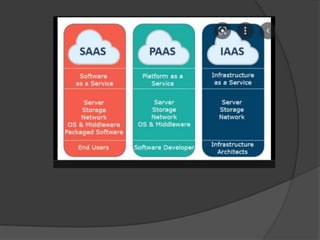
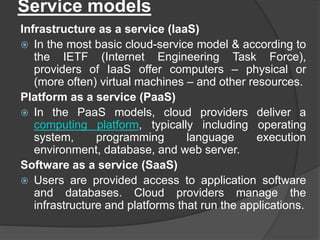
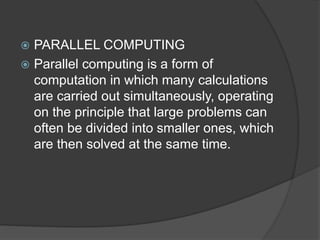
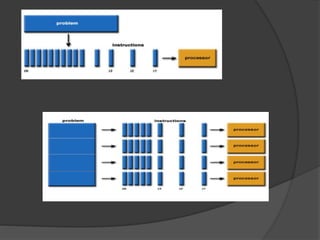
The document discusses various topics related to computing models and technologies. It defines client/server computing as a model where functions are distributed between client processes that request services and server processes that provide services. It also discusses distributed computing using multiple interconnected computers, cloud computing which delivers computing services over the Internet, mobile computing using portable hardware and software, and potential future computing technologies like predictive analytics, cognitive computing using artificial intelligence, and autonomic computing with self-managing networks.