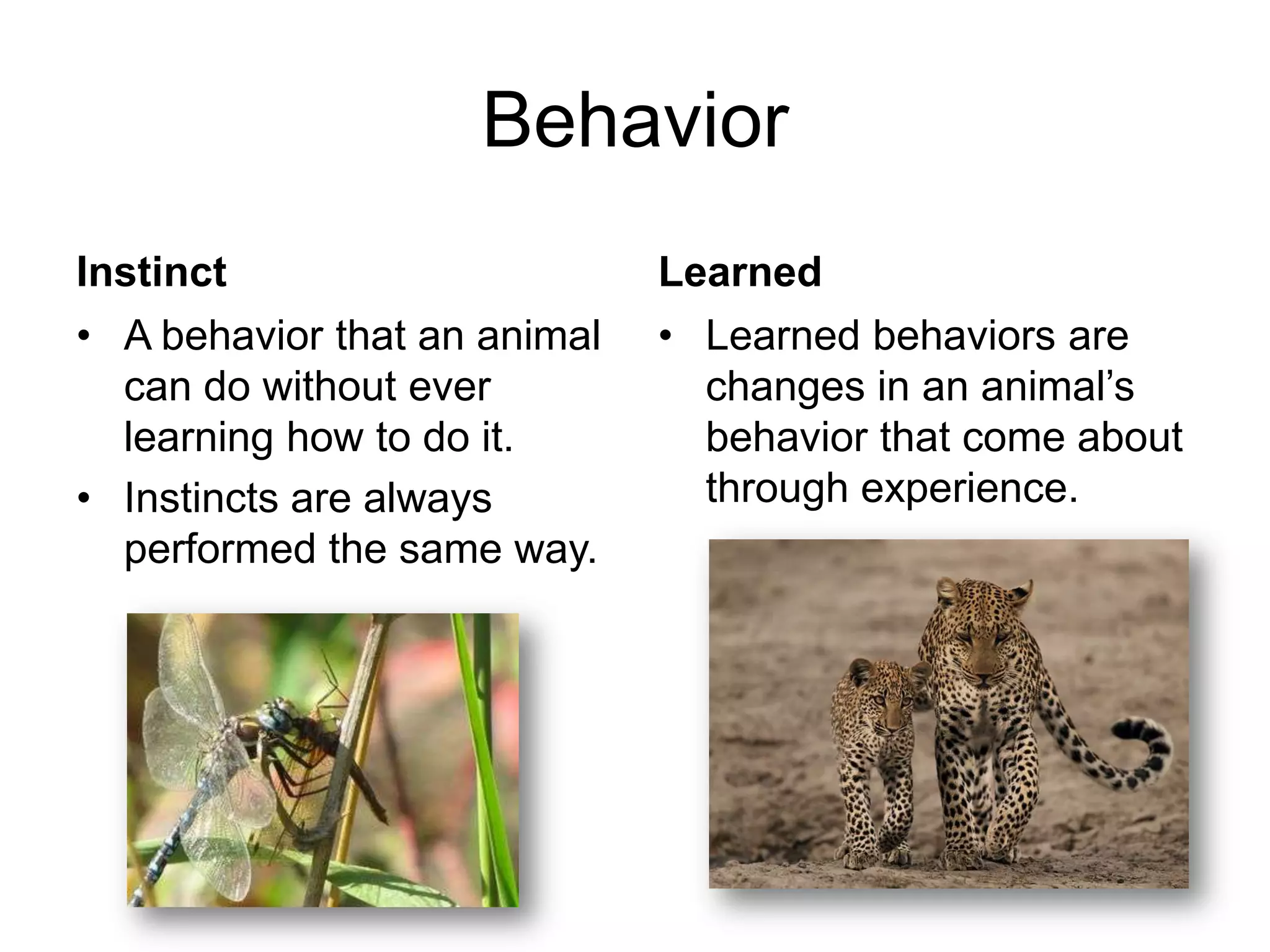
This document discusses how living things adapt to survive in their environments. It provides examples of physical, behavioral, life cycle, and population adaptations in animals and plants. These adaptations include a shark's teeth for catching prey, a pangolin's scales for protection, a moth's eyespots to deter predators, a lemur's strategy of raising young one at a time for survival, and variations in a finch's beak size enabling it to access different food sources on the Galapagos Islands. The document emphasizes that adaptations help organisms survive and reproduce in their habitats.