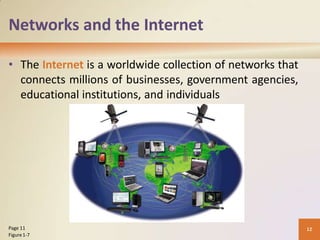
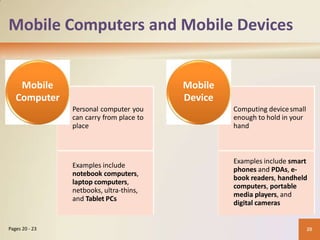
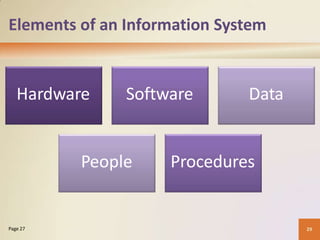
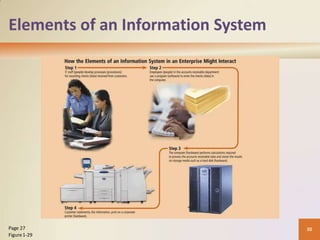
This document provides an overview of basic computer concepts including defining computers and their components, networks and the internet, types of computer software, different categories of computers and users, and applications of computers in society. It explains that a computer processes data into information, identifies the five main components, and discusses advantages and disadvantages of computer use. Networks and the internet are defined and their benefits explained. Various types of computer users and how they interact with computers are also outlined.