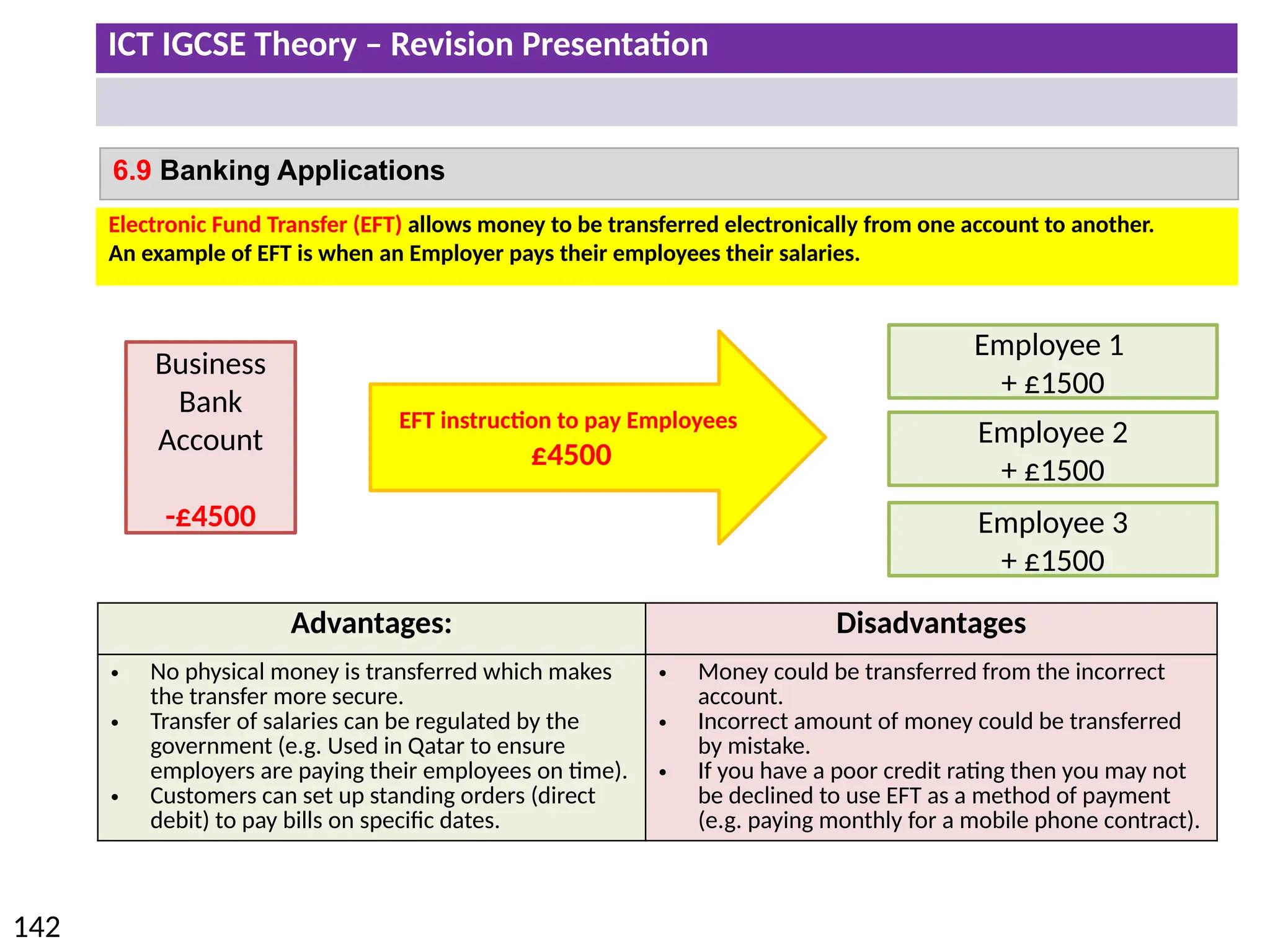
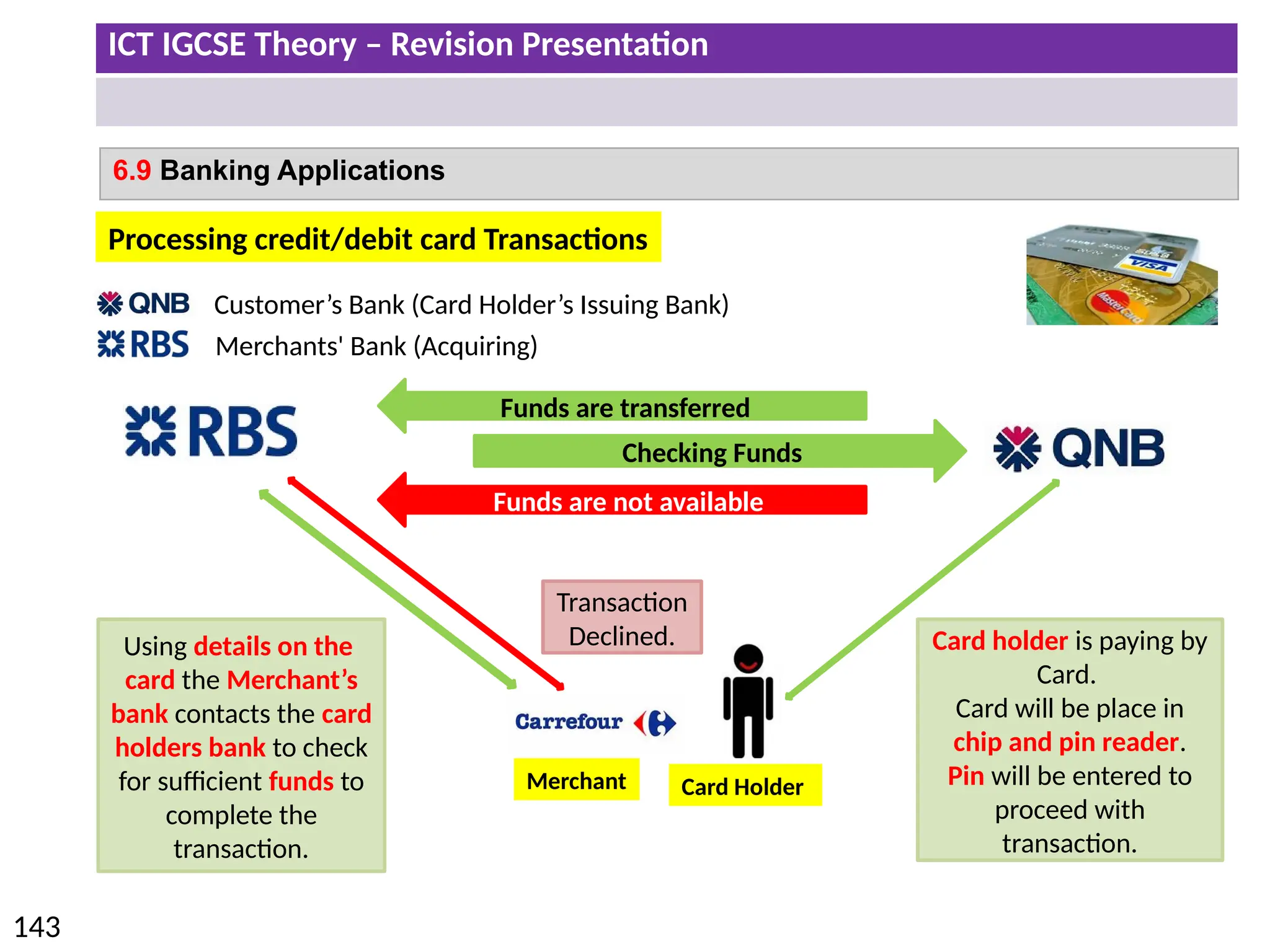
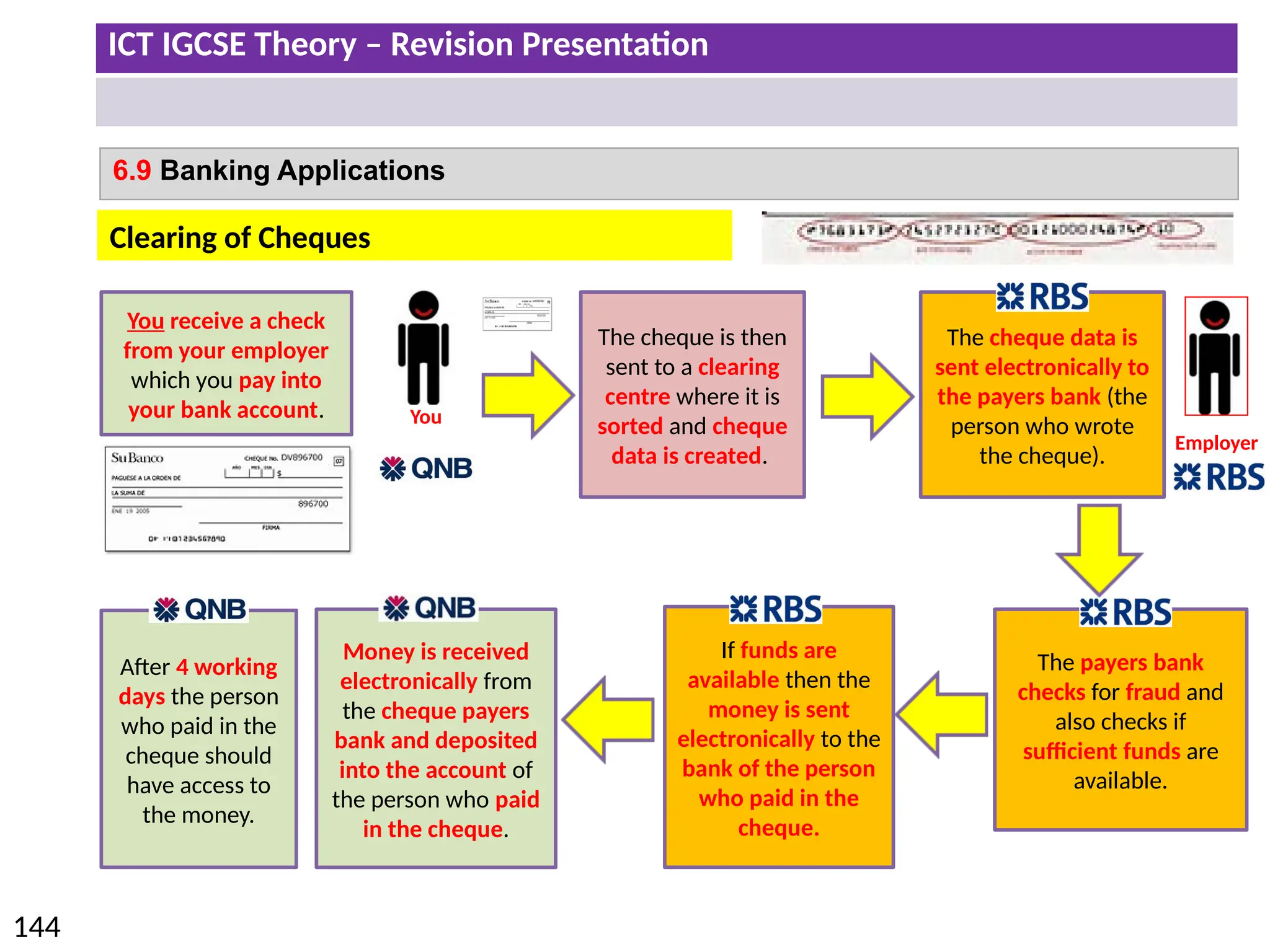
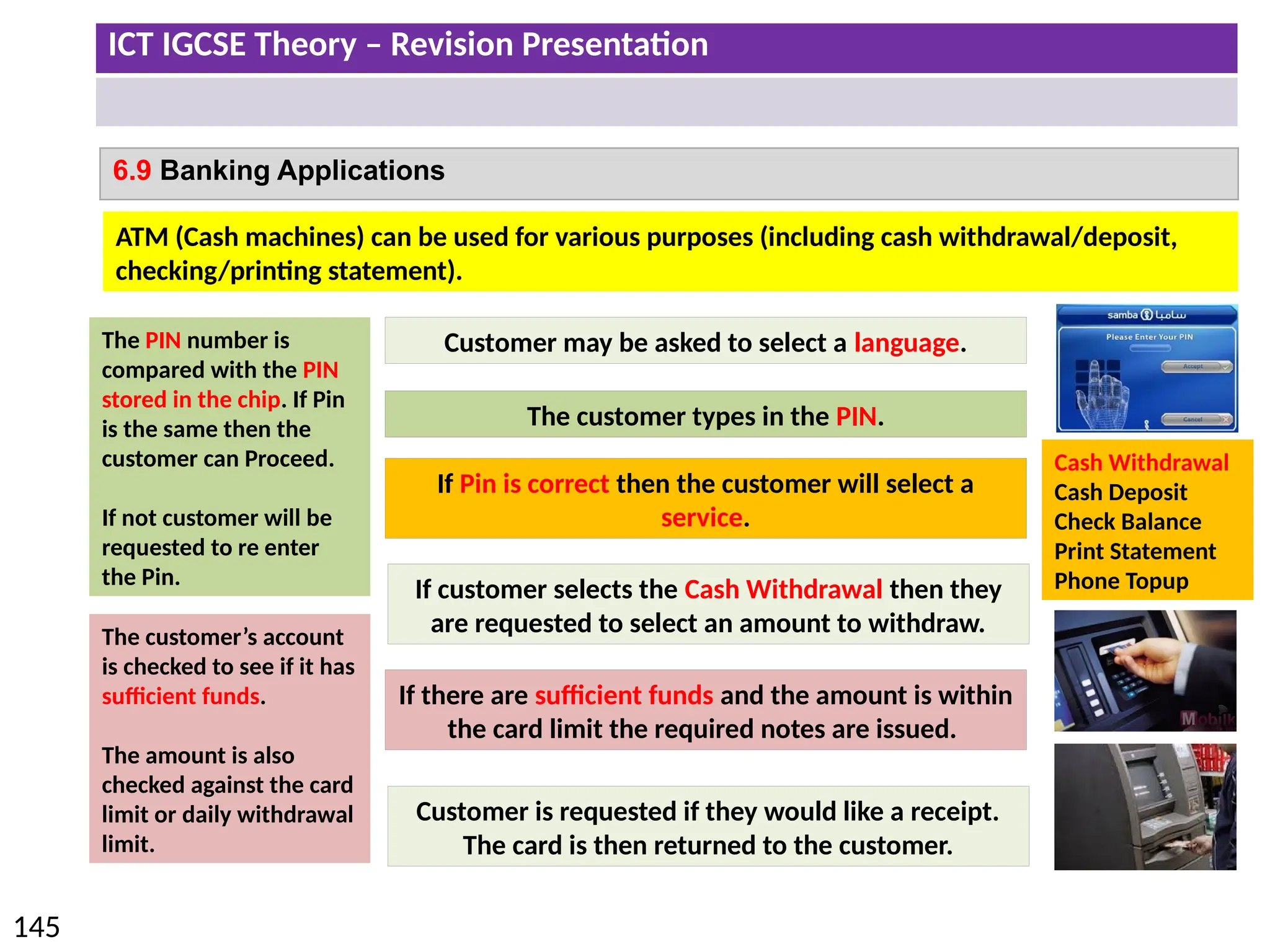
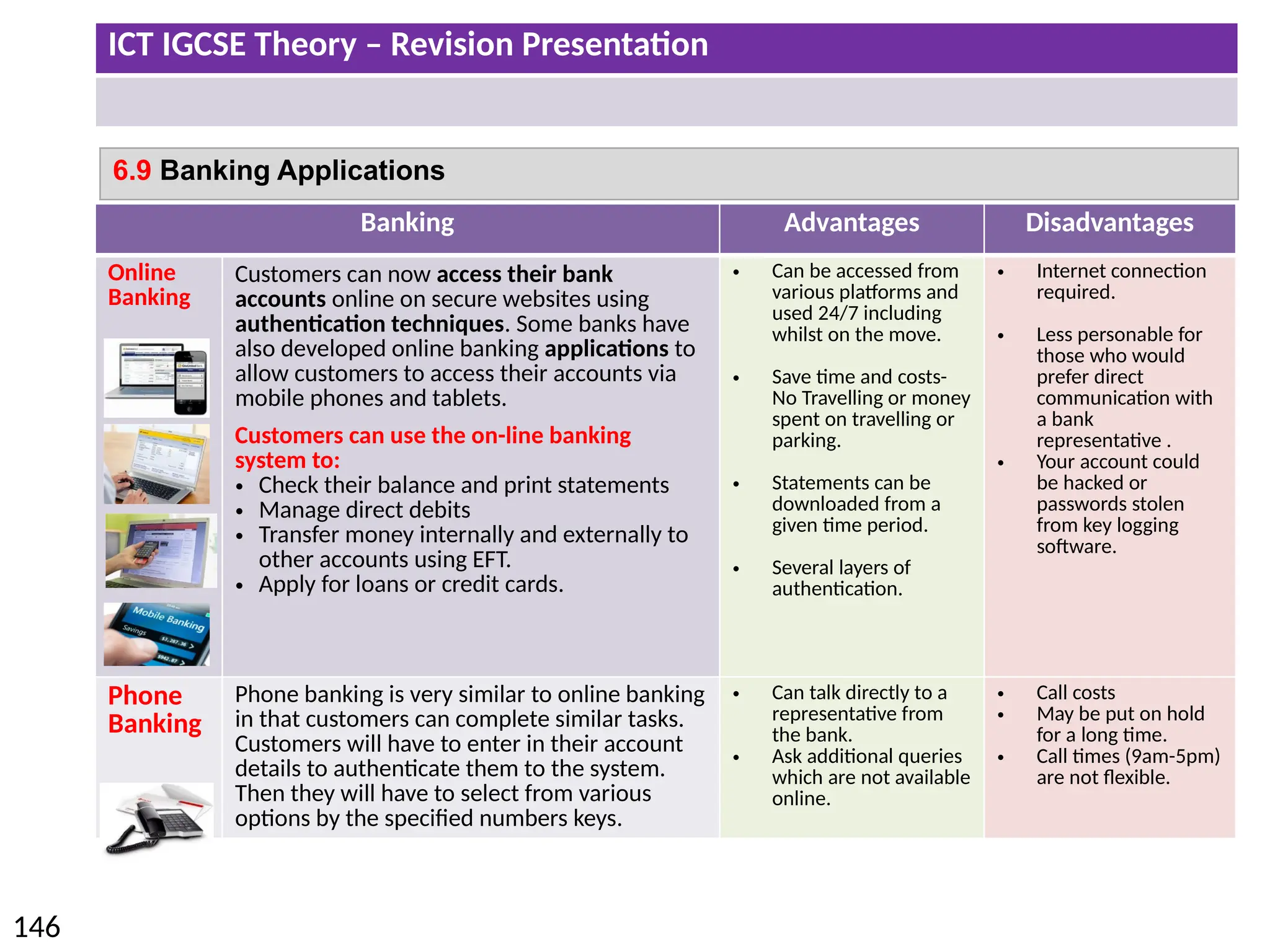
