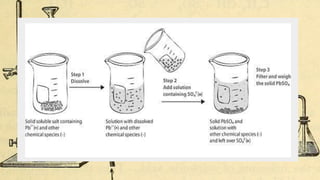
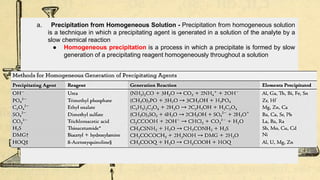
Gravimetric analysis methods determine the mass of a compound to quantify the analyte. Precipitation gravimetry is the most common method, where the analyte is precipitated from solution and the precipitate is filtered, dried, and weighed. Ideal precipitates are easily filtered, insoluble, and have a known composition. Factors like particle size, supersaturation, and electrolyte addition affect precipitation and coprecipitation. Other gravimetric methods include volatilization, where the analyte is converted to a known gas, electrogravimetry by electrodeposition, and thermogravimetry which measures mass changes with temperature.