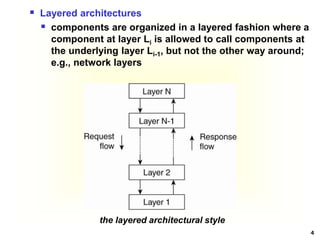
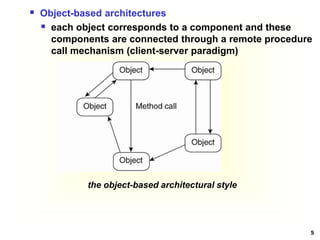
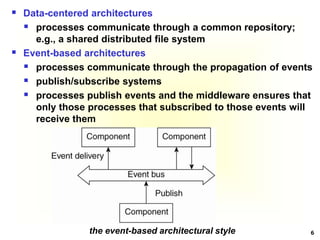
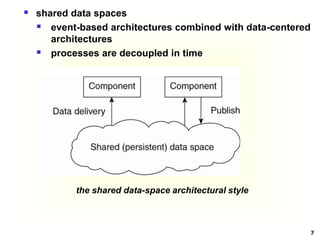
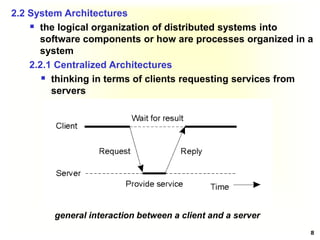
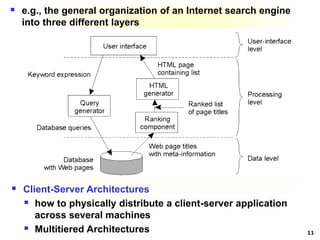
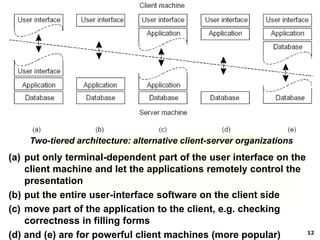
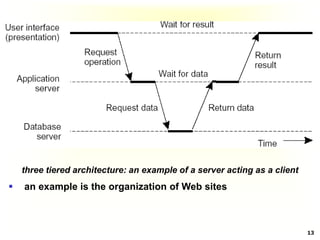
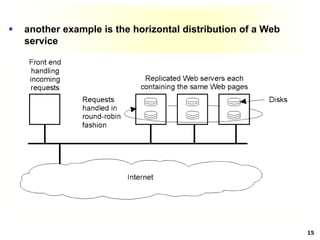
This document discusses software architectures and system architectures. It describes different architectural styles like layered, object-based, data-centered, and event-based that organize software components logically. It also discusses centralized architectures with clients requesting services from servers and decentralized architectures with peer-to-peer and horizontal distribution. Centralized architectures can be organized into two-tiered and three-tiered structures, while decentralized architectures involve vertical and horizontal distribution of components across machines.