catalysis and applications
- 1. Module Catalysis Dr. S. H. Burungale
- 2. Catalysis Contents Introduction Classification of catalytic reactions Types of Catalytic reactions Characteristics of catalytic reactions Mechanisms of catalysis Industrial applications Short answer Questions
- 3. Introduction The rate of chemical reaction may bechanged by presence of small amount of a foreign material in a reaction . The foreign material remains unchanged at the end of the chemical reaction is known as catalyst. Greek -Keta – wholly and lein means process. The catalysis was first introduced by JONS JACOB BERZELIUS IN 1835.
- 4. Definition : Any substance which alters the rate of chemical reaction and remains unaffected chemically during that reaction is known as catalyst and the phenomenon as catalysis . Role of catalyst 1.It Initiate the reaction 2.Specific path of reaction 3.To avoids the side products of the reaction.
- 5. Classification of catalytic reaction Homogeneous Heterogeneous Reactants and catalyst are in same phase Reactants and catalyst are in different phase
- 6. Homogeneous Catalytic reaction: When reactants and catalyst are present in one and same phase in a catalytic reaction is called as Homogeneous Catalytic reaction and this phenomenon Homogeneous Catalysis 1.Oxidation of sulphur dioxide . 2SO2 + O2 2SO3 gas gas gas 2. Oxidation of carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide 2CO + O2 2CO2 gas gas gas NO (g) NO (g)
- 7. 3.Hydrolysis of urea by urease H2N-CO-NH2 +H2O NH3 +CO2 Liquid 4. Hydrolysis of ester by HCl ester to Acetic acid and ethyl alcohol 5.Inversion of cane sugar by sulphuric acid Cane sugar to Glucose and Fructose Urease (Liquid)
- 8. Heterogeneous Catalytic reaction: When reactants and catalyst are present in different phases in a catalytic reaction is called as Heterogeneous Catalytic reaction and this phenomenon Heterogeneous Catalysis. 1. Manufacture of Ammonia by Habers process N2(g) +3H2(g) 2NH3 2. Oxidation of sulphur dioxide .to sulphur troxide Fe/Mo ( s) 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3 Pt ( s)
- 9. Types of Catalysis The Catalytic reactions are again subdivided into following 1.Positive catalysis 2. Negative catalysis 3. Auto catalysis 4.Induced catalysis 5. Acid base Catalysis 6.Enzyme catalysis
- 10. 1.Positive Catalysis : A catalyst which accelerates or increases the rate of the chemical reaction. Example , 1. Preparation of Oxygen by potassium perchlorate 2KClO3 2KCl + 3O2 2. N2(g) +3H2(g) 2NH3 3. 2SO2(g) +O2(g) 2SO3 MnO2 heat Fe/Mo V2O5
- 11. 2.Negative Catalysis : A catalyst which retarded or decreases the rate of the chemical reaction. •Decomposition of Hydrogen peroxide is controlled by Sulphuric acid The rate of reaction decreases by H2SO4 Oxidation of sodium sulphites by glycero in presence of air to sodium sulphates 2H2O2 2H2O +O2 decomposition H2SO4
- 16. 4.Induced Catalysis :When one reaction influences the rate of other reaction, which does not occur under ordinary conditions, the phenomenon is known as induced catalysis. Some examples are as follows, (i) Sodium arsenite solution is not oxidised by air. If, however, air is passed through a mixture of the solution of sodium arsenite and sodium sulphite, both of them undergo simultaneous oxidation. The oxidation of sodium sulphite, thus, induces the oxidation of sodium arsenite. (ii) The reduction of mercuric chloride with oxalic acid is very slow, but potassium permanganate is reduced readily with oxalic acid. If, however, oxalic acid is added to a mixture of potassium permanganate and both are reduced simultaneously. The reduction of potassium permanganate, thus, induces the reduction of mercuric chloride.
- 17. 5. Acid base catalysis
- 19. 6.Enzyme catalysis Maltose is converted to two molecules of glucose by the enzyme maltase, which hydrolyzes the glycosidic bond. Commercial maltose is produced from starch that has been treated with barley malt.
