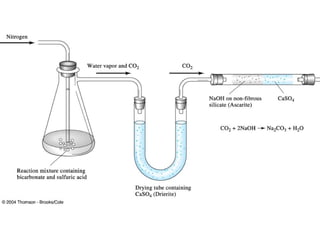
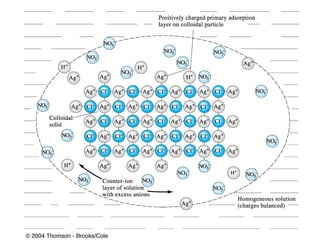
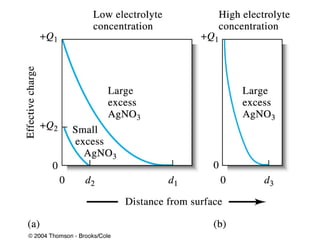
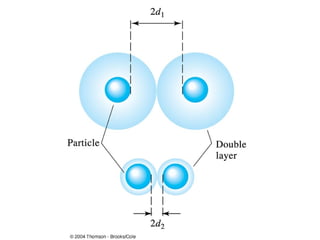
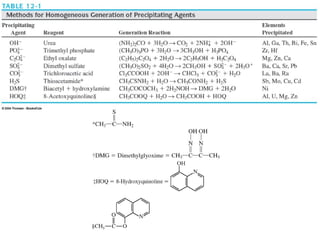
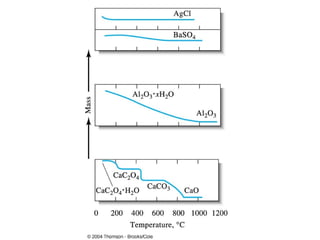
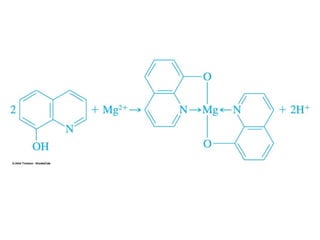
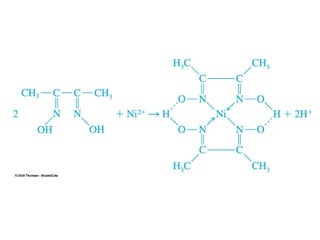
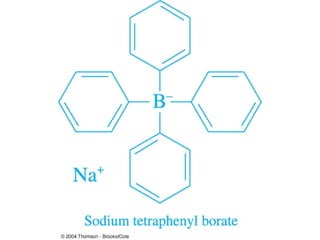
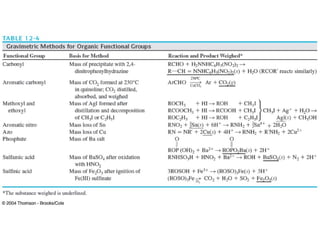
Gravimetric analysis methods measure the mass of a substance. There are two types: precipitation and volatilization. Precipitation converts the analyte into an insoluble precipitate using a reagent. The precipitate is filtered, washed, dried and weighed. Volatilization converts the analyte or its decomposition products into a gas which is collected and weighed. An ideal precipitate is easily filtered, insoluble, stable, and has a known composition when dried or ignited. Particle size and purity affect filtration and washing effectiveness. Larger, crystalline particles are preferred over colloidal particles. Experimental conditions like temperature, concentration and mixing rate affect particle size and purity. Drying and ignition remove solvents and