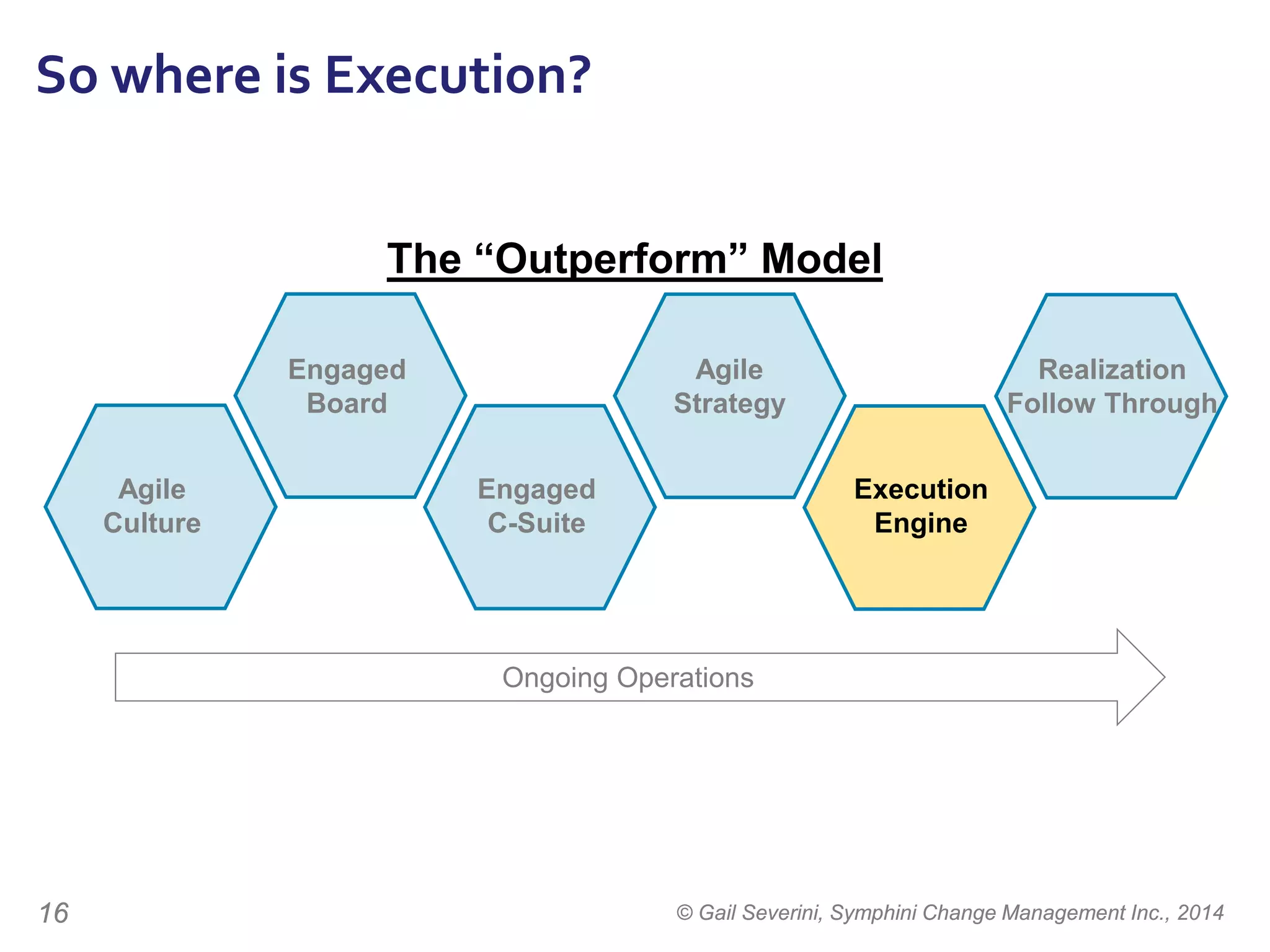
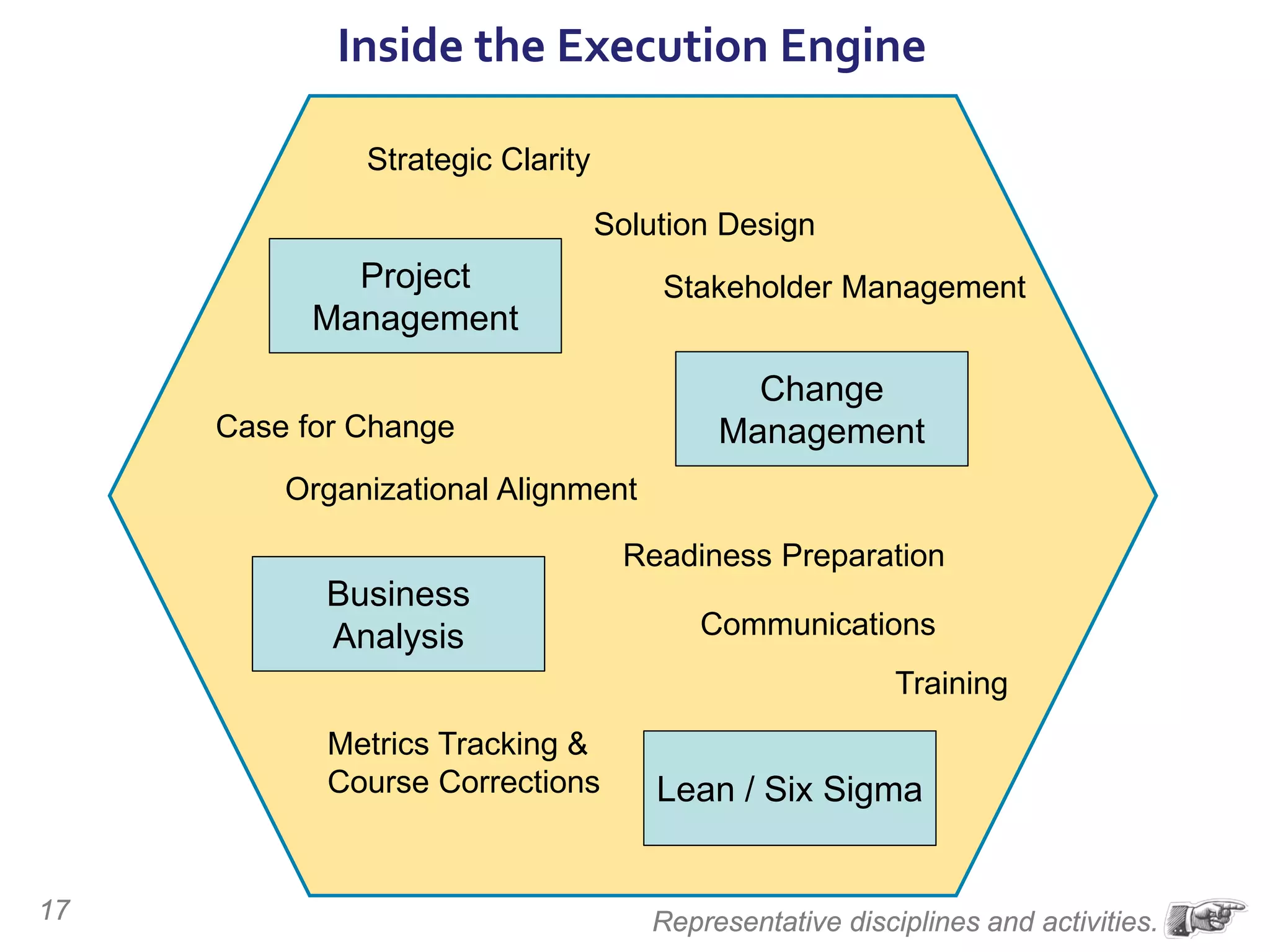
