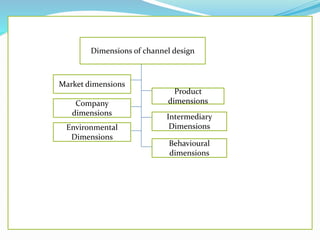
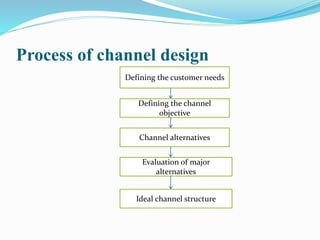
This document discusses channel design and the process of developing an effective channel structure. It outlines five key dimensions to consider: market, product, company, intermediary, and environmental. When designing channels, companies should define customer needs, channel objectives, evaluate alternatives based on economic, control and adaptive criteria, and select an ideal structure. An effective channel design meets criteria of effectiveness, efficiency, equity, scalability and flexibility, and involves decisions around channel members and partners.