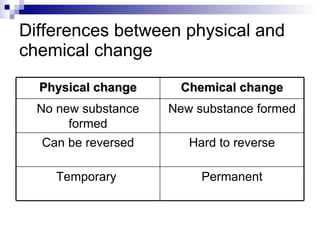
The document discusses two types of changes: physical changes and chemical changes. It provides examples of each type of change and notes that chemical changes result in new substances being formed, while physical changes do not. The document also compares and contrasts physical and chemical changes. It notes that chemical changes are permanent and difficult to reverse, while physical changes are temporary and can be reversed.