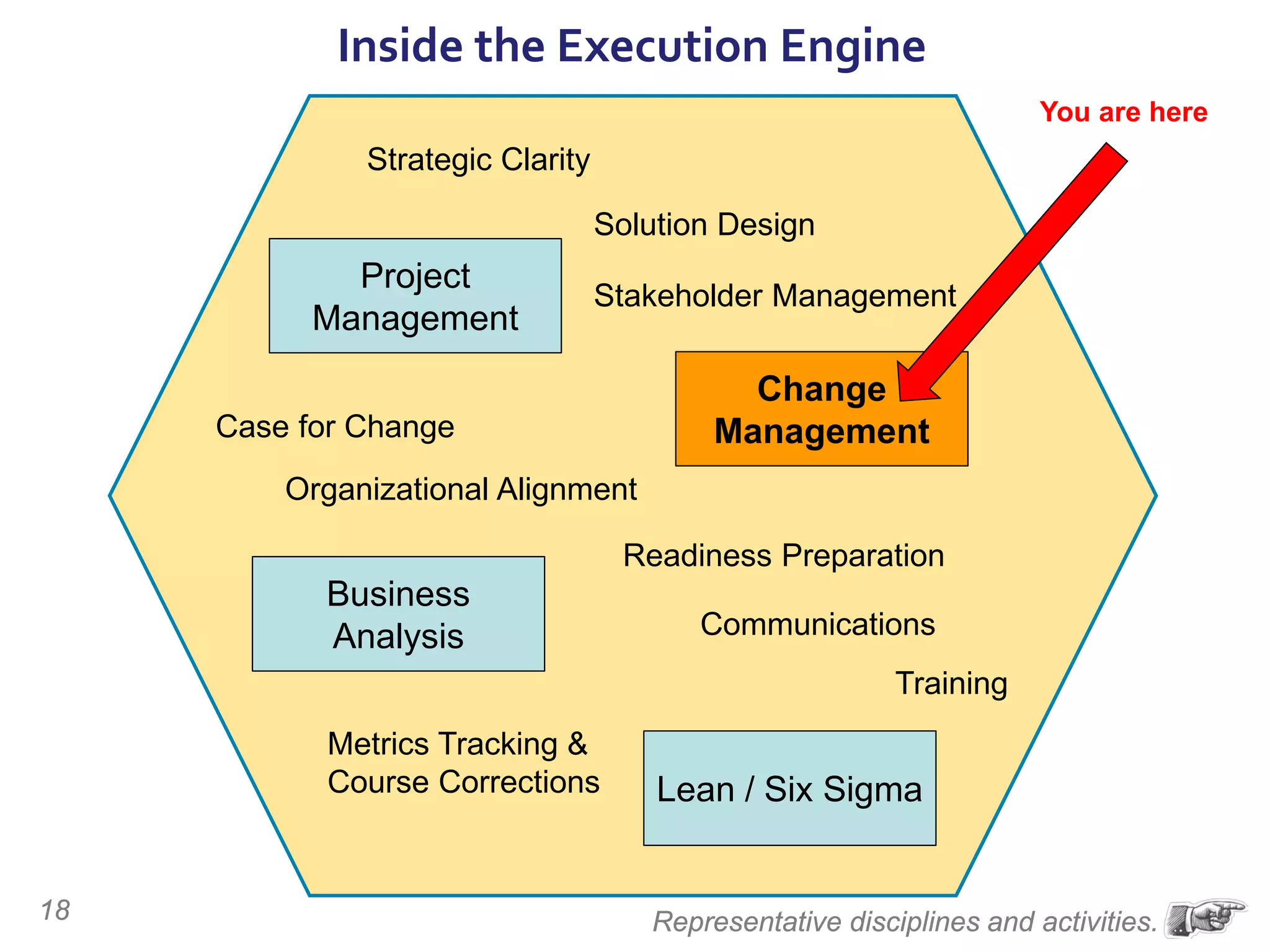
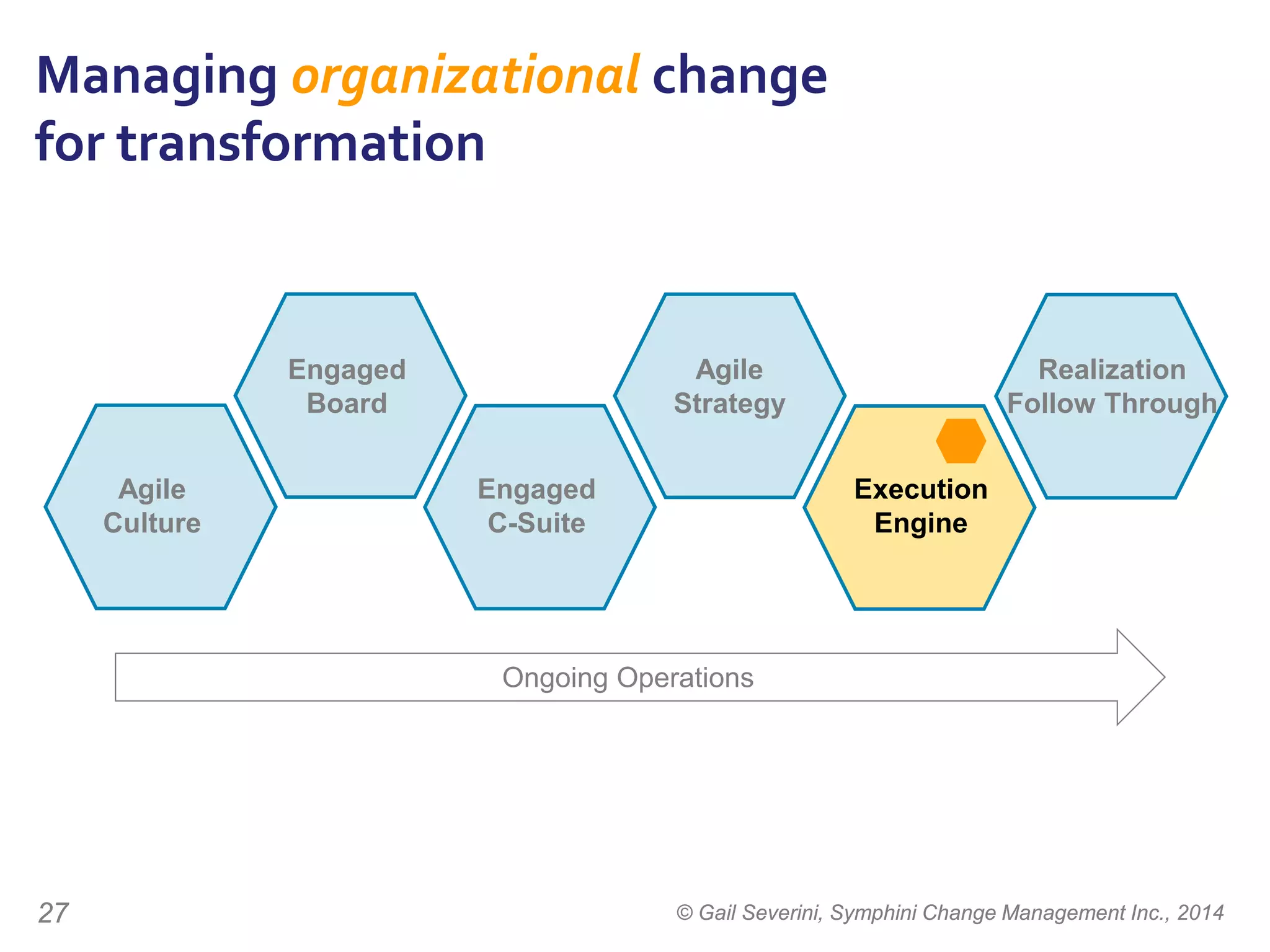