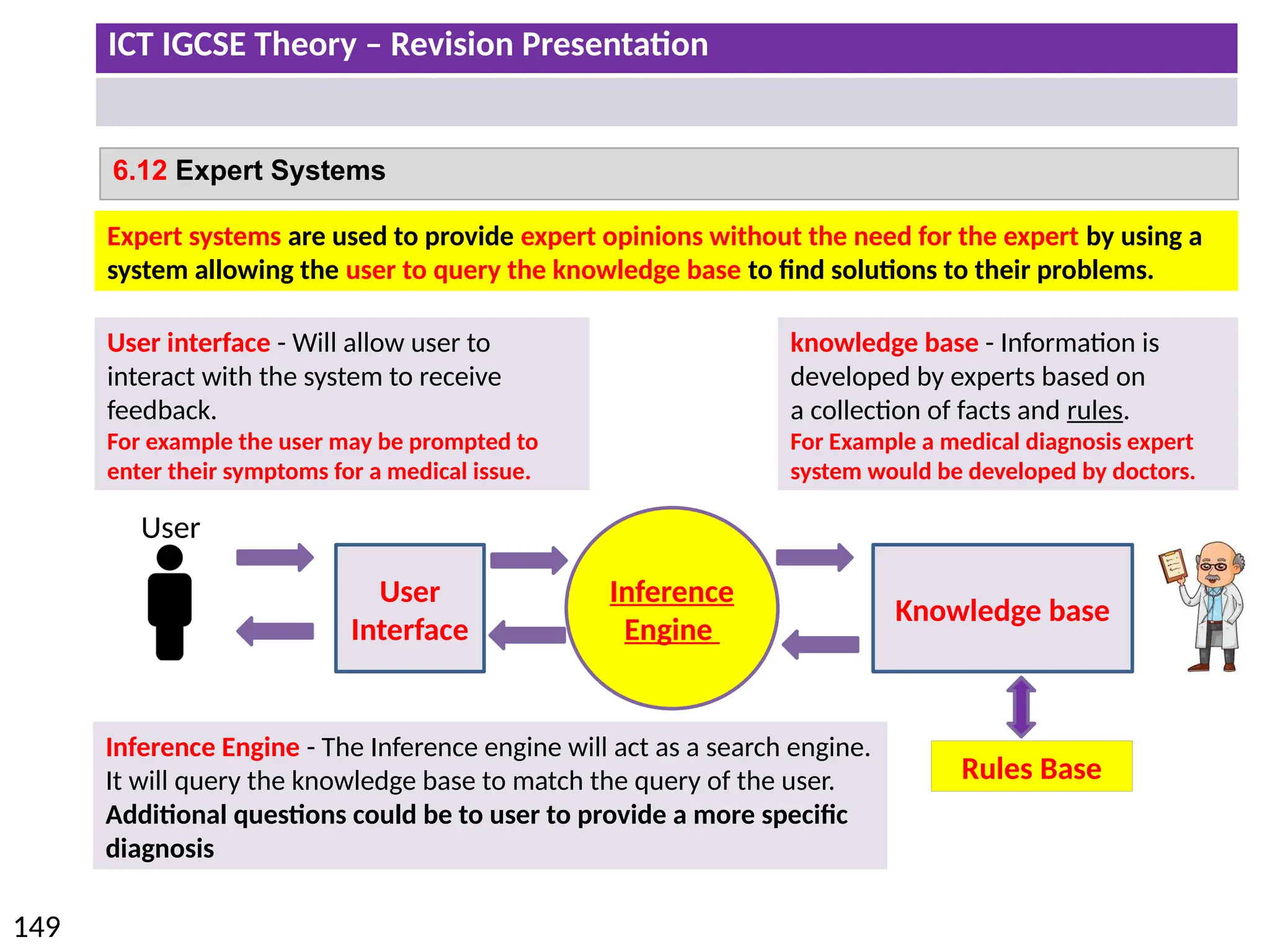
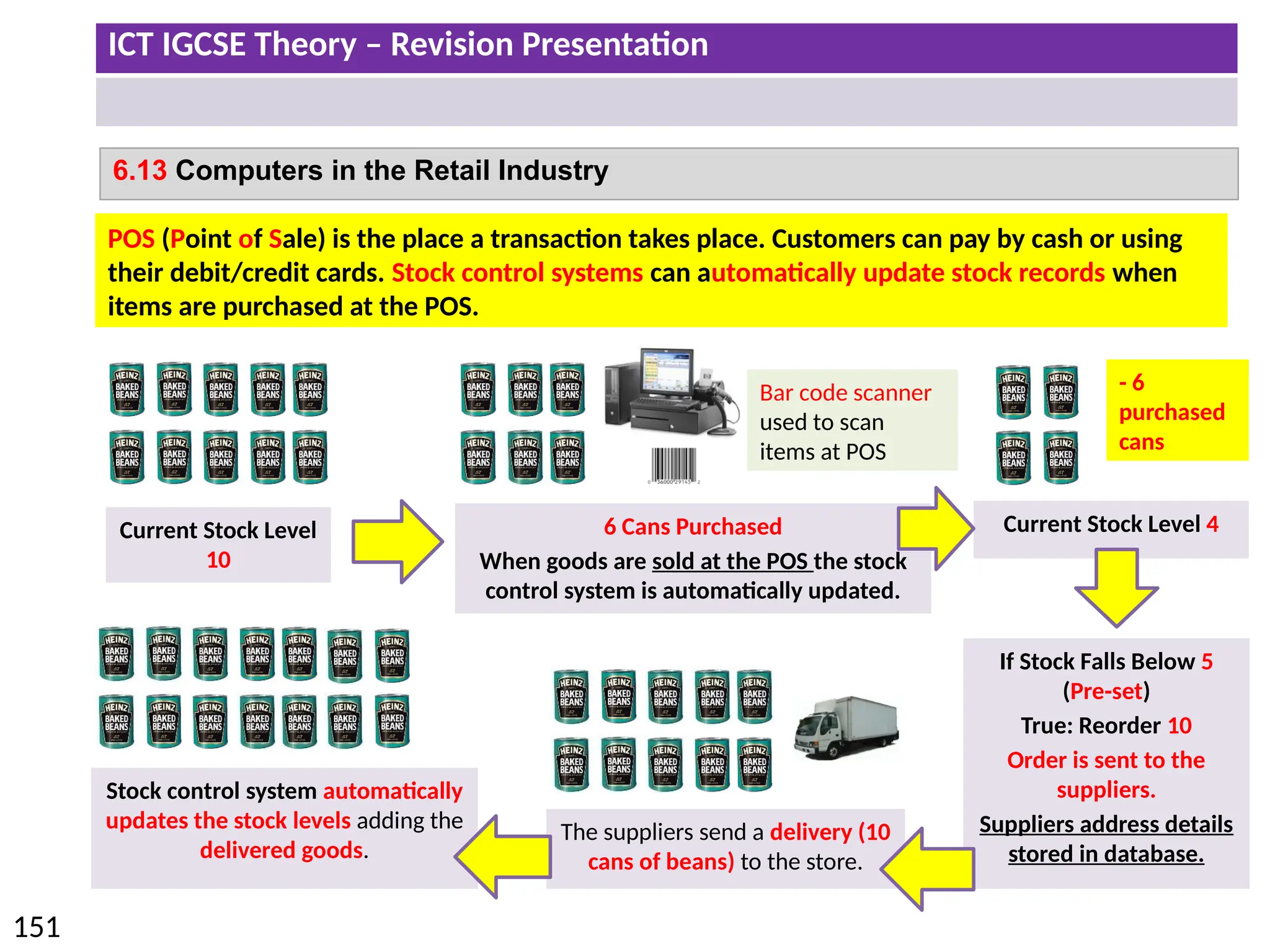
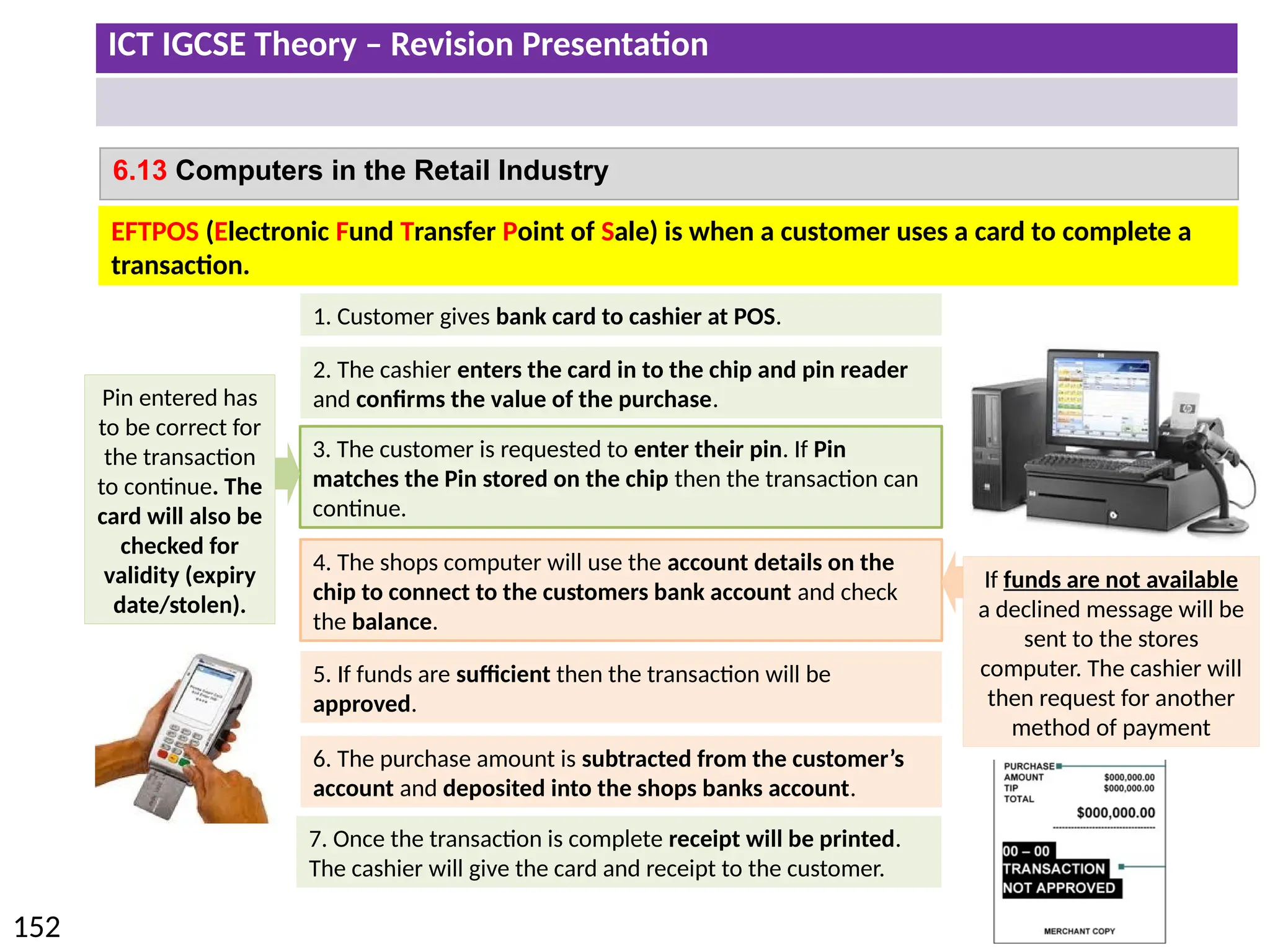
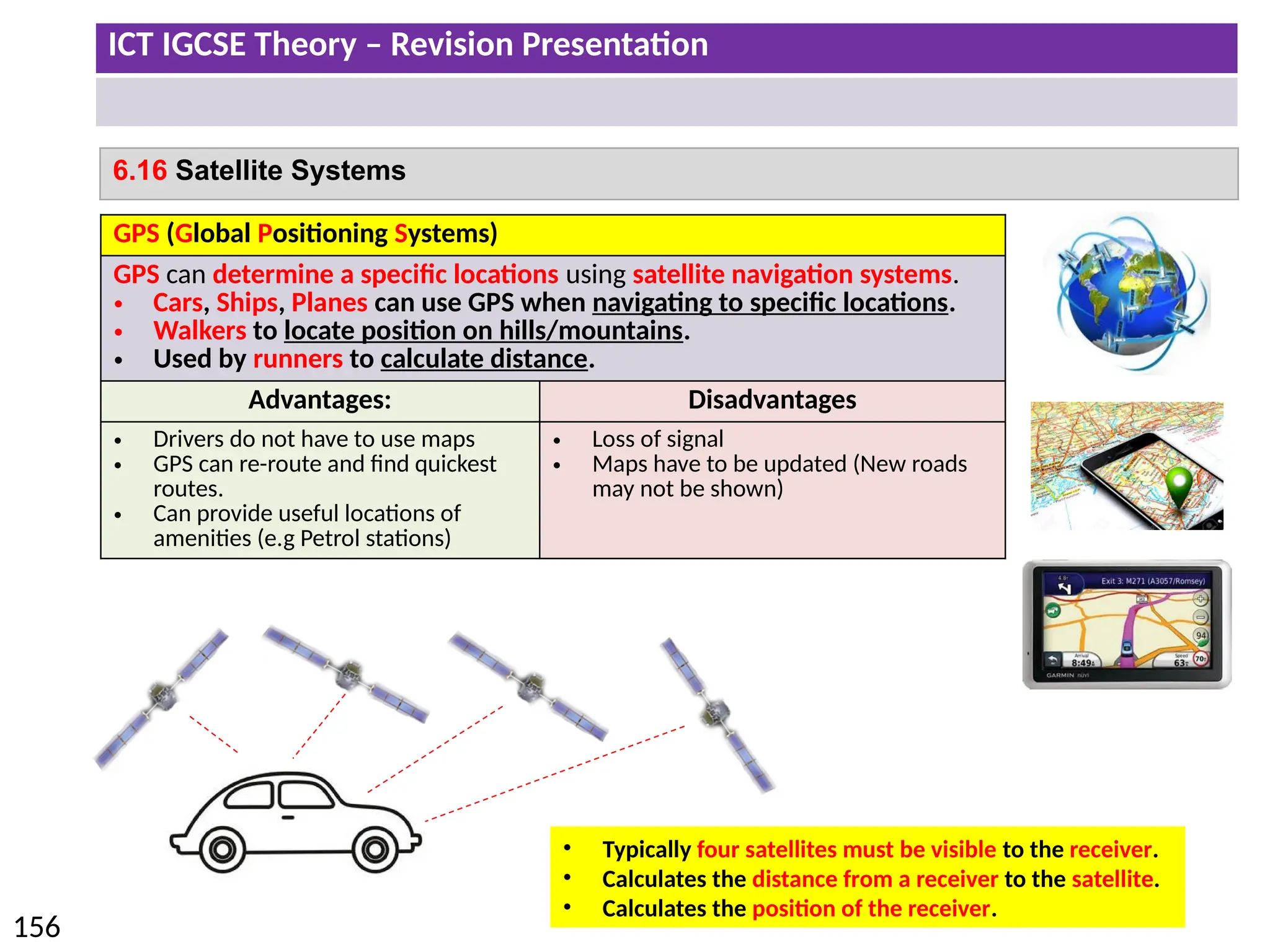
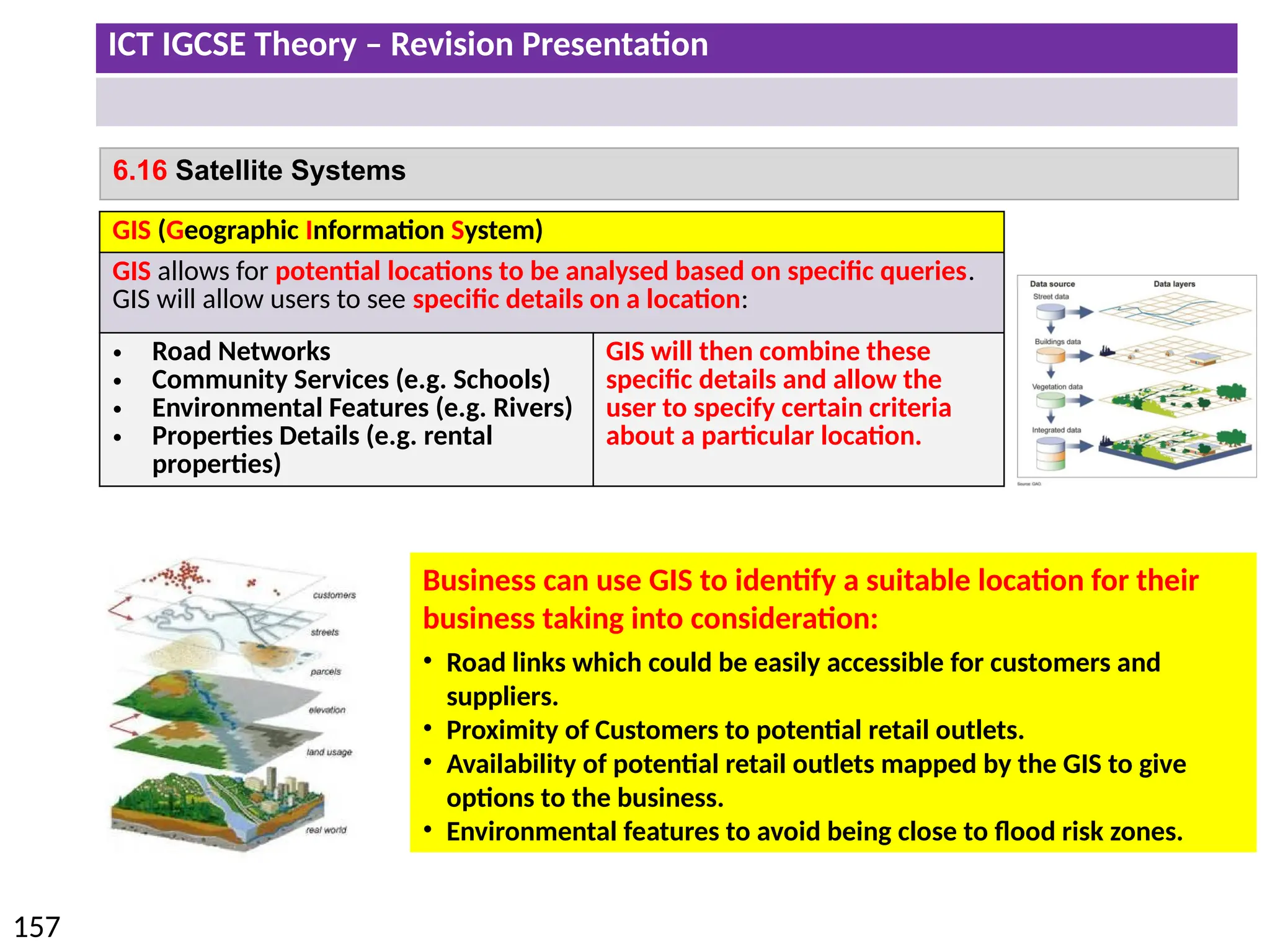
