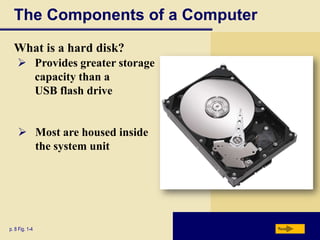
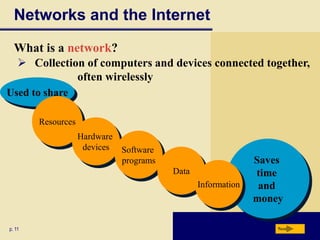
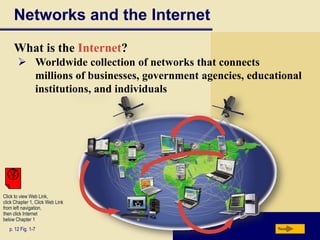
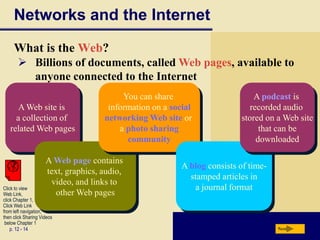
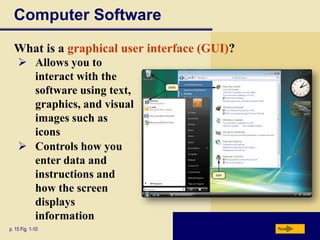
Computers are everywhere and understanding how to use them is important. The document defines a computer and describes its basic components including the processor, memory, storage devices, input/output devices, and communications devices. It discusses different types of computers and how they are used in various settings like homes, small offices, businesses, and mobile environments. Networks and the internet allow people and computers to share resources and information on a global scale. The document outlines the basic elements of an information system and provides examples of computer applications in fields like education, healthcare, science and more.