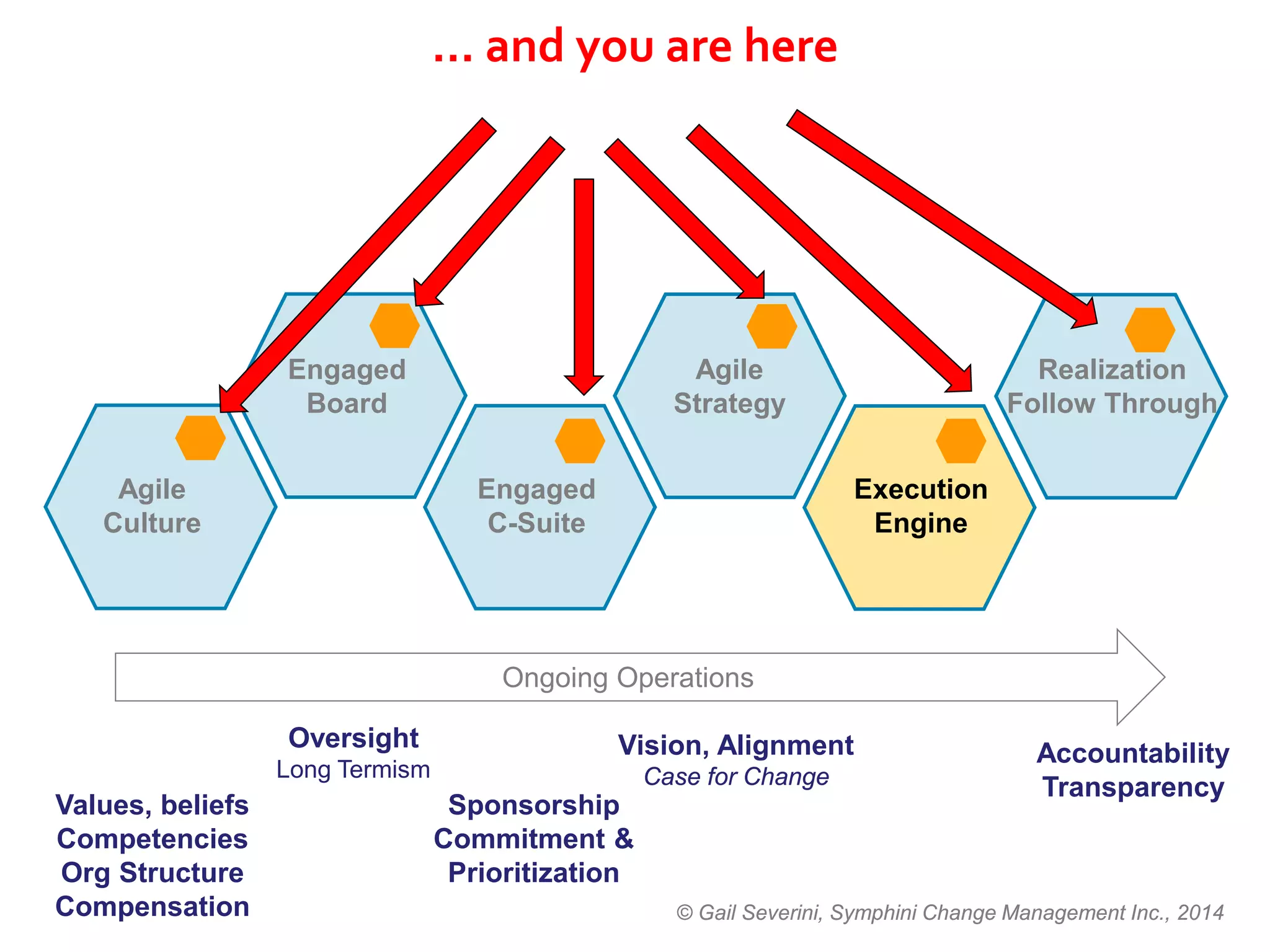
