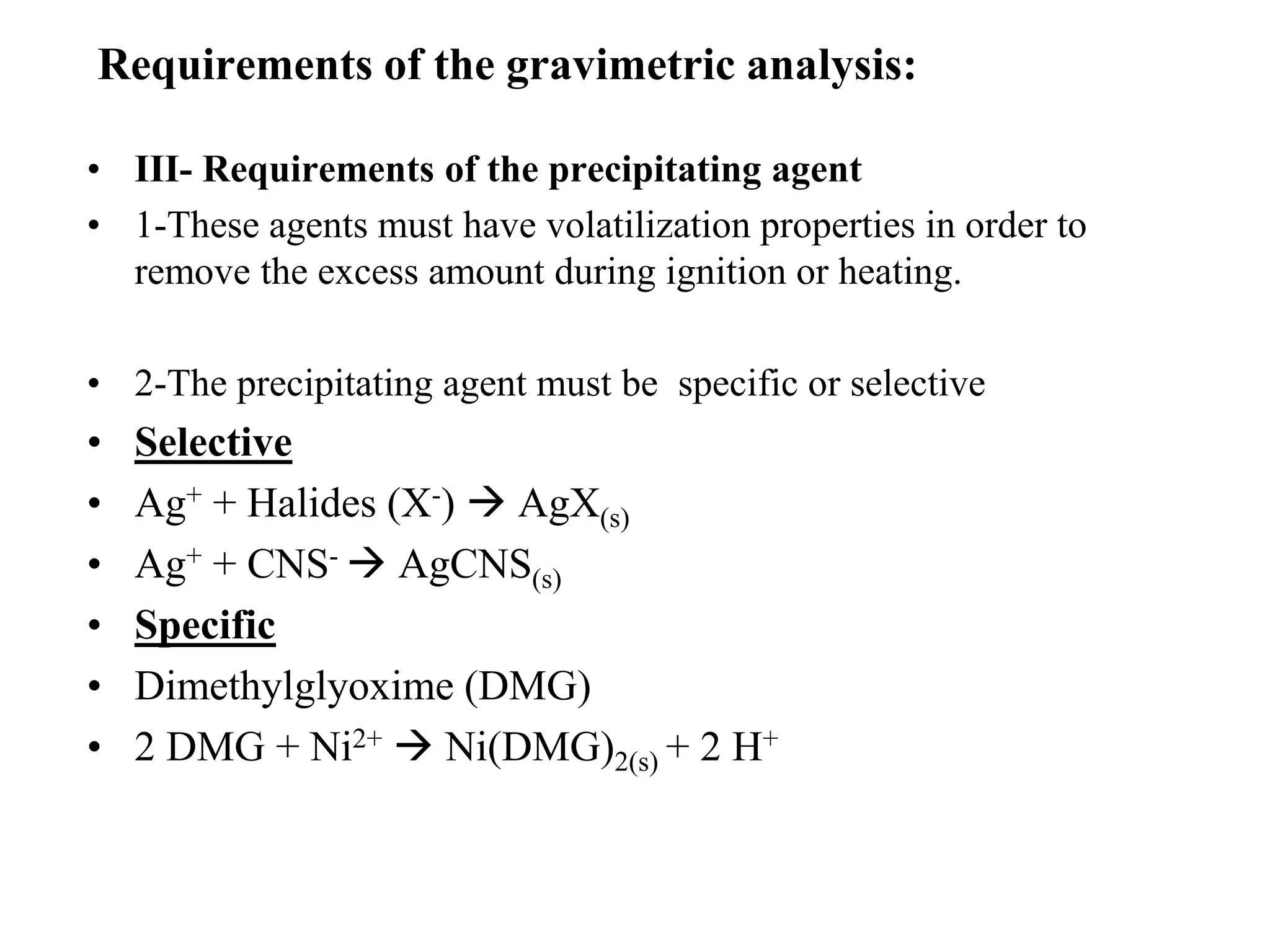
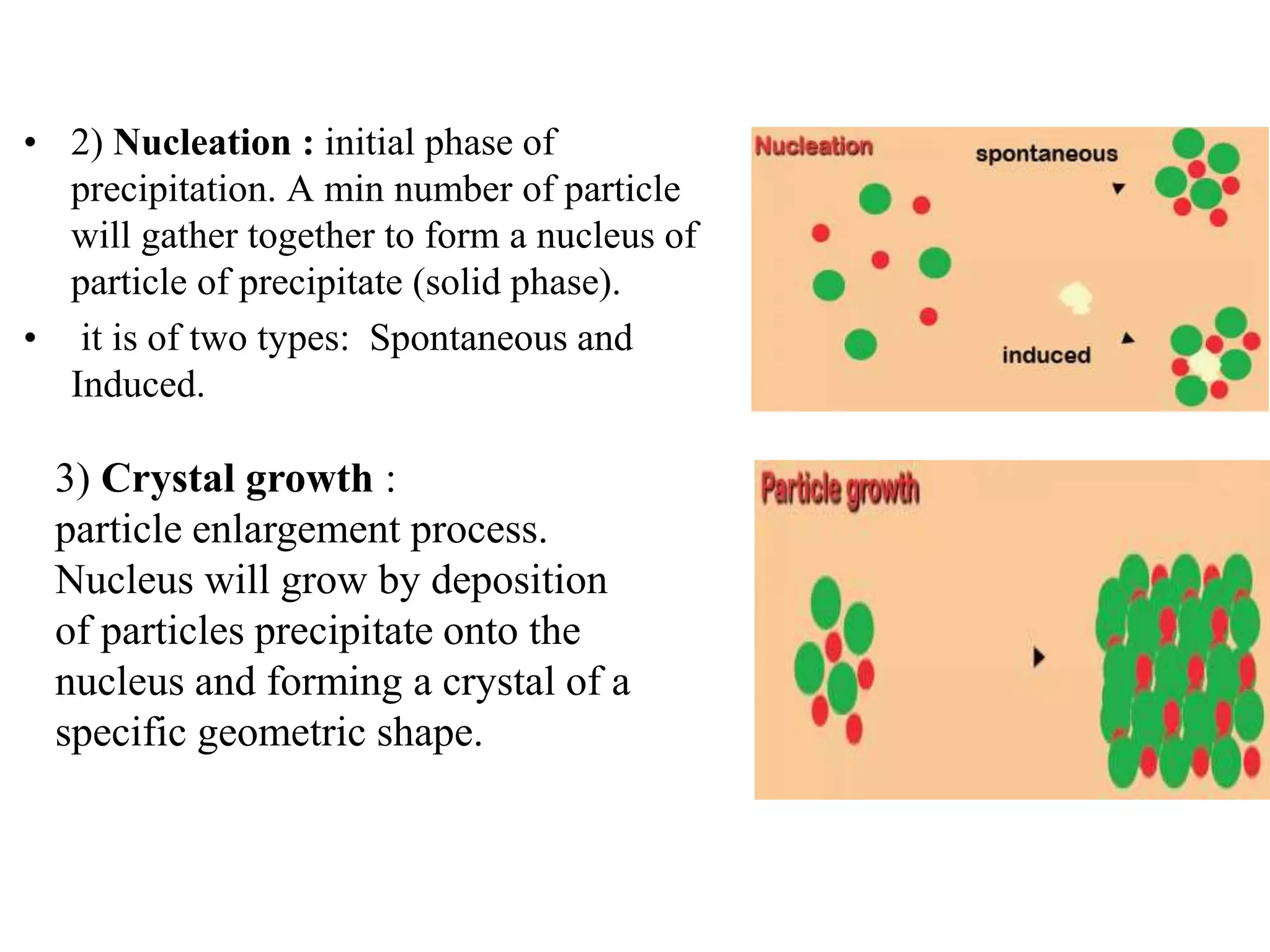
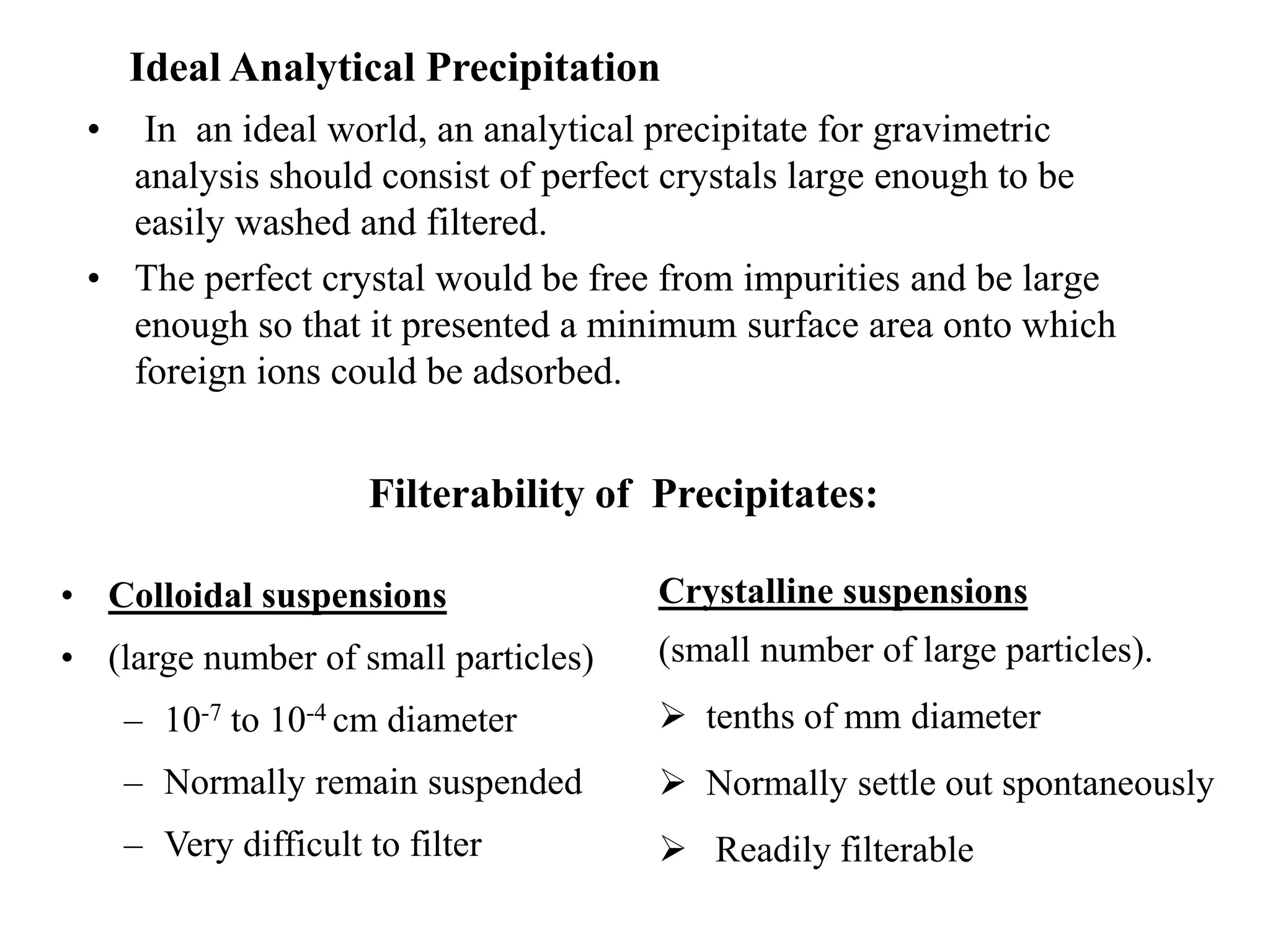
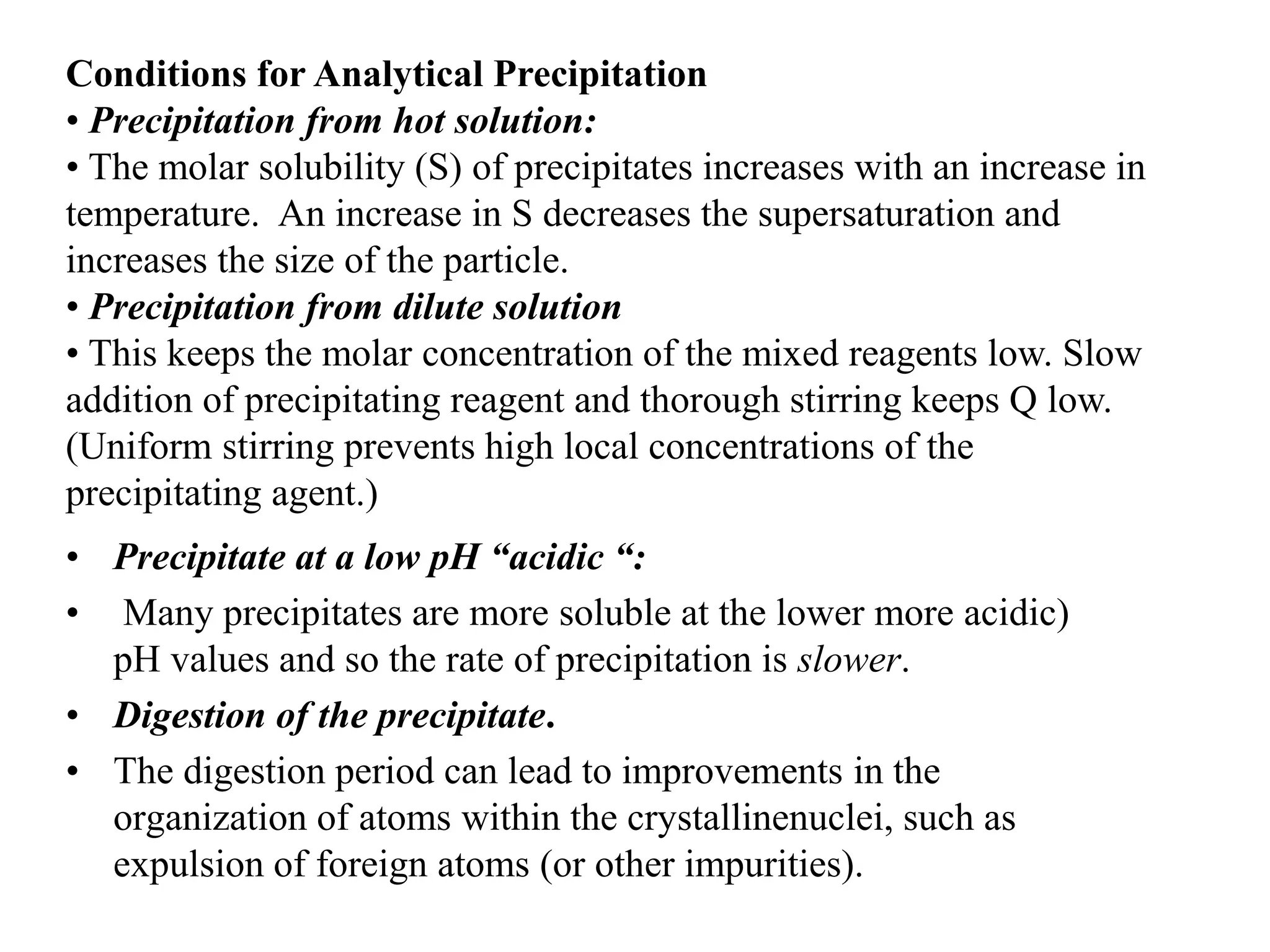
Gravimetric analysis is a quantitative analytical method where the amount of analyte is determined by measuring the mass of a pure substance. It involves converting the analyte into a solid precipitate through precipitation, volatilization, electrolysis, or thermogravimetry. The precipitate is then filtered, washed to remove impurities, dried, and weighed. Key steps include preparing the sample solution, precipitating the analyte, digesting