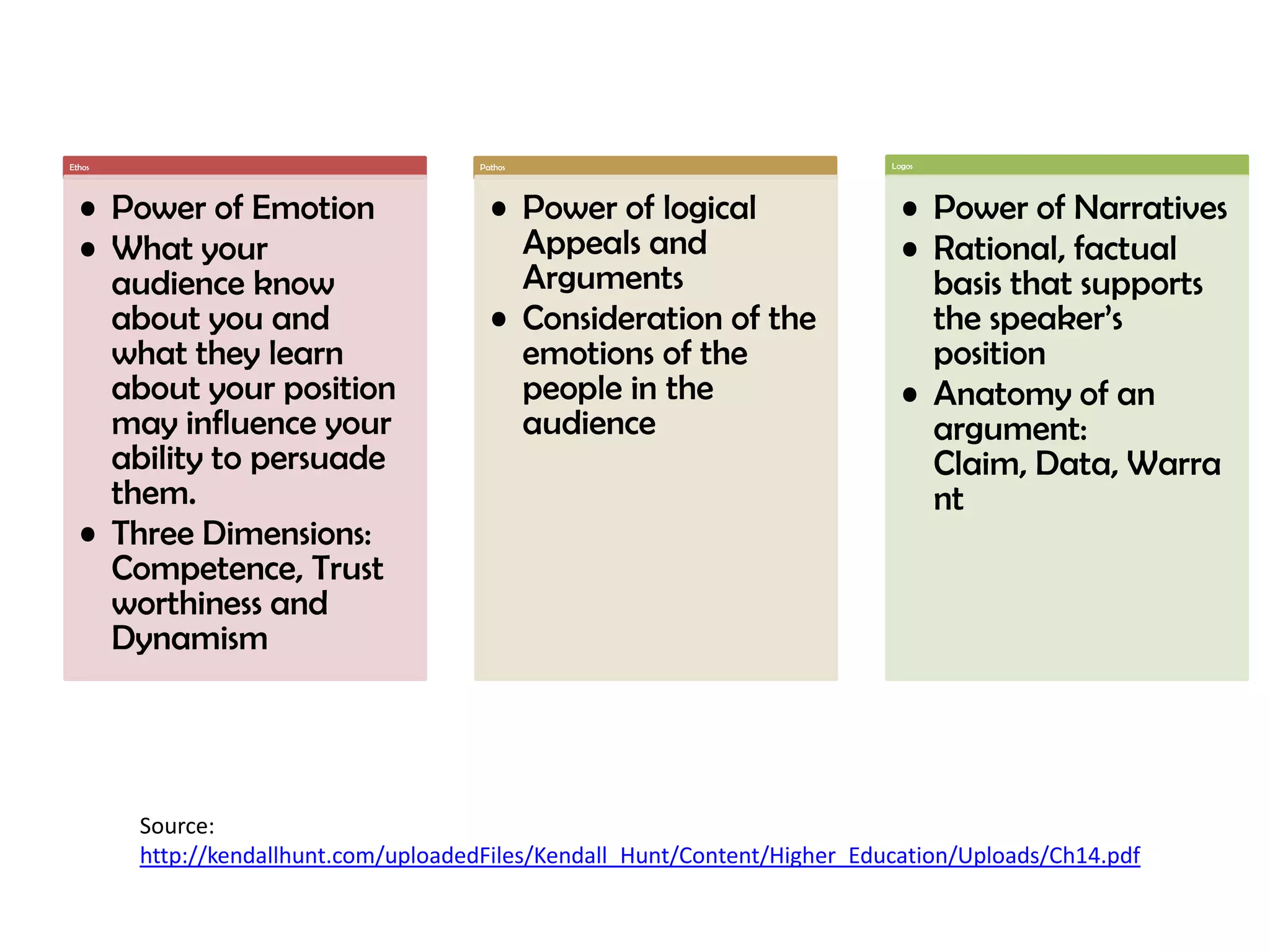
The document discusses different types of speeches categorized by delivery, purpose, and content. There are four types of delivery: impromptu, extemporaneous, memorized, and manuscript. The purposes covered are informative, persuasive, ceremonial, entertainment, and inspirational. Informative speeches can follow spatial, categorical, causation, or comparative designs. Persuasive speeches aim to convince, stimulate, or actuate. Ethos, pathos, and logos are three types of persuasion. Propositions can be of value, policy, or fact. Various specific speech types are also outlined such as valedictory, acceptance, toast, roast, and news casting speeches.