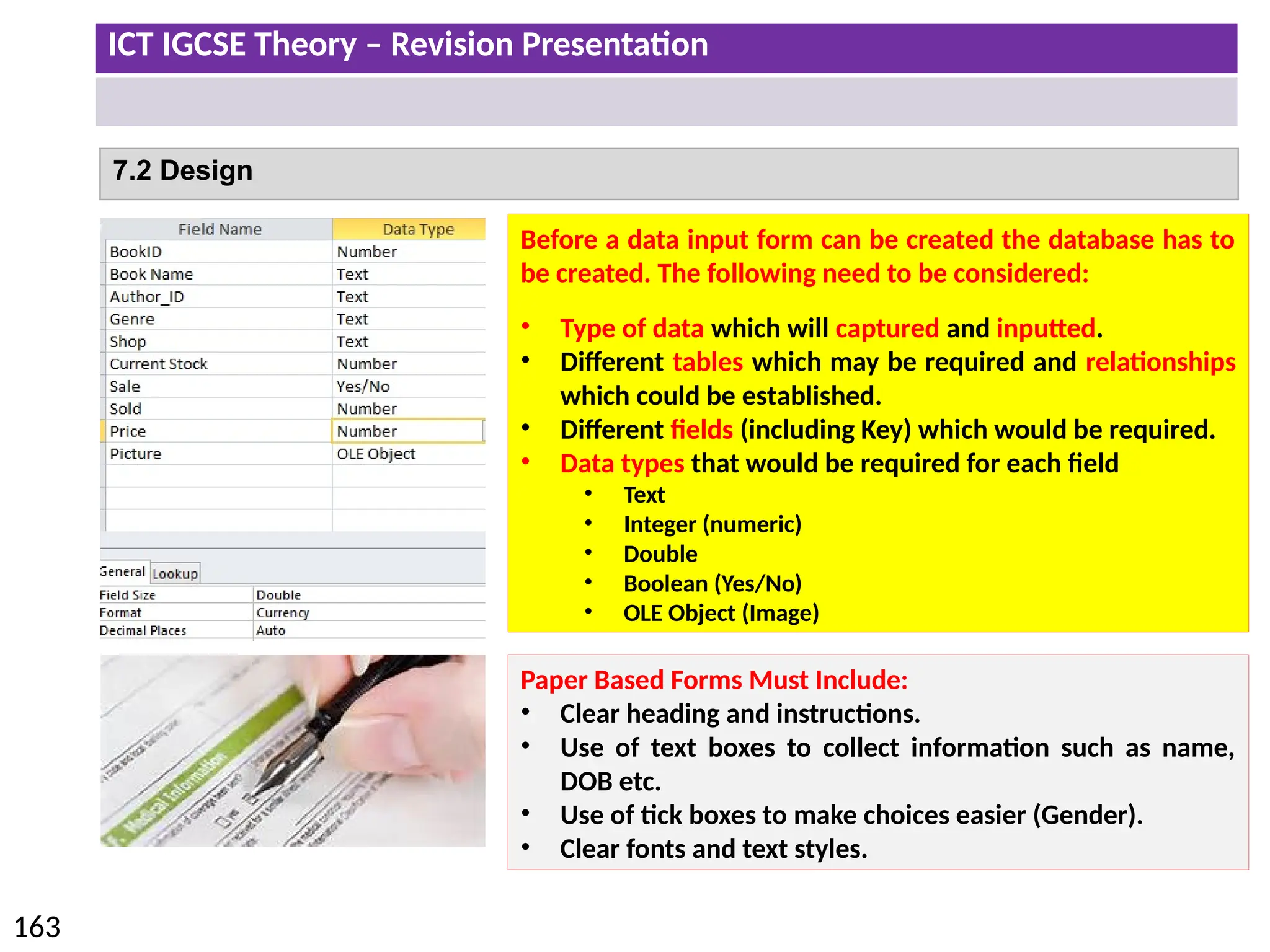
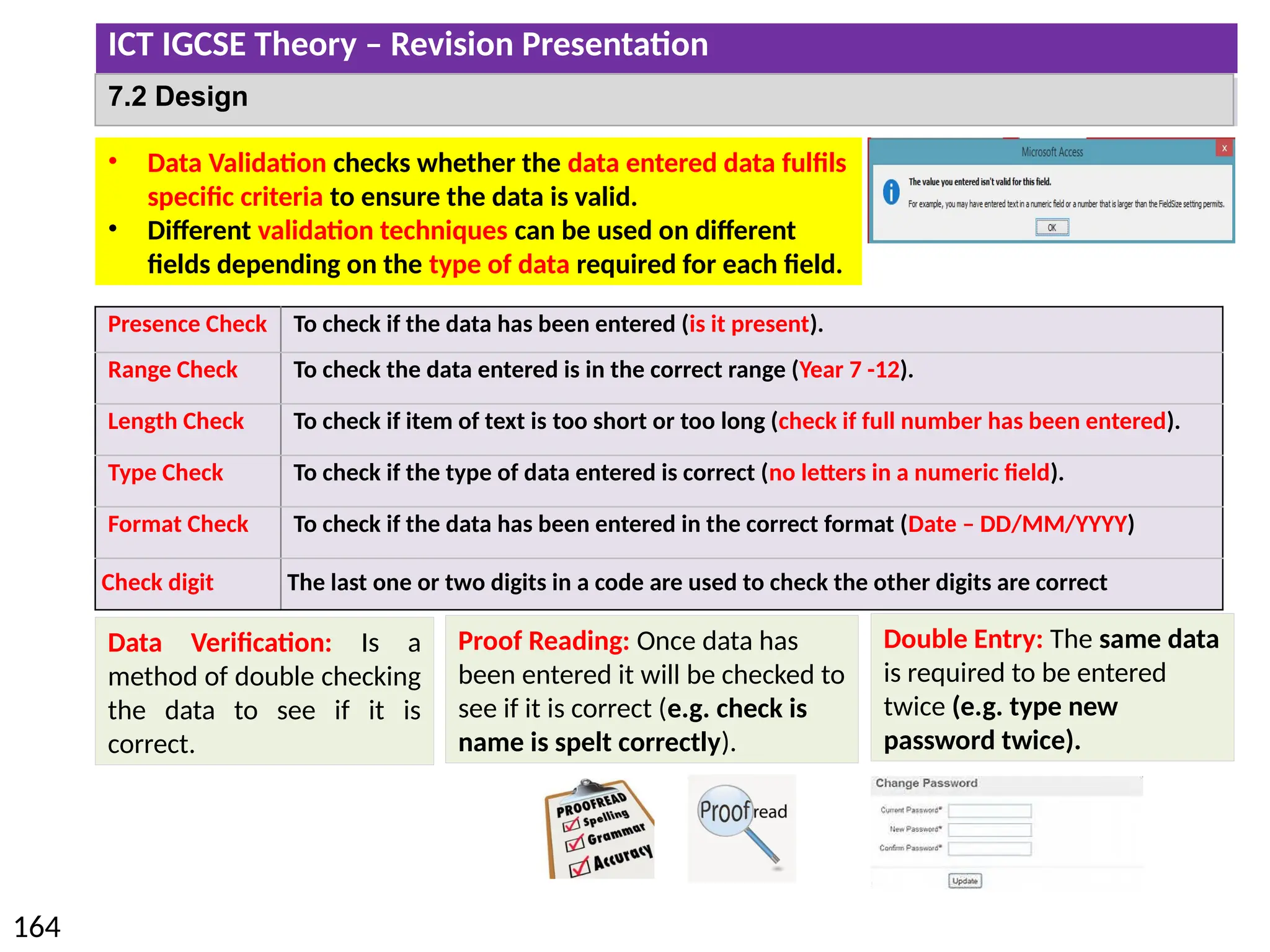
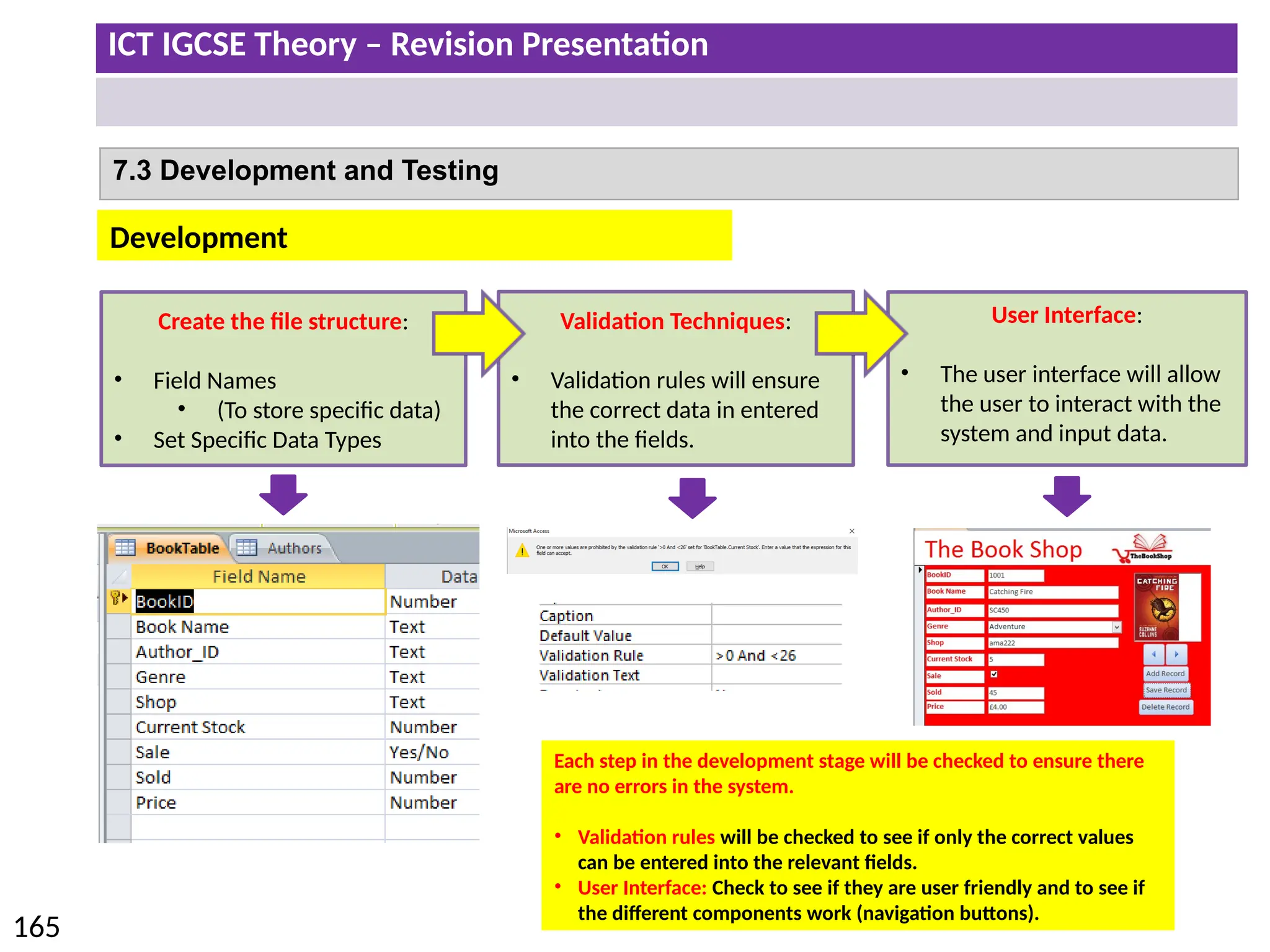
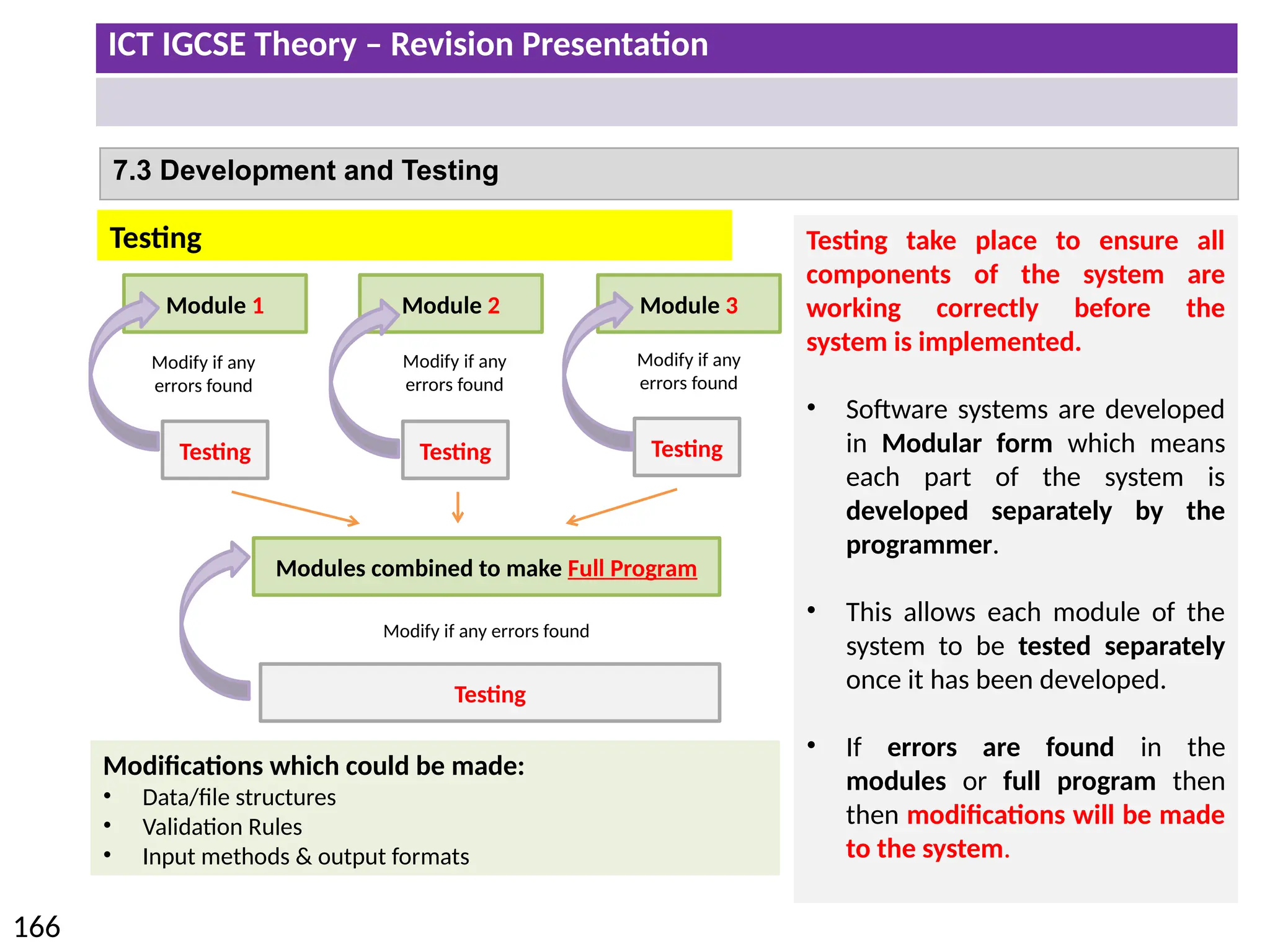
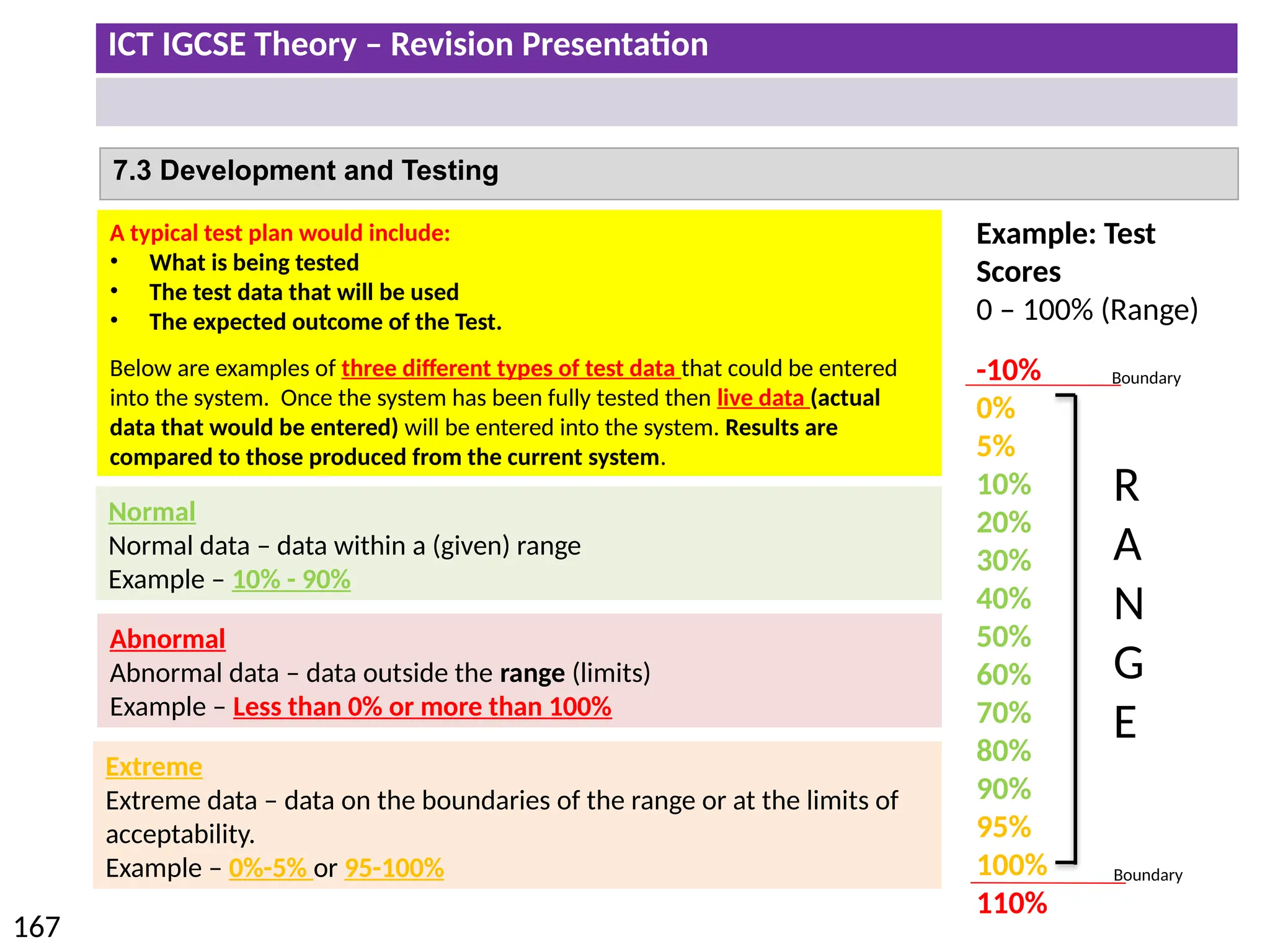