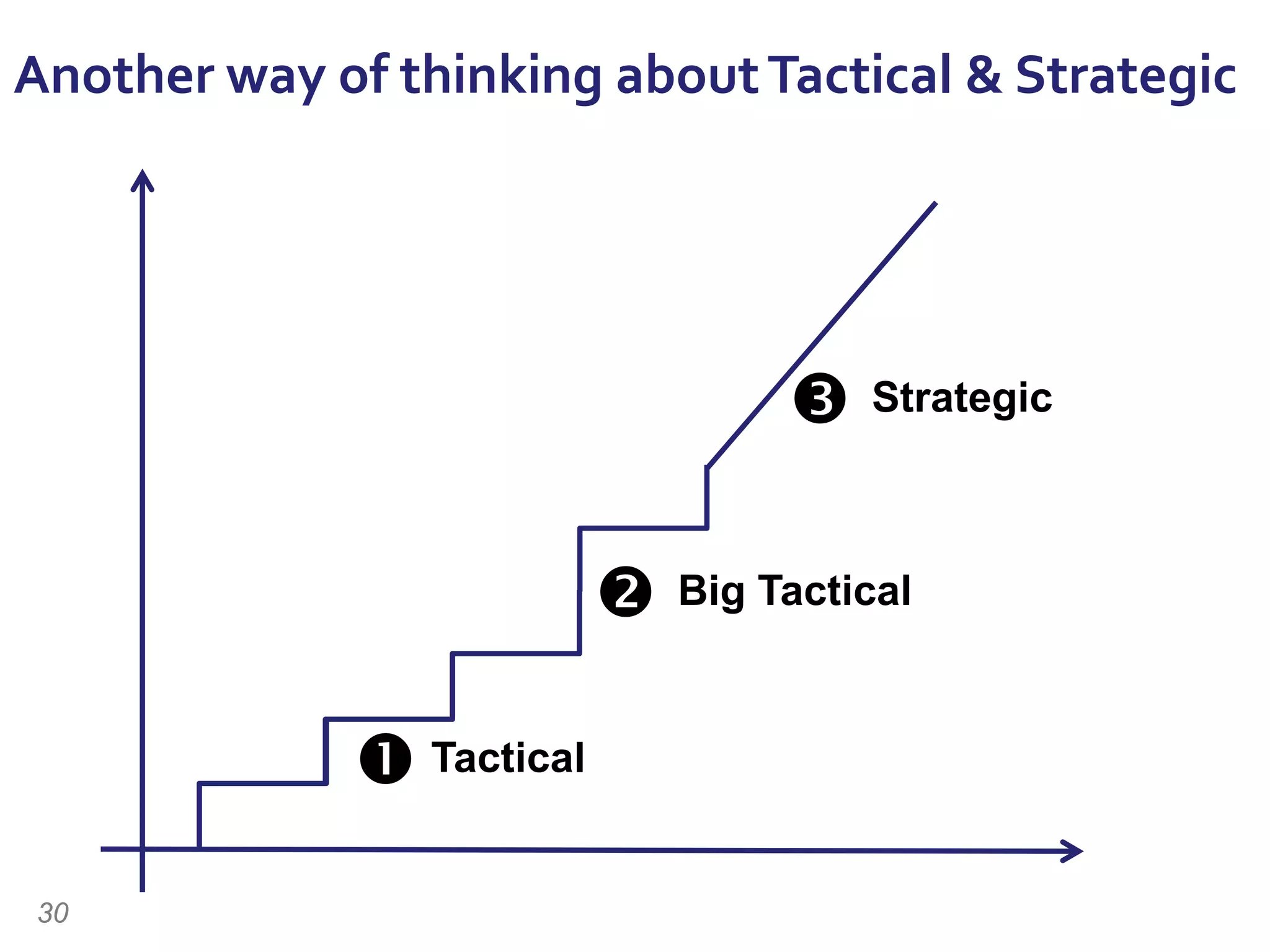
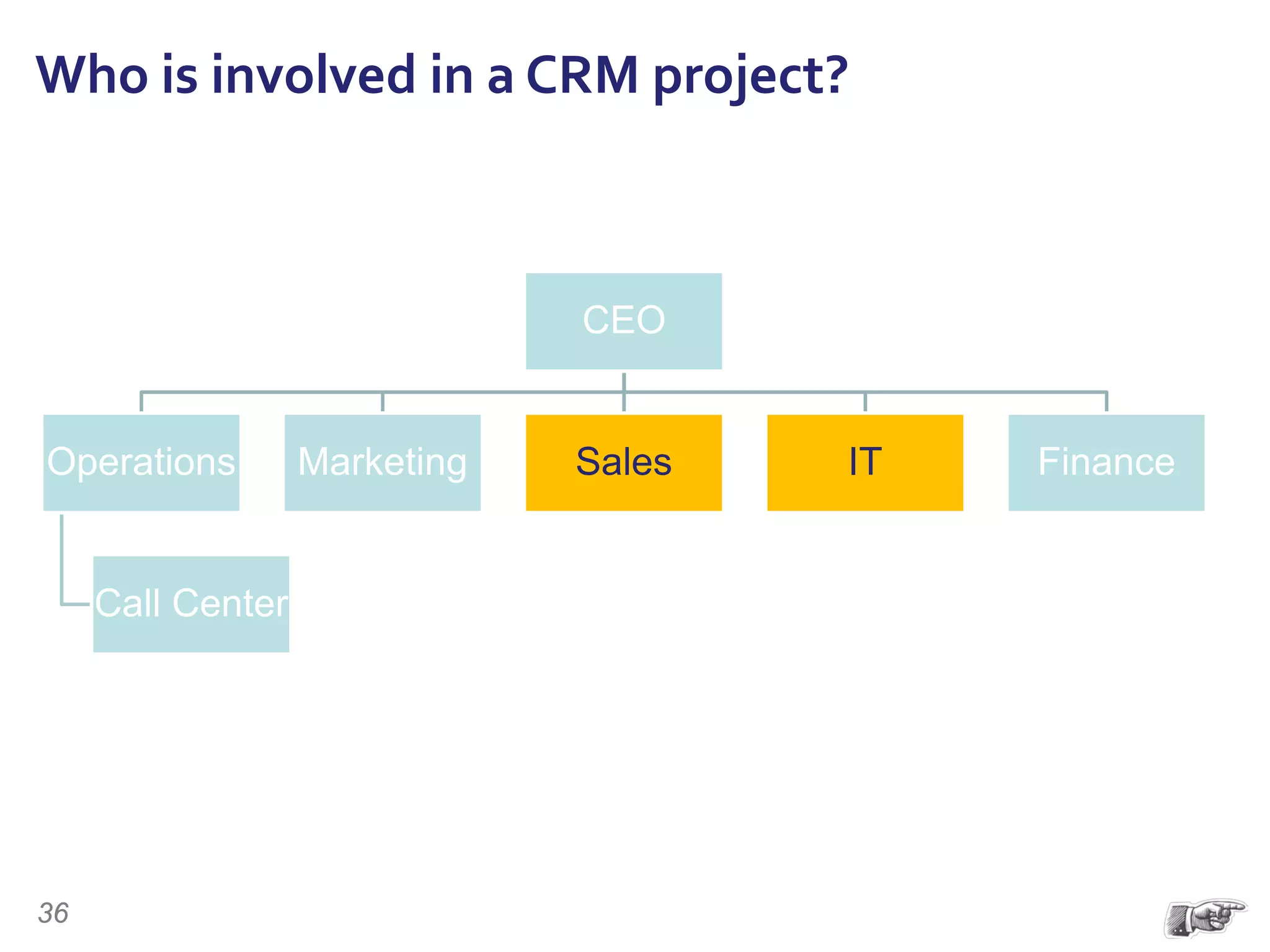
