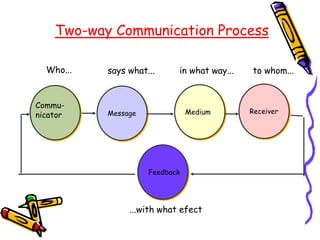
This document is a PowerPoint presentation about effective speech delivery. It discusses what constitutes good delivery, including conveying ideas clearly without being distracting. It covers various methods of delivery such as reading from a manuscript, reciting from memory, impromptu speaking, and extemporaneous speaking. The presentation also discusses elements of voice like volume, pitch, rate, and pauses. Body language aspects like eye contact, gestures and movement are addressed. It emphasizes the importance of practicing delivery through rehearsal and receiving feedback. The document concludes with tips for preparing for and managing audience question and answer sessions.