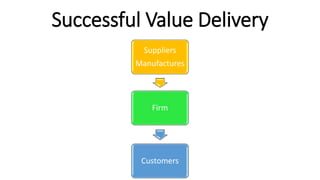
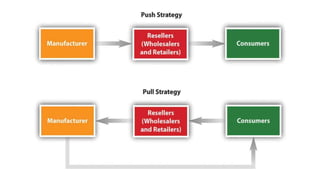
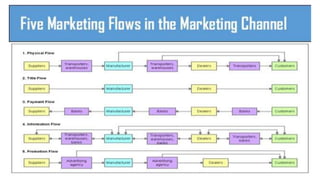
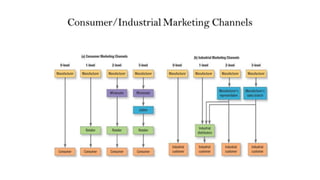
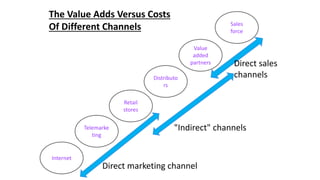
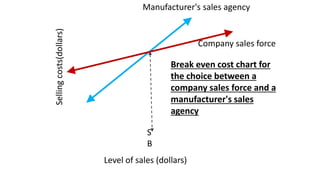
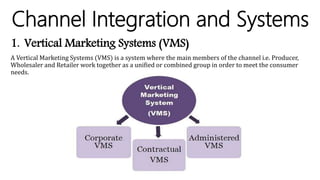
This document discusses marketing channels and channel management. It begins by defining key channel concepts like push and pull strategies, multichannel marketing, omnichannel marketing, and integrated marketing channels. It then covers channel functions, levels, and member functions. The rest of the document discusses channel design decisions, evaluating alternatives, managing channel members, and resolving conflicts.