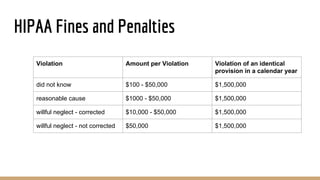
The document outlines the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), a federal law established in 1996 to protect the privacy and security of health data. It explains key terms such as protected health information (PHI), the responsibilities of covered entities and business associates, and the significance of the four main HIPAA rules: privacy, security, enforcement, and breach notification. Compliance involves implementing administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to ensure the confidentiality and security of PHI.