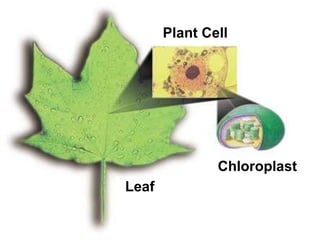
1. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants produce their own food using carbon dioxide, water and sunlight through the action of chlorophyll.
2. The key requirements for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide, water, sunlight, and chlorophyll. Photosynthesis produces glucose and releases oxygen as a byproduct.
3. The rate of photosynthesis is affected by light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature - it proceeds fastest at around 40°C and declines above and below this temperature range.