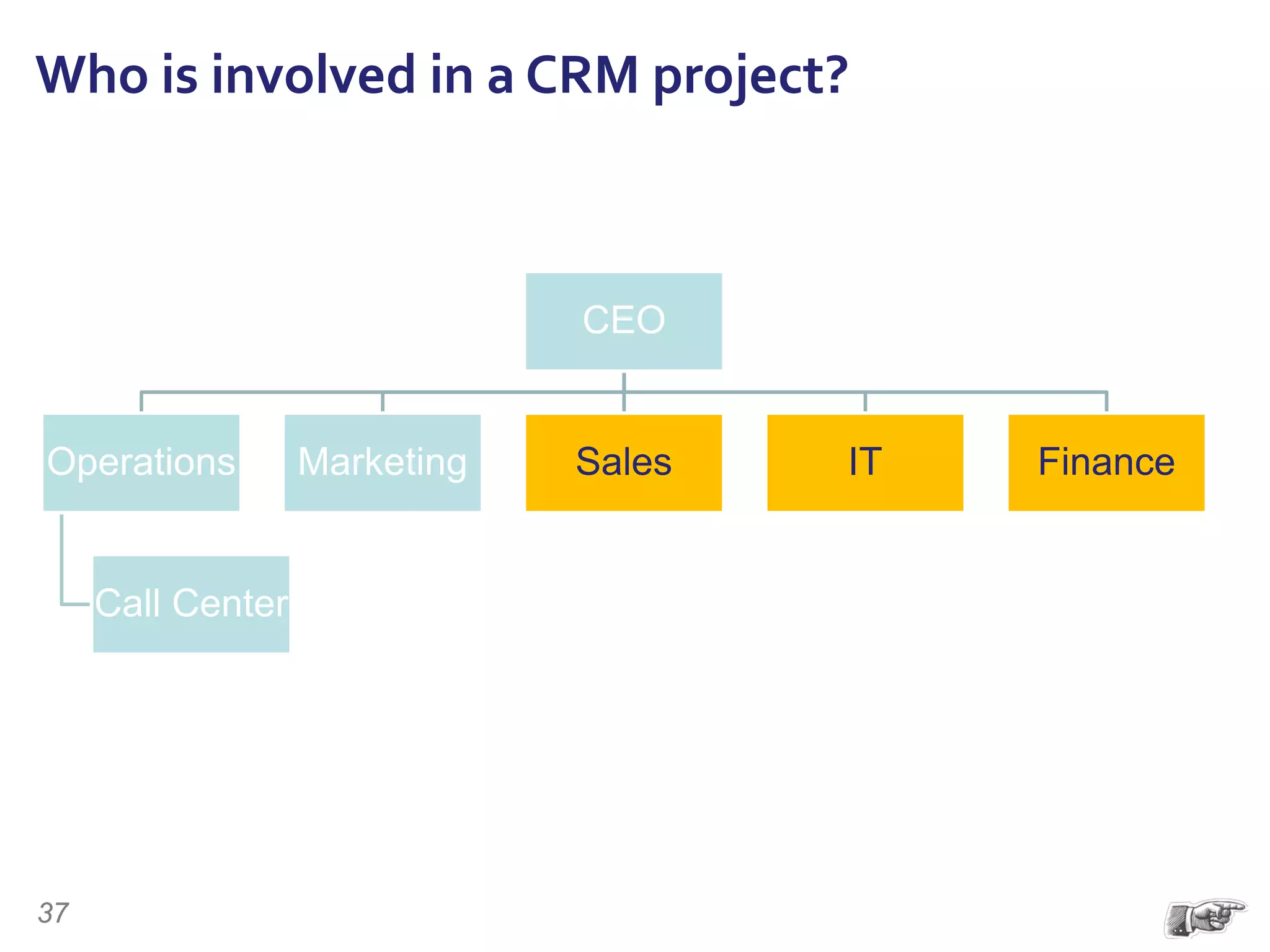
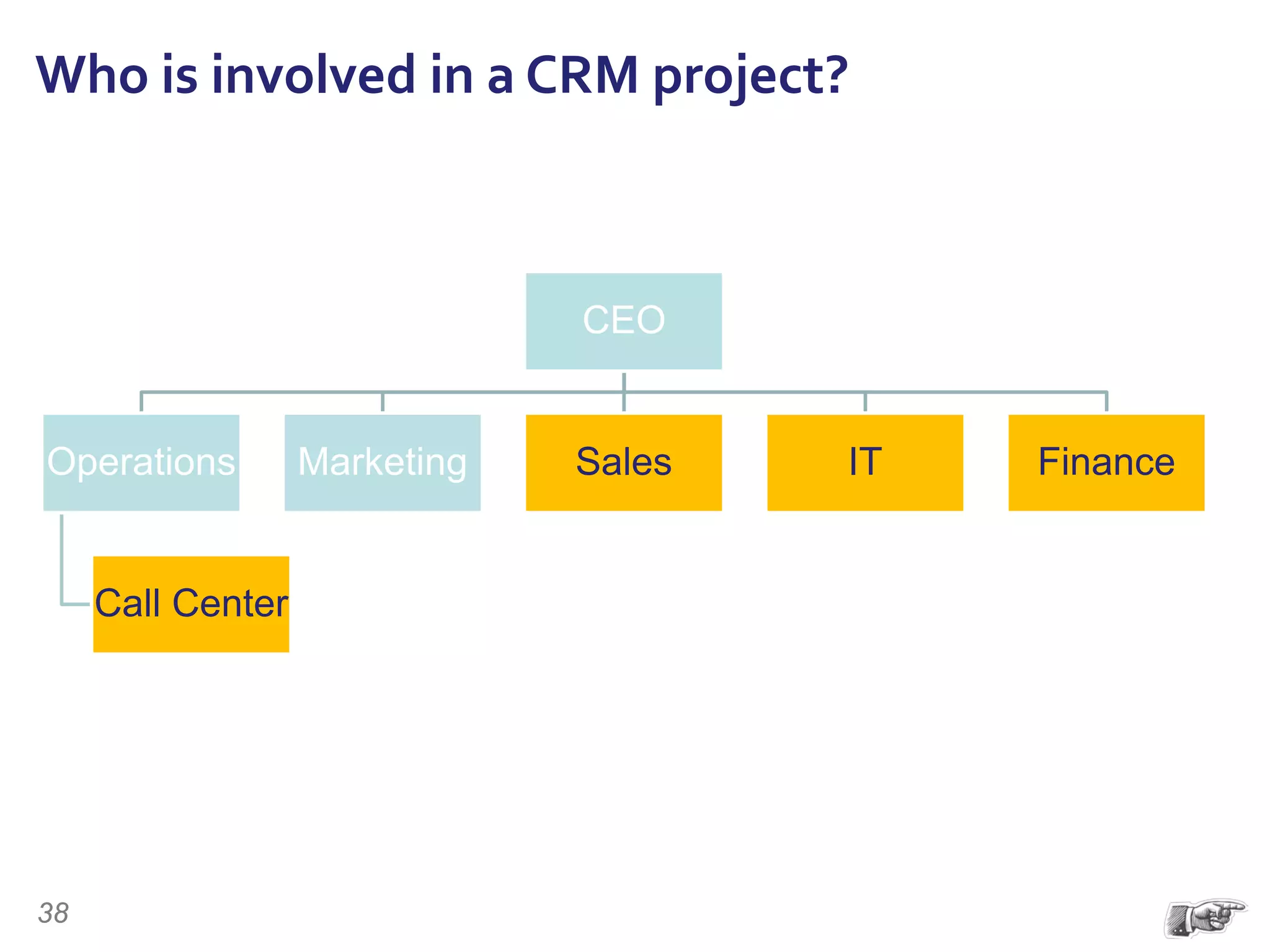