and filtering the precipitate, washing to remove trapped impurities, drying or igniting, and calculating the mass of analyte based on the final weighted form. Conditions like supersaturation, particle size, and washing solutions must be carefully controlled to obtain accurate and precise results.

























![• AgCl(s) Ag+ + Cl-
• KSP = [Ag+][Cl-]
BaSO4(s) ----> Ba2+(aq) + SO4
2-(aq)
Ksp = [Ba2+][SO4
2-]
PbCl2(s) -----> Pb2+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
Ksp = [Pb2+][Cl-]2
Ag2CrO4(s) 2 Ag+ + CrO4
2-
KSP = [Ag+]2[CrO4
2-]
The solubility product constant, Ksp, is the product of the concentrations
of the ions involved in solubility equilibrium, each raised to a power equal
to the stoichiometric coefficient of that ion in the chemical equation for
the equilibrium.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gravimetryall-230610073352-19c51fd2/75/Gravimetry-ALL-ppt-32-2048.jpg)

![Examples
Sol. S mol/L
Ksp
Sol. Pr.
General
Formula
AgCl / PbSO4
( Ksp )1/2
S2
[M] [ A]
MA
PbI2 / Ag2S
( Ksp / 4 )1/3
4S3
[M] [ A]2
MA2
Fe(OH)3 / La(IO3)3
( Ksp / 27 )1/4
27S4
[M] [ A]3
MA3
Bi2S3
( Ksp / 108 )1/5
108S5
[M]2 [ A]3
M2A3
The relation between Ksp and solubility:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gravimetryall-230610073352-19c51fd2/75/Gravimetry-ALL-ppt-34-2048.jpg)








![Diverse Ion Effect on Solubility:
• Presence of diverse ions will increase the solubility of
precipitates due to shielding of dissociated ion species.
• KSP
o and Activity Coefficients
• AgCl(s)(AgCl)(aq) Ag+ + Cl-
• Thermodynamic solubility product KSP
o
• KSP
o = aAg+
. aCl- = [Ag+]ƒAg+
. [Cl-]ƒCl-
• KSP
o = KSP ƒAg+
. ƒCl-
• KSP = KSP
o/(ƒAg+
. ƒCl)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gravimetryall-230610073352-19c51fd2/75/Gravimetry-ALL-ppt-44-2048.jpg)