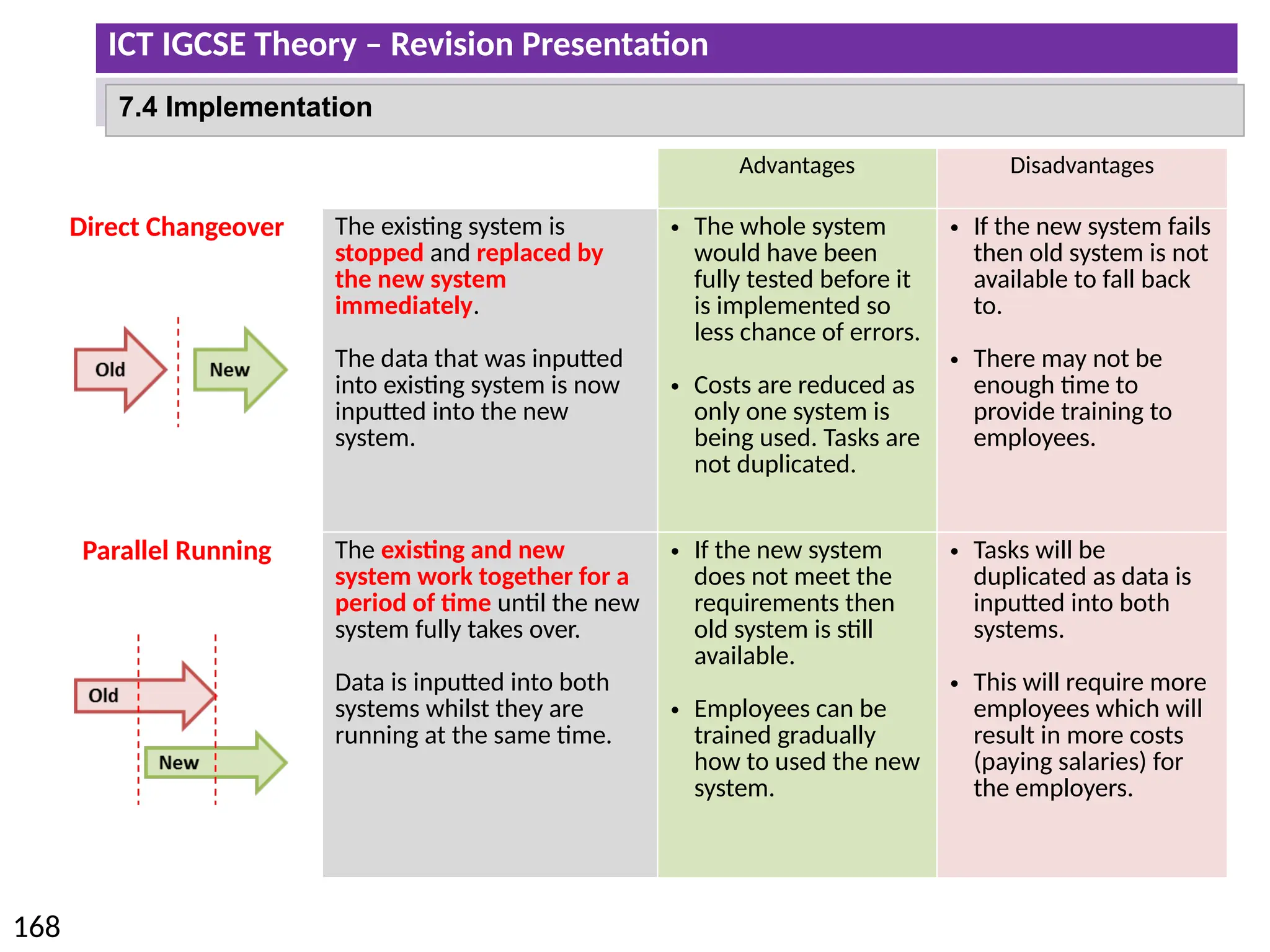
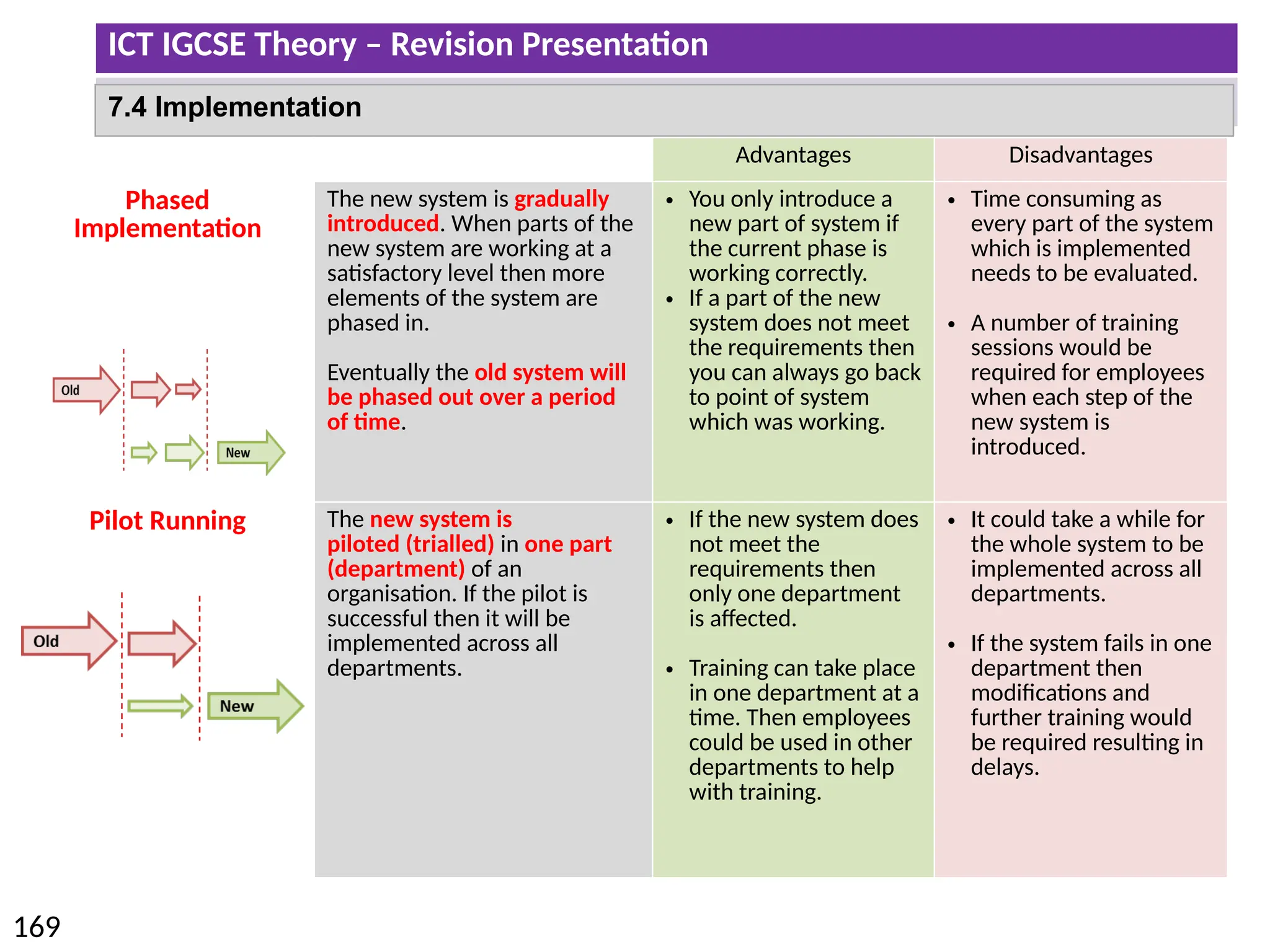
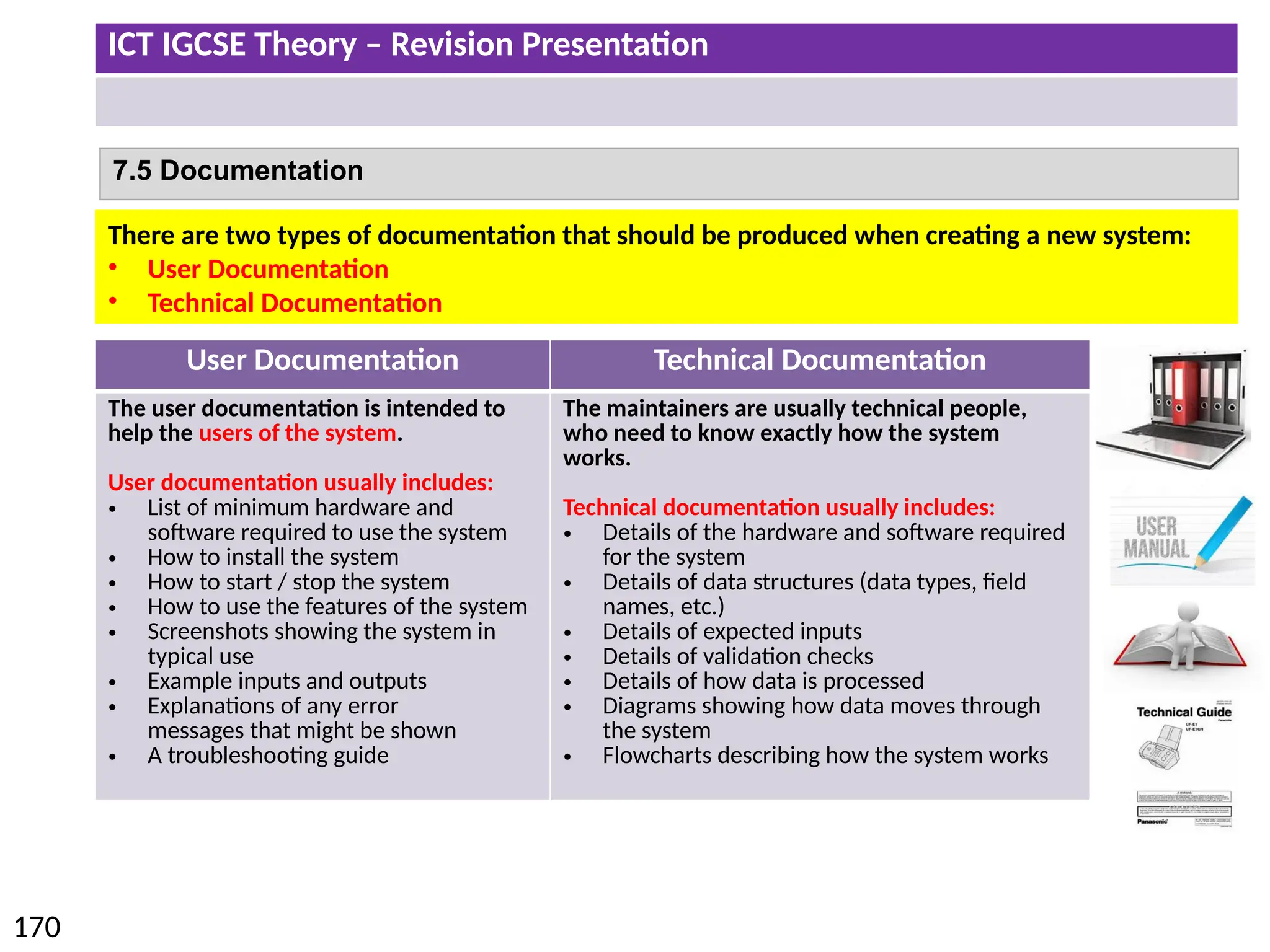
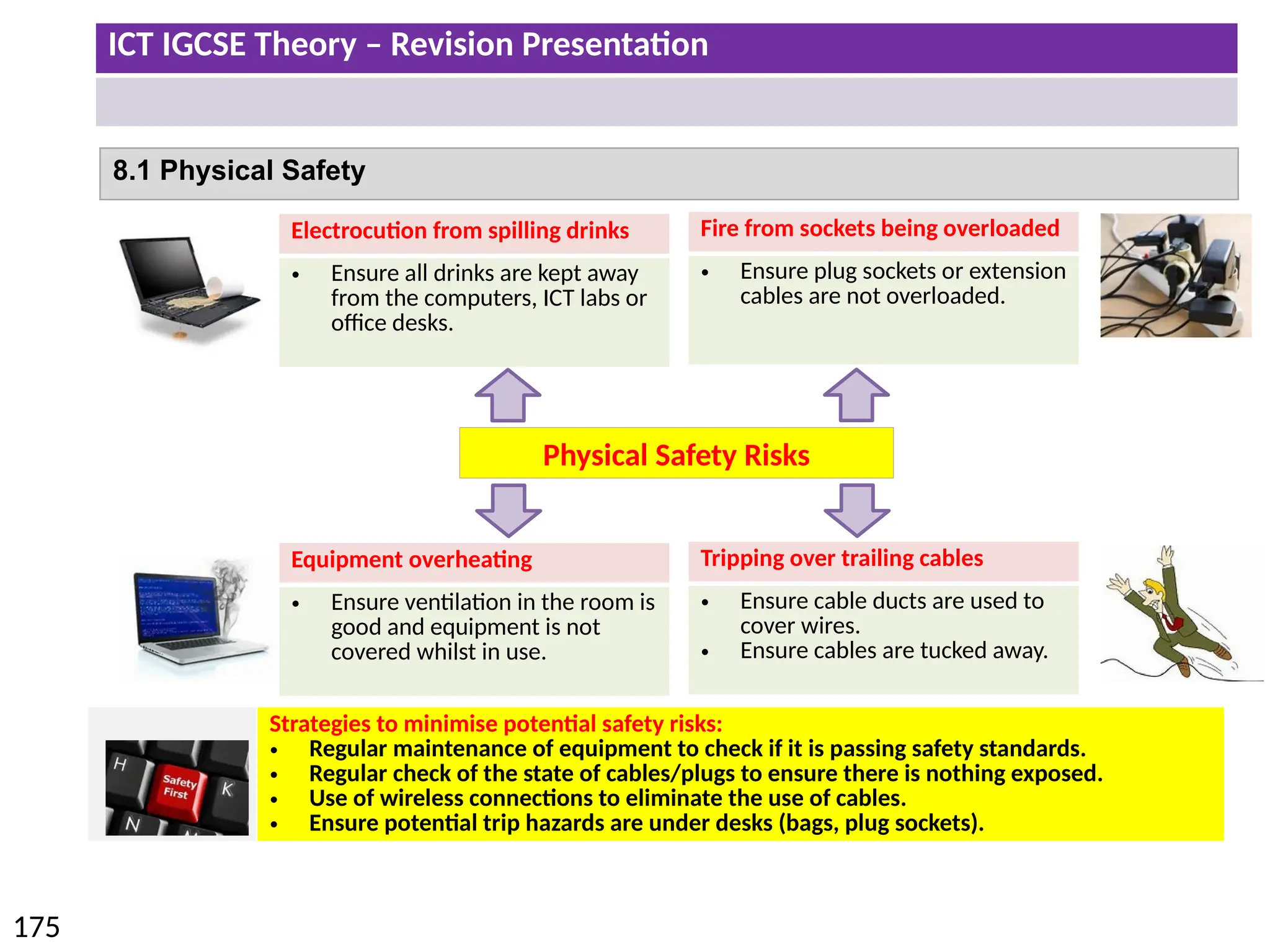
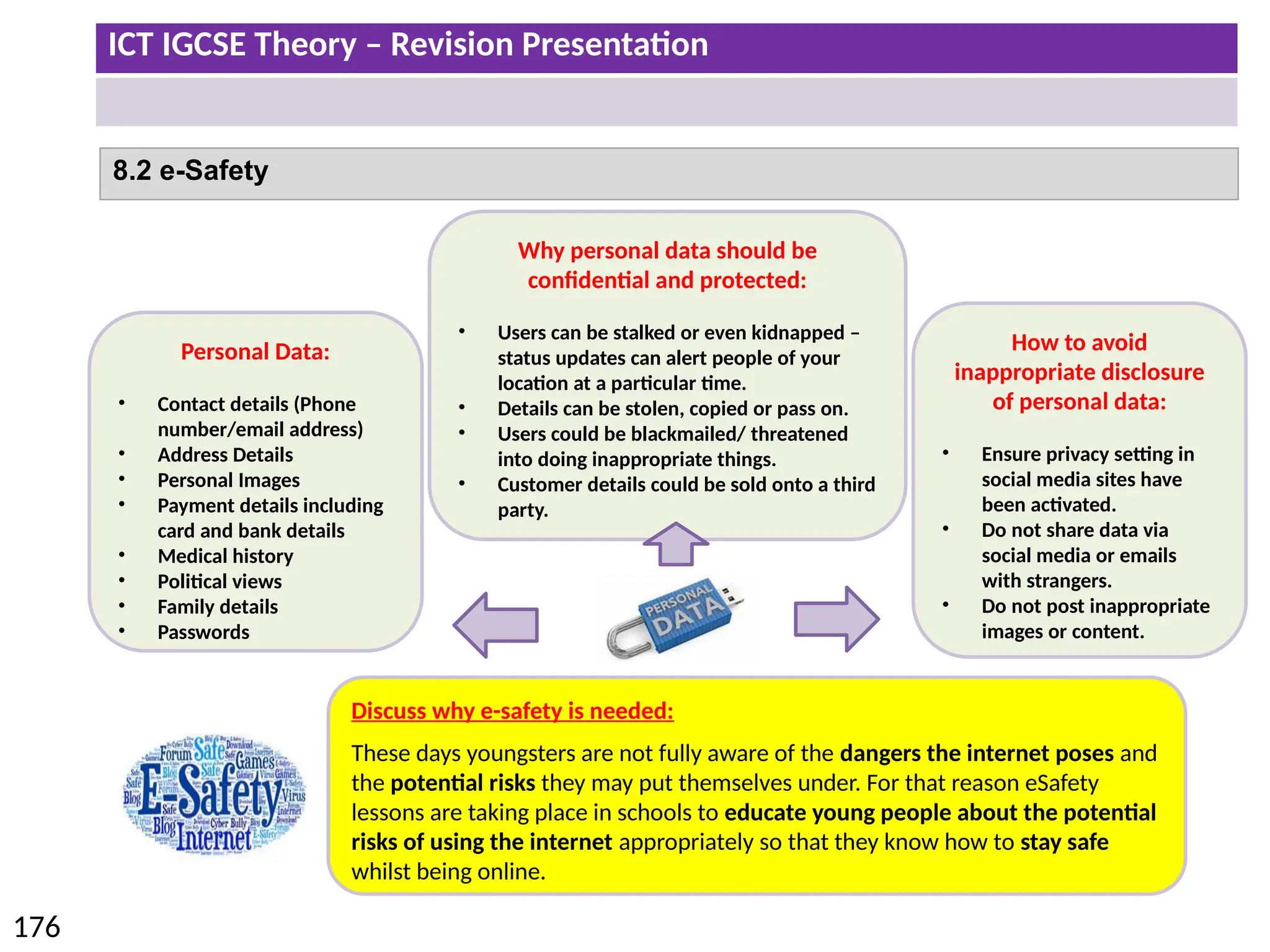