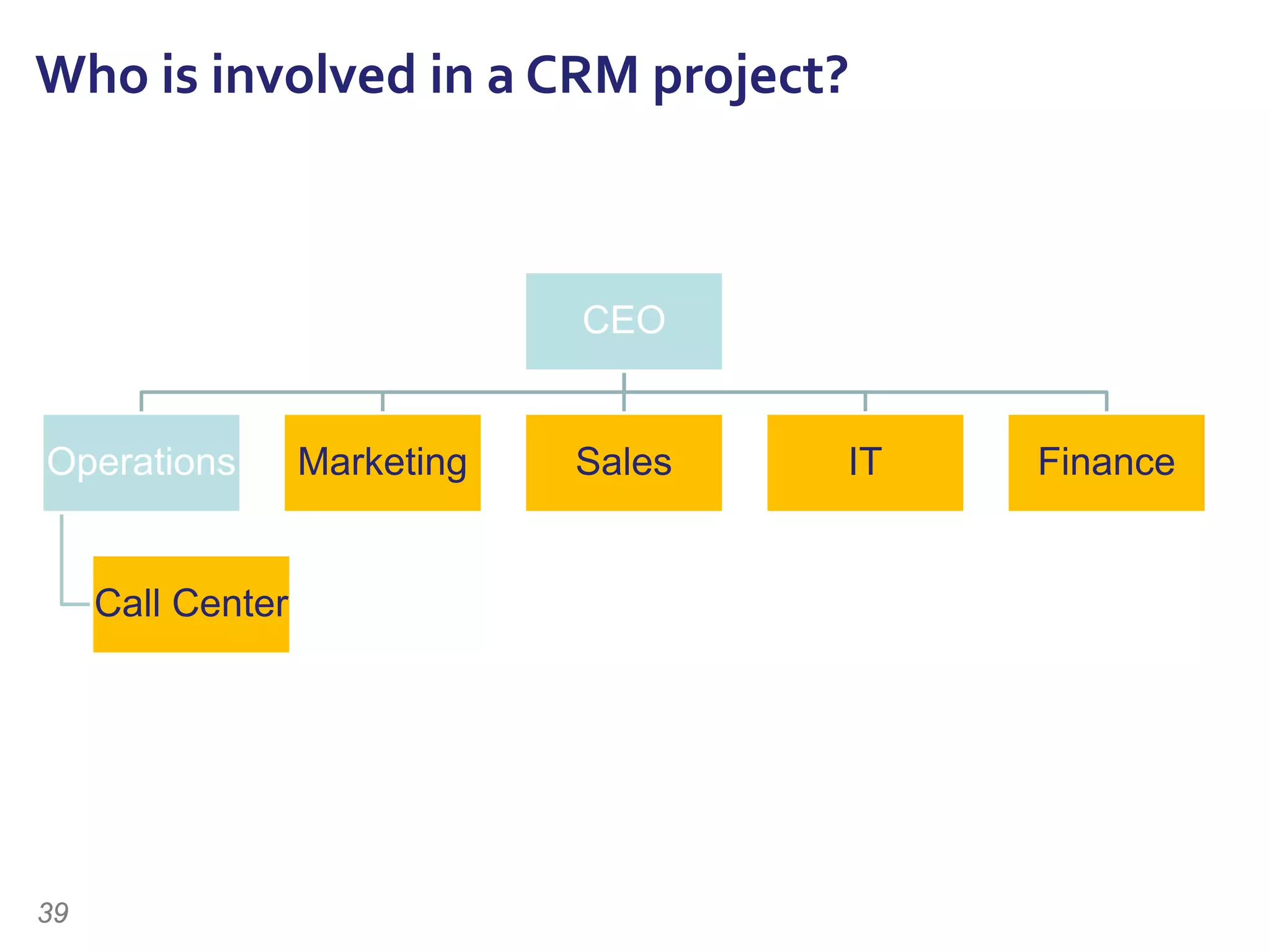
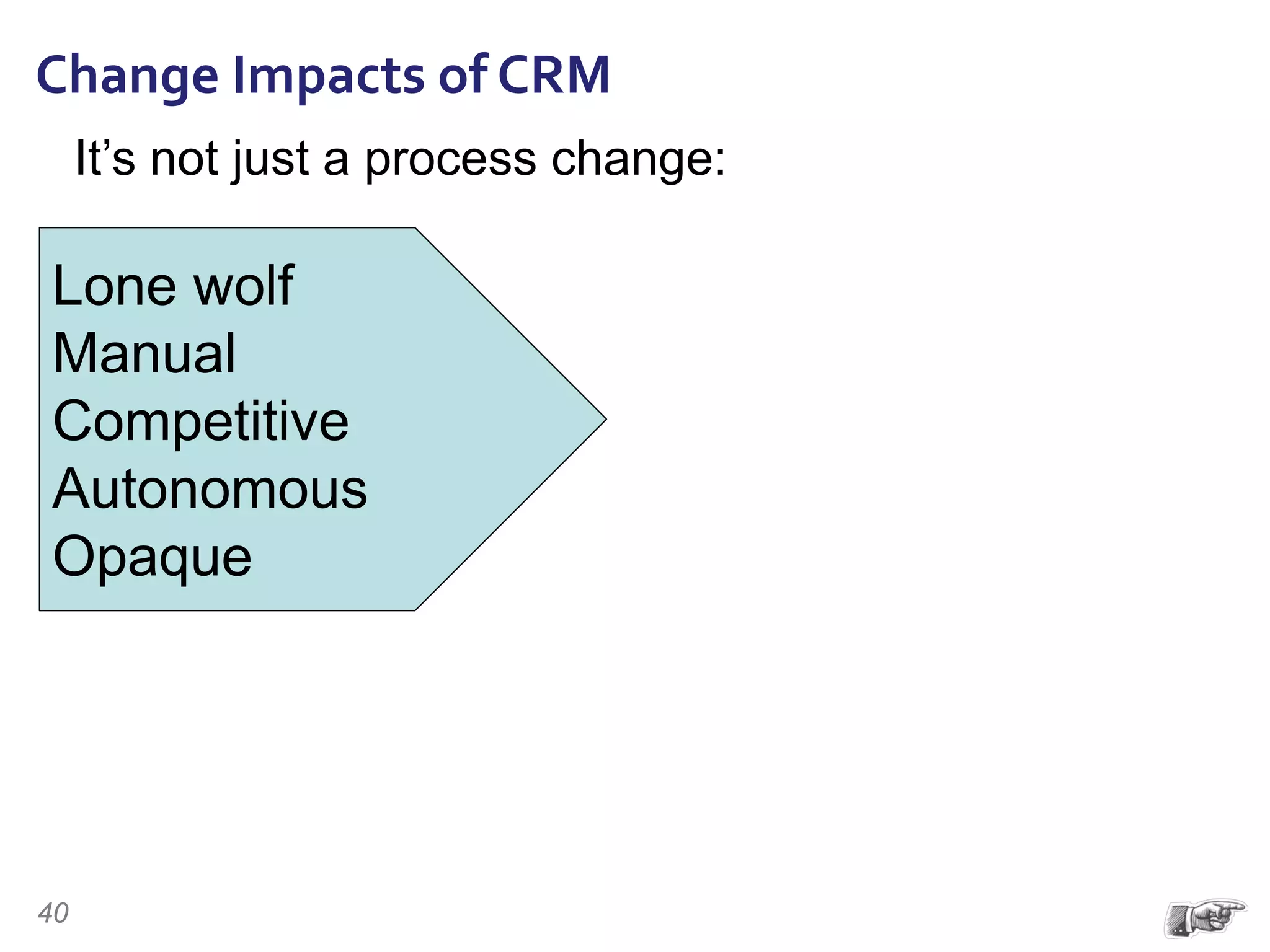
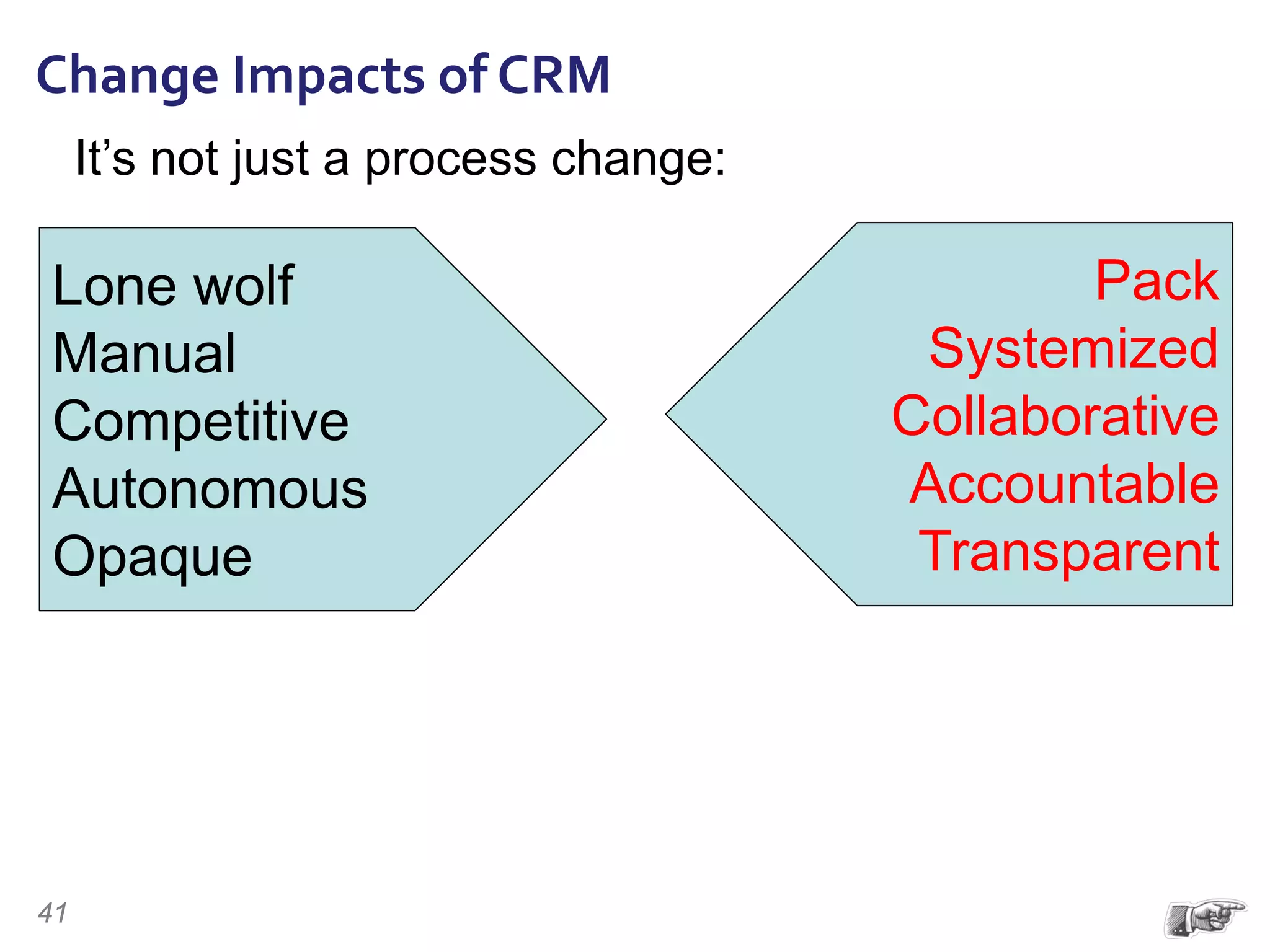
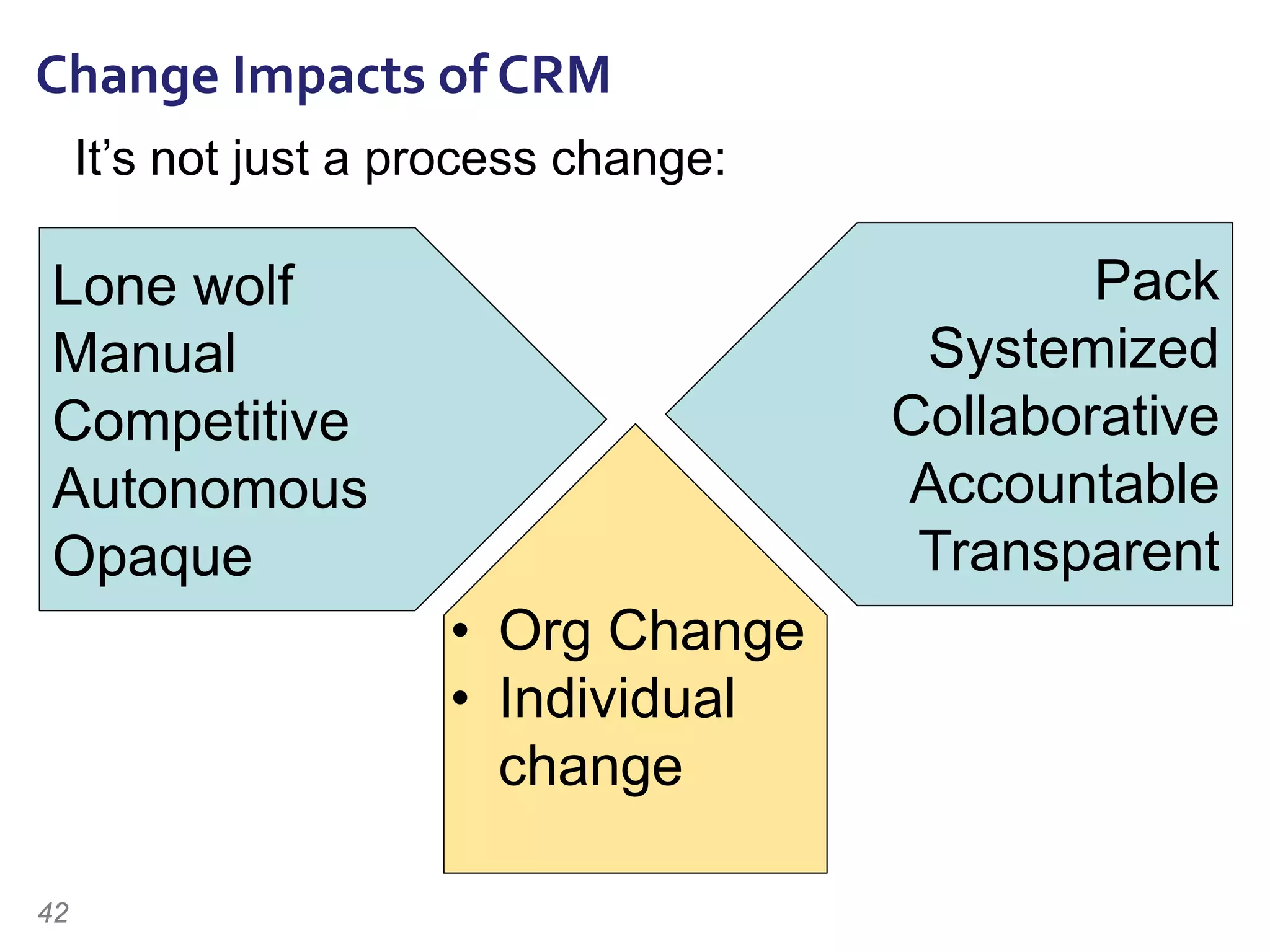
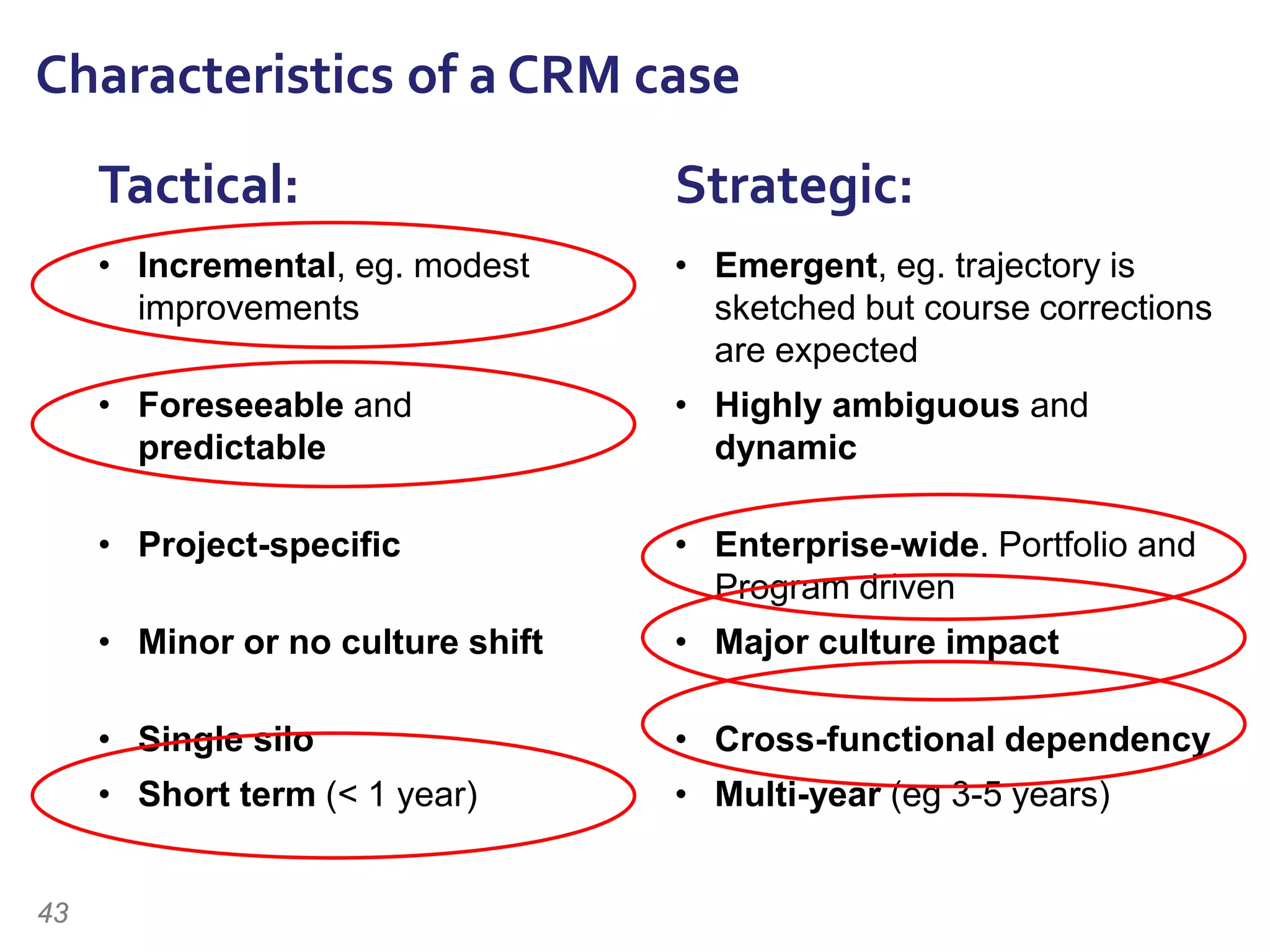