- 20. Characteristics of Catalytic reactions Criteria or characteristics of catalysts i. The mass and chemical composition of catalyst should remain unchanged at the end of the reaction. ii. A small amount of catalyst is enough to bring about an appreciable change in the rate of chemical reaction. For example, even 1 mg of fine platinum powder is enough to catalyze the combination of 2.5 liters of a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen to form water. However, there are some reactions that uses significant amount of catalyst. iii. For solid catalyst, the use in powder form increases the activity of catalyst by increasing its surface area. iv. For a reversible reaction, catalyst does not change the position of equilibrium but helps to attain the equilibrium faster. v. Catalysts are specific in action (like a key can open a particular lock). For example, manganese dioxide can catalyze the decomposition of potassium chlorate but not potassium nitrate or other substances. A catalyst
- 21. Mechanisms of Catalysis THEORIES OF CATALYSIS There are two main theories to explain catalysis. 1. Intermediate compound formation theory 2. Adsorption theory In general, the intermediate compound formation theory applies to homogeneous catalytic reactions and the adsorption theory applies to heterogeneous catalytic reactions.
- 22. 1. The Intermediate Compound Formation Theory According to this theory, the catalyst first forms an intermediate compound with one of the reactants. The compound is formed with less energy consumption than needed for the actual reaction. The intermediate compound being unstable combines with other reactant to form the desired product and the catalyst is regenerated
- 24. For example, a reaction of the type A + B ---- c---- > AB which occurs in presence of a catalyst C, may take place as A+C (Catalyst) ---- --- > AC (Intermediate) AC + B -- --- --- > AB(Product) + C(Catalyst) Many catalytic reactions can be explained on the basis of this theory.
- 25. The catalytic oxidation of SO2 to SO3 in the lead chamber process probably takes place as; 2 NO (Catalyst) + O2 --- ---- > 2NO2 Intermediate Compound NO2 + SO2 --- --- > SO3 (Product) + NO (Catalyst)
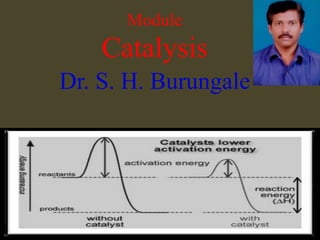
- 27. In a thermodynamically feasible chemical reaction, when addition of a small amount a chemical substance increases the rate of attainment of chemical equilibrium but the substance itself does not undergo any chemical change, then the reaction is called a catalytic reaction. The substance that enhances the reaction rate is called a catalyst. Catalysts work by providing alternative mechanism involving a different transition state of lower energy. Thereby, the activation energy of the catalytic reaction is lowered compared to the uncatalyzed reaction
- 28. Adsorption Theory This theory has been developed to explain the mechanism of a reaction between two gases catalyzed by a solid catalyst, i.e., heterogeneous catalysis. In this process, the reaction is initiated by the adsorption of reactant molecules on the surface of the catalysts. The adsorption process results from the residual forces on the catalyst surface. Let us consider a reaction; A (g) + B (g) C (g) + D (g) It involves the following steps:
- 29. Step I: Adsorption of reactant molecules The reactant molecules A and B strike on the catalyst surface. The reactants molecules adsorb on the surface by weak Vander Waals forces or by partial chemical bond. Step II: Formation of activated complex The adsorbed reactants combine together to give intermediate activated complex which is unstable. Step III: Decomposition of activated complex or formation of product The unstable activated complex decomposes to form product, which are held to the catalyst surface by weak force or chemical bond.
- 30. Step IV: Desorption of products The products are desorbed or released from the surface of the catalyst. The products are stable and can exist independently.
- 31. Industrial applications of Catalysts Applications of catalysis The applications of catalysis are summarised as follows. Process i. Haber's process for the manufacture of ammonia. ii. Ostwald's process for the manufacture of nitric acid. iii. Lead chamber process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid. iv. Contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid. v. Deacon's process for the manufacture of chlorine. vi. Bosch's process for the manufacture of hydrogen. vii. Hydrogenation of vegetable oils Oil + H2 -- > Vanaspati ghee viii. Bergius process for the synthesis of petrol from coal.
- 32. Questions and Answer 1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a catalyst? a) It participates in the reaction b) It enhances the equilibrium rate c) It activates equilibrium d) It initialises the reaction View Answer 2. 2. Which of the following will decrease the rate of reaction? a) Catalytic poison b) Positive catalyst c) Negative catalyst d) Catalytic promoters
- 33. Thank You