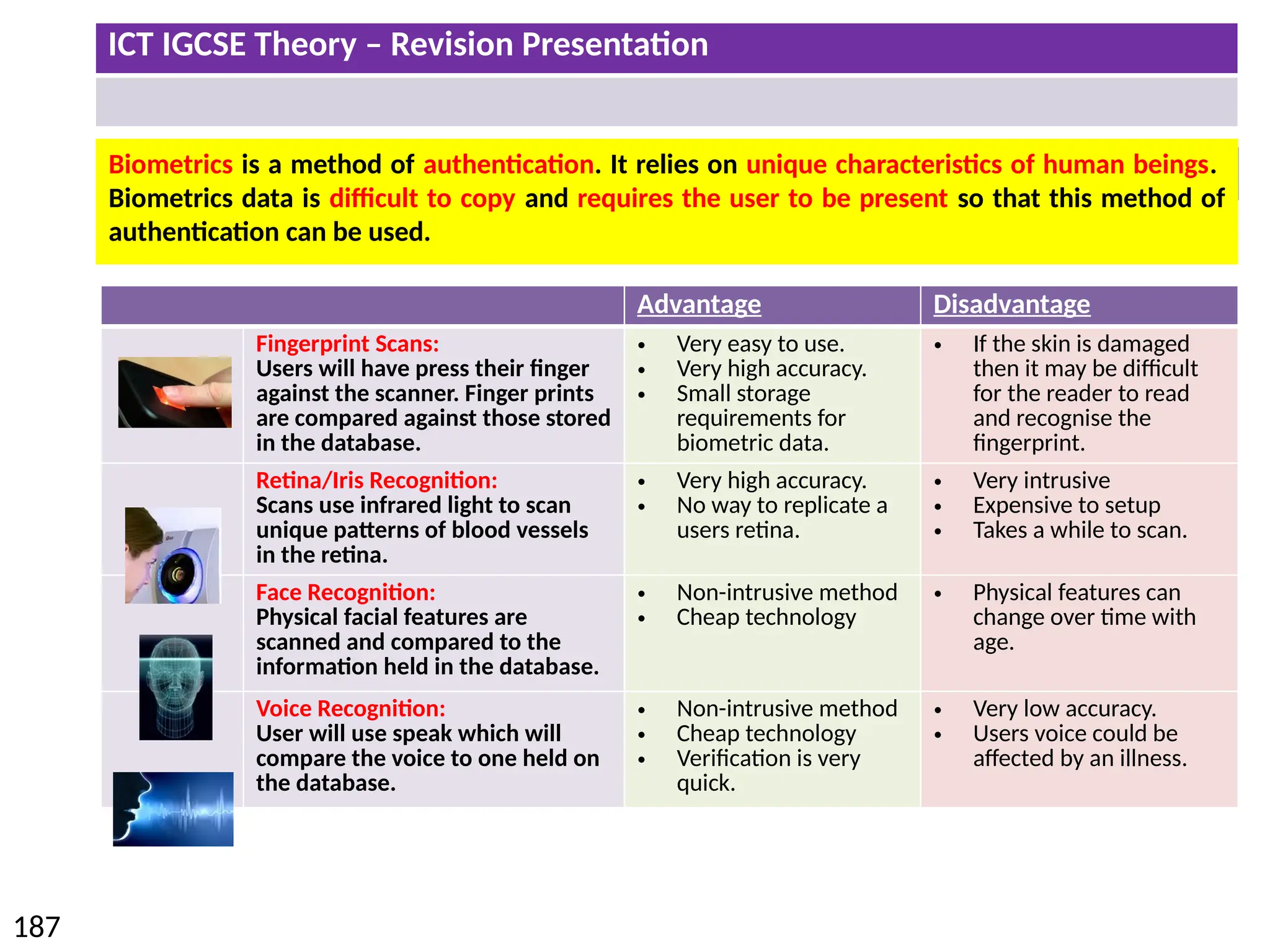
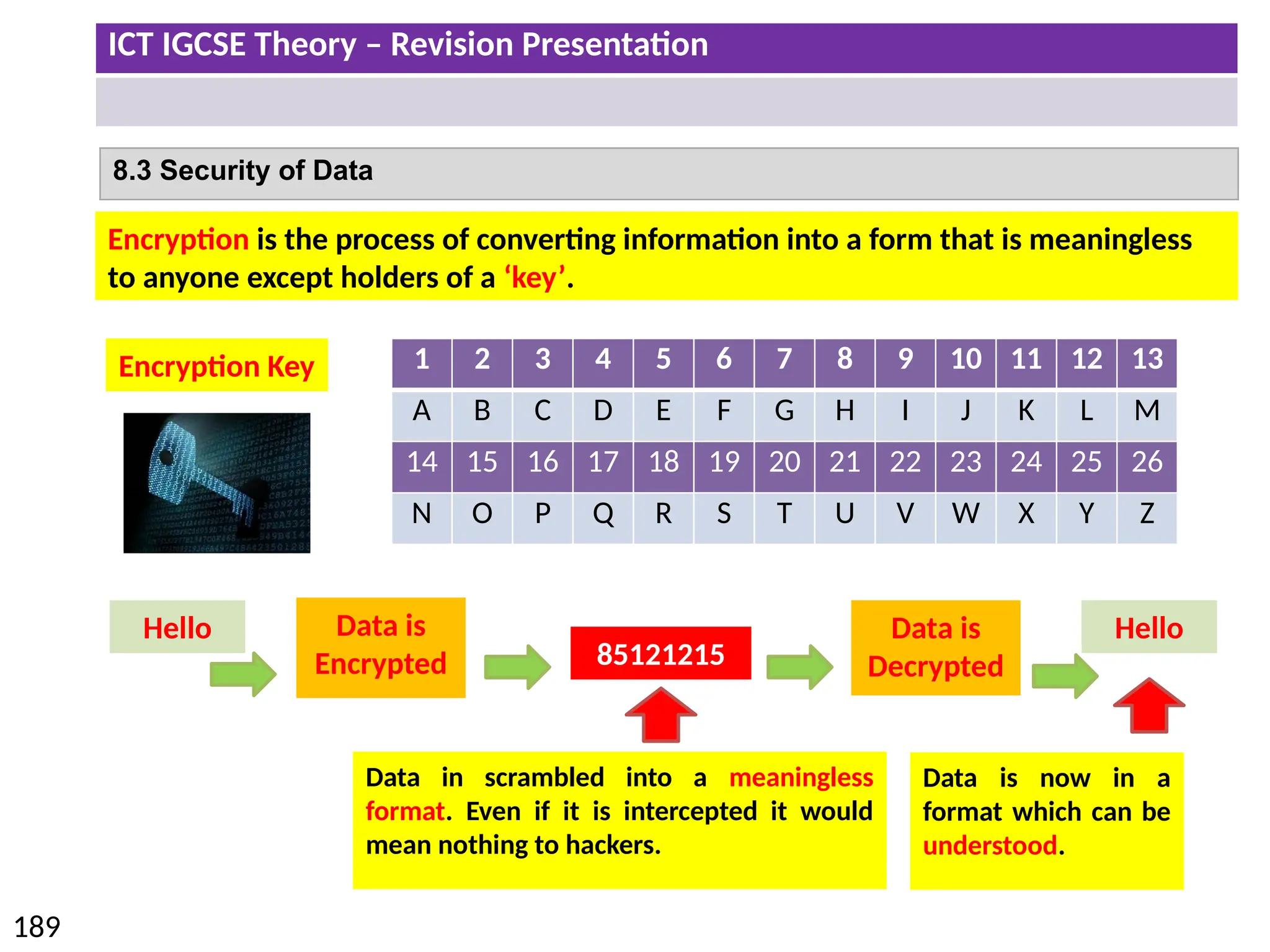
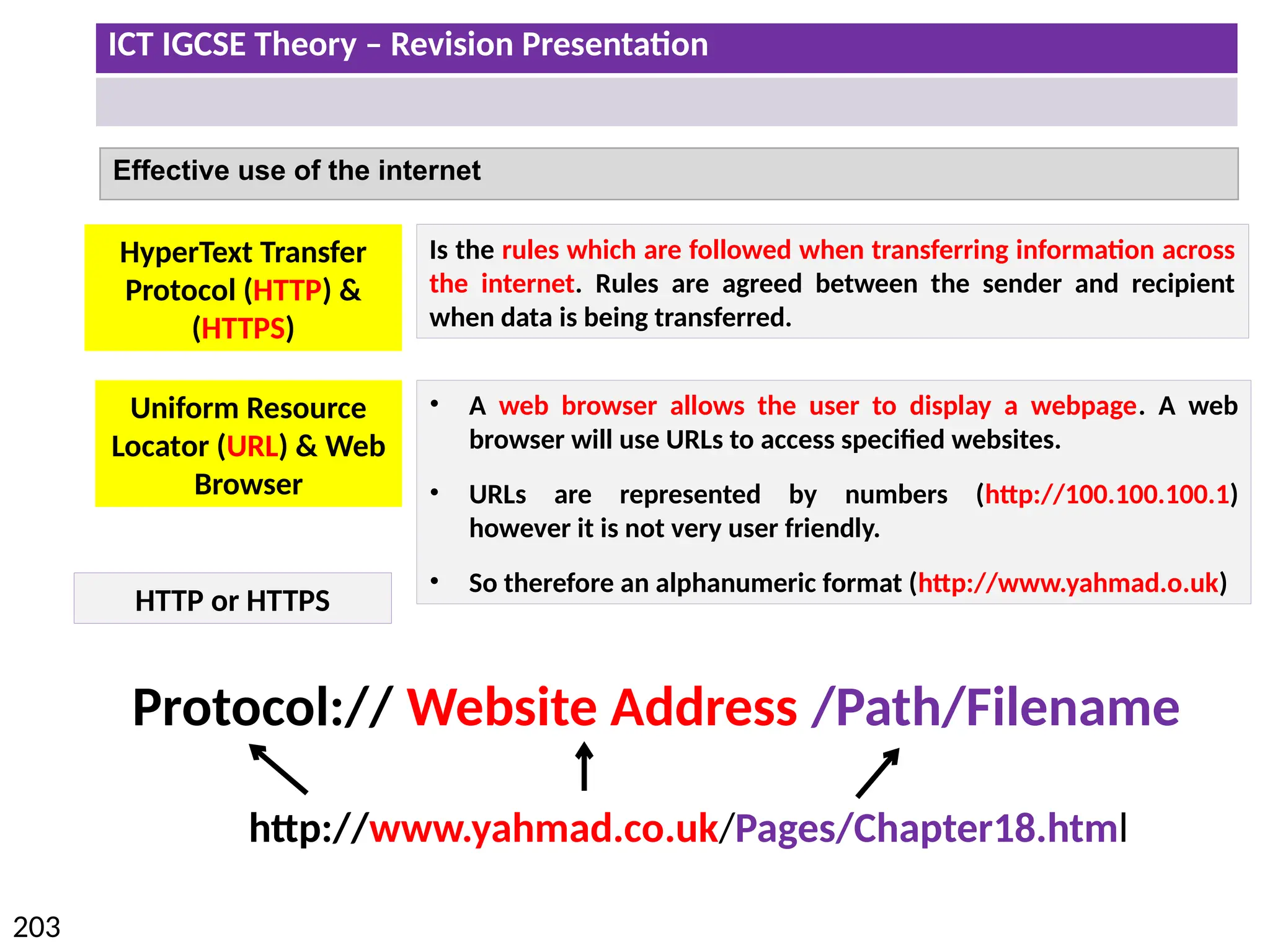
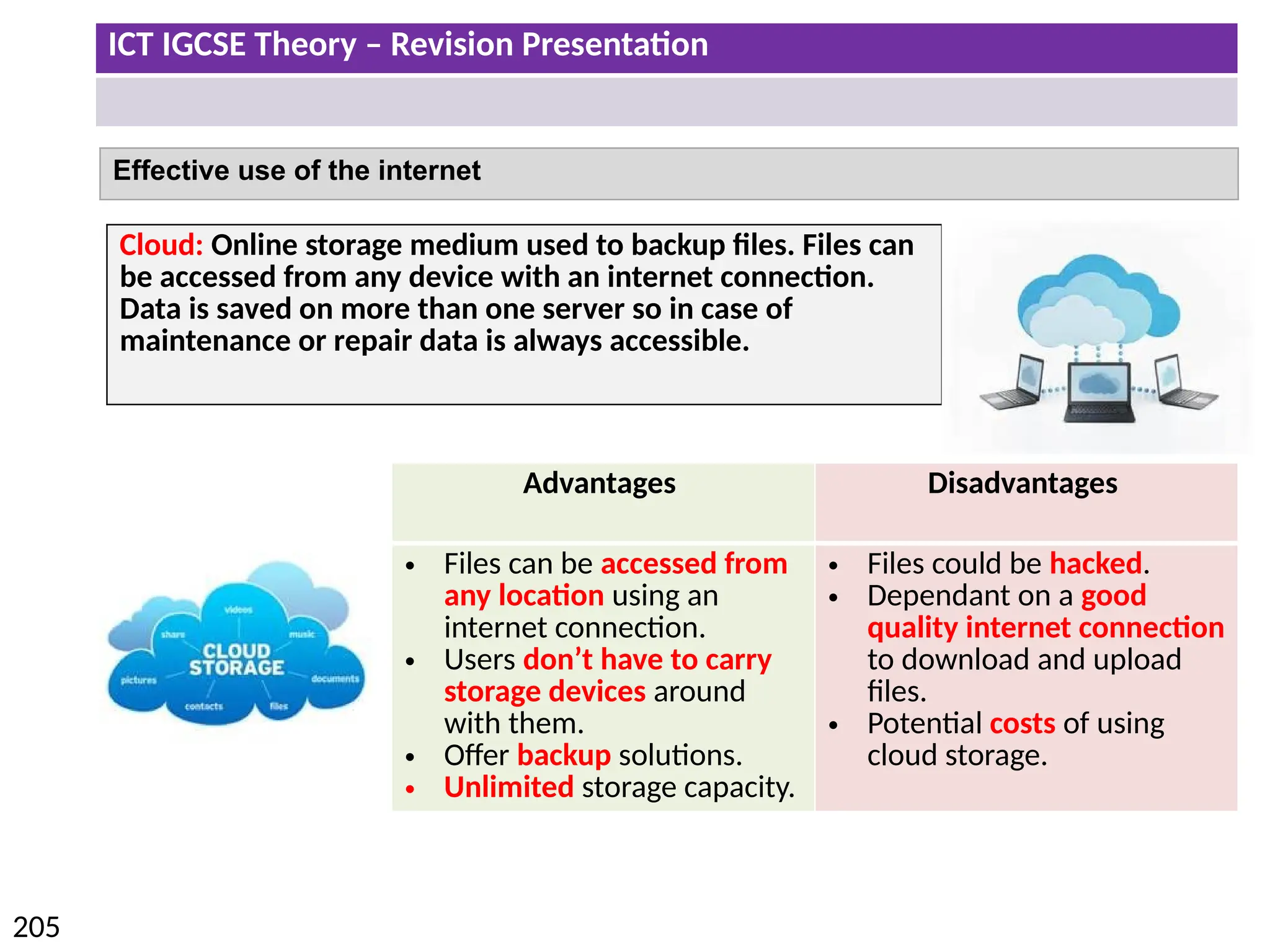
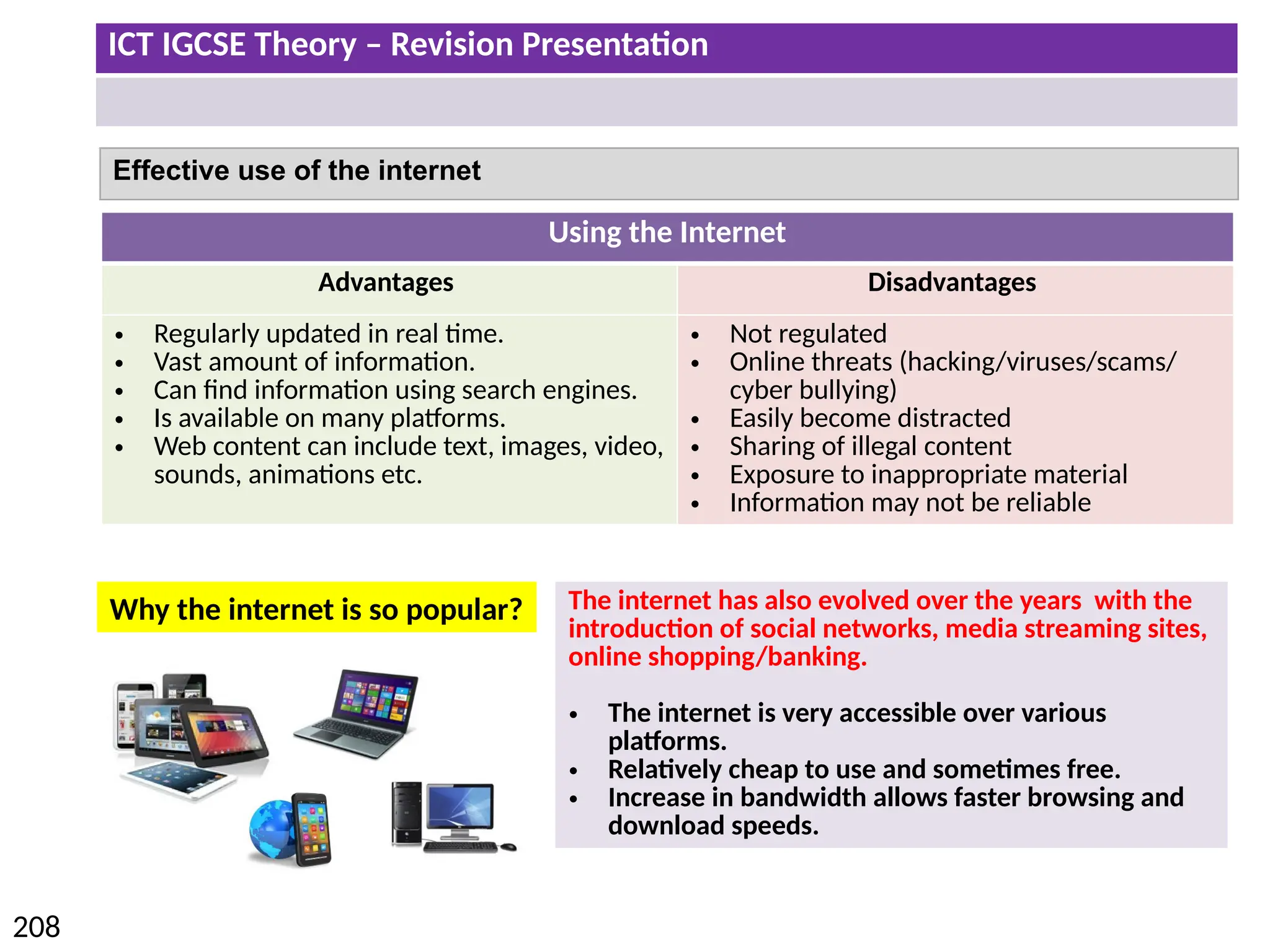
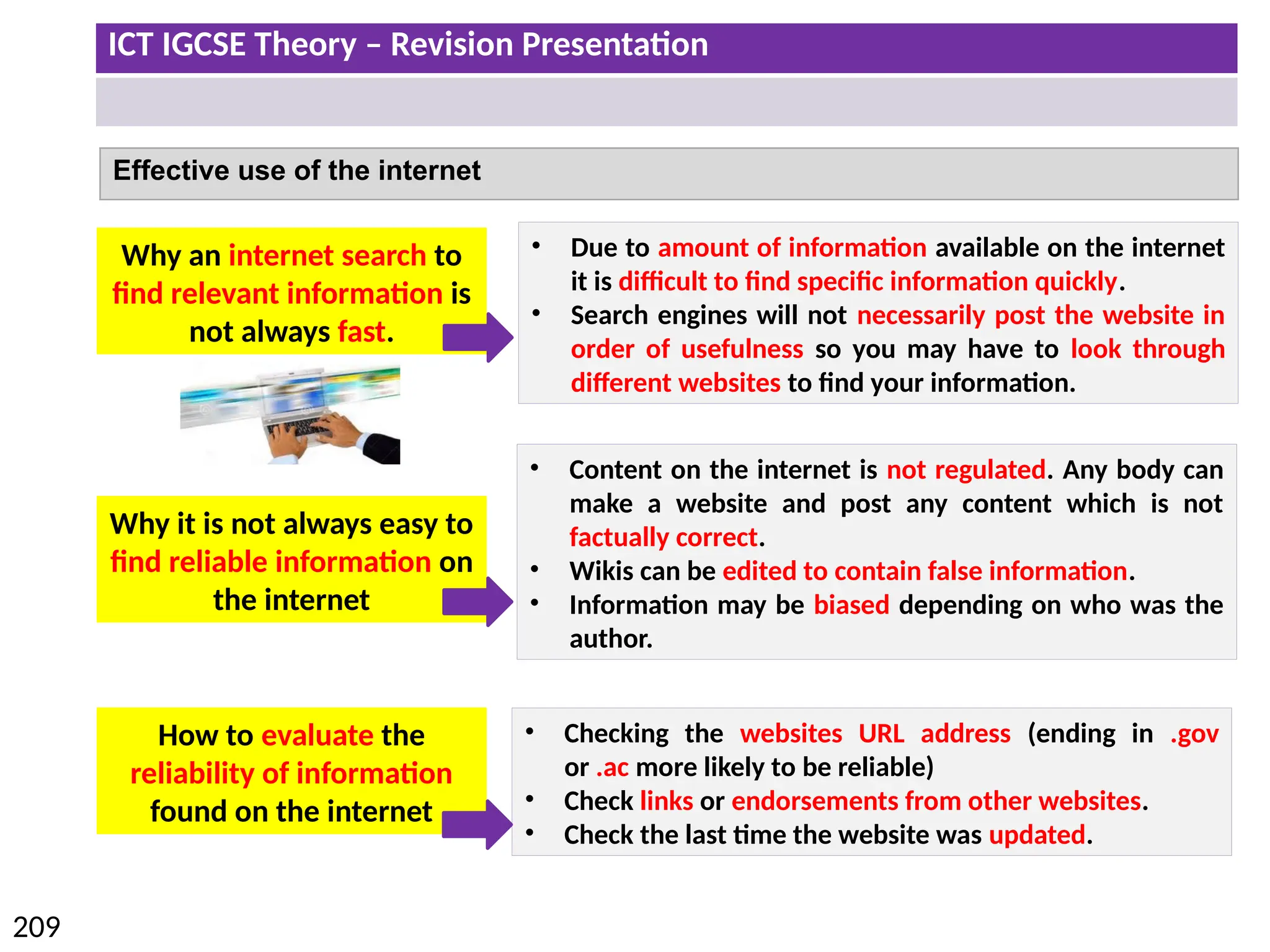
The document provides a comprehensive overview of hardware and software concepts for ICT IGCSE revision, detailing types of hardware (internal and external) and their functions, as well as the distinctions between application software and system software. It explains key components like the CPU, memory types (RAM and ROM), input/output devices, and storage solutions, alongside characterizations of various computer types (desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones) and their uses. Additionally, the document touches on operating systems and emerging technologies impacting everyday life.