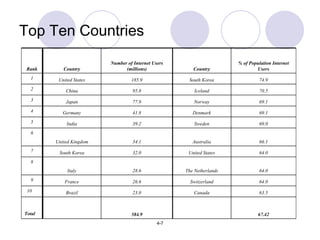
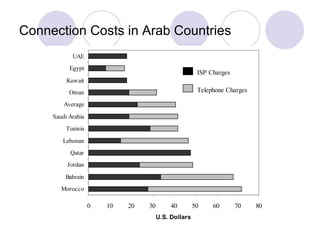
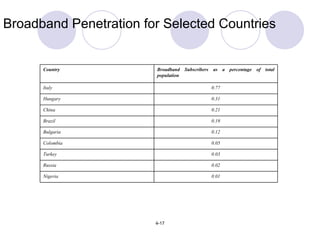
This chapter discusses trends in global internet usage and online purchasing behavior. It outlines how marketers must consider factors like computer and phone access, credit card availability, connection speeds, and electricity issues when developing e-marketing strategies in different markets. The chapter also covers the challenges and opportunities for e-marketing in emerging economies, and how the digital divide between developed and developing nations impacts international business.