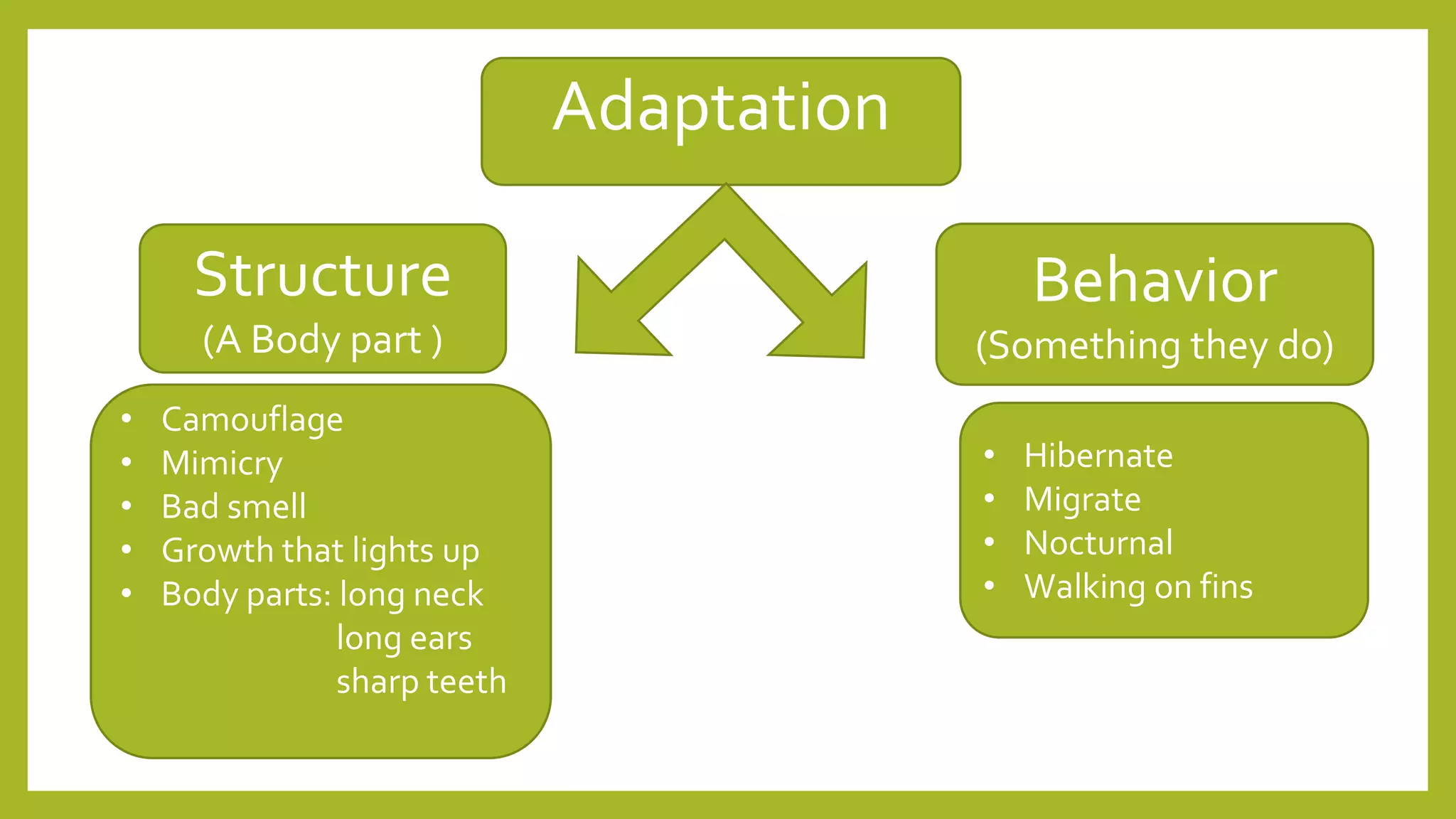
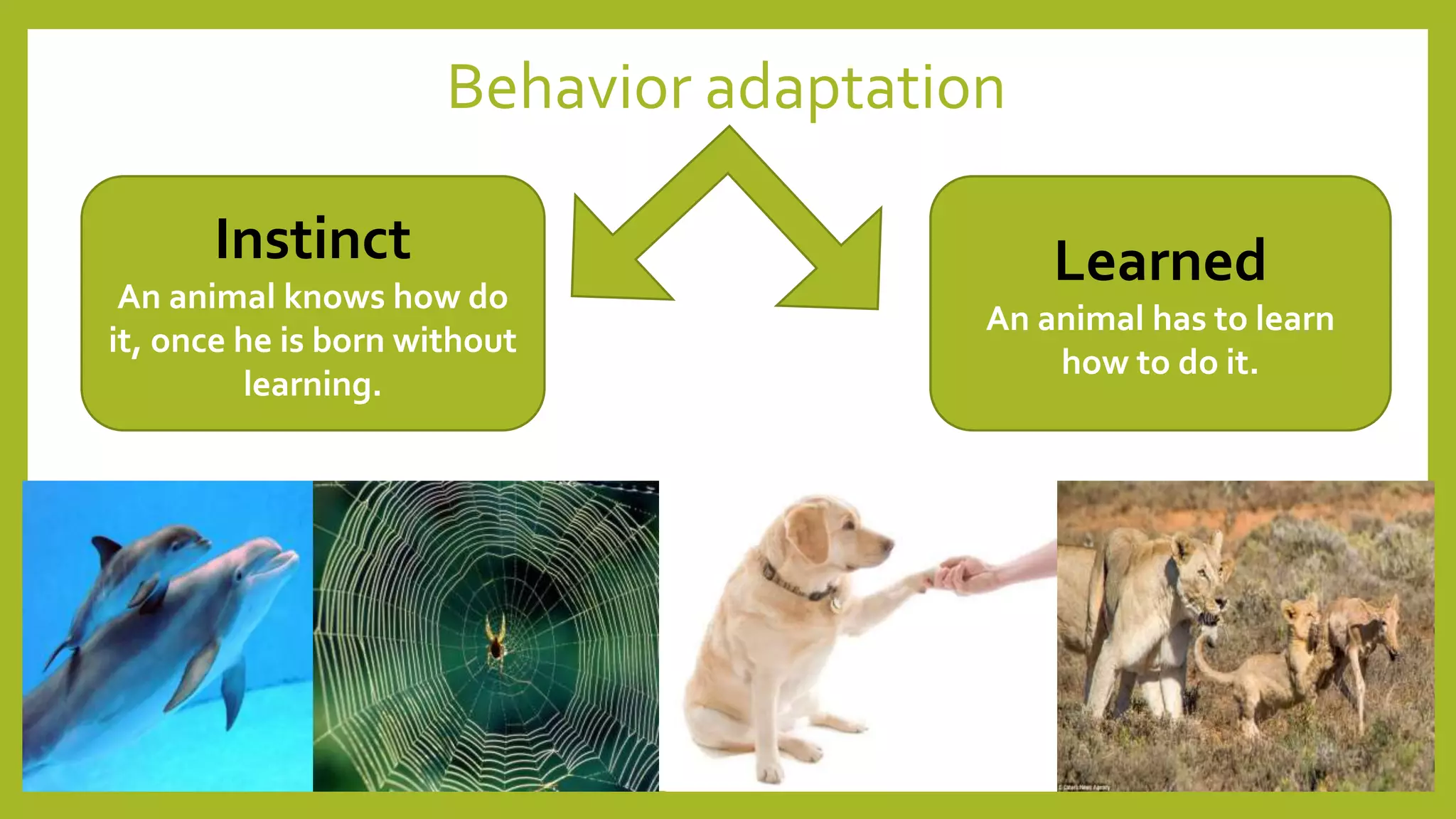
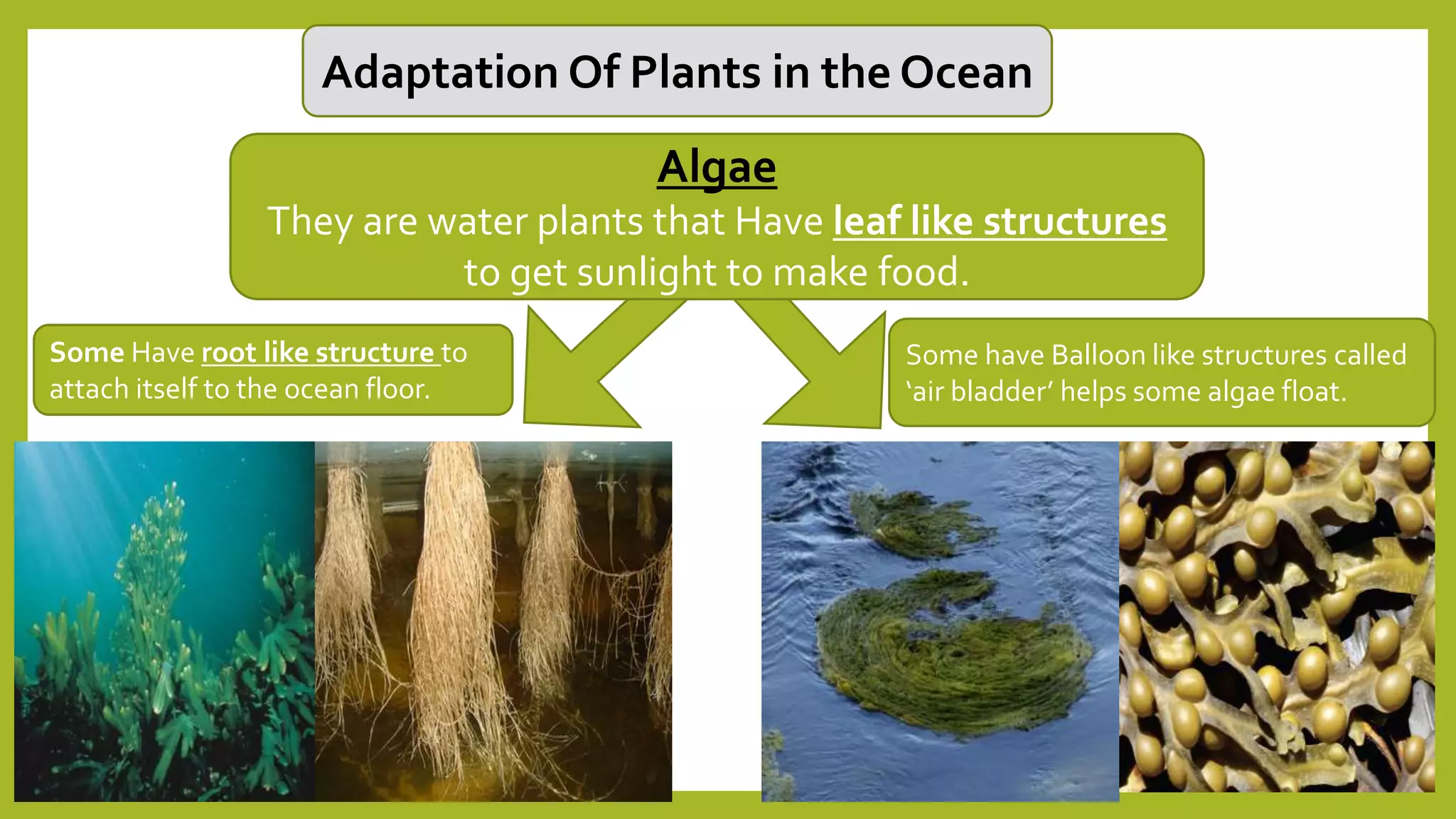
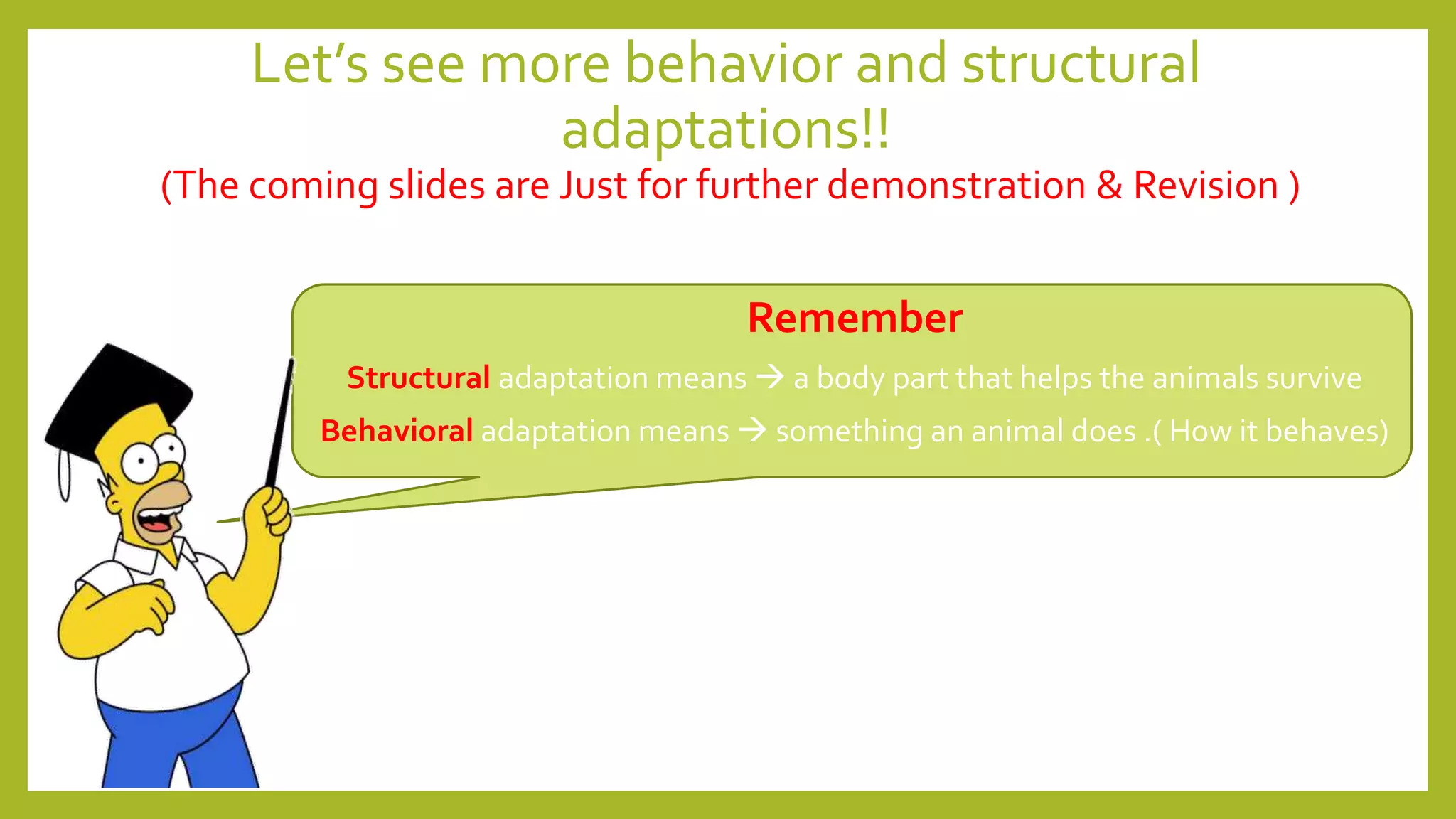
Animals must adapt to survive in their ecosystems. Adaptations are structural or behavioral traits that help animals survive. Structural adaptations include camouflage, mimicry, and physical traits like teeth and body size. Behavioral adaptations consist of instincts like swimming and learned behaviors such as migration. Animals use adaptations like camouflage, hibernation, and nocturnal behavior to cope with challenges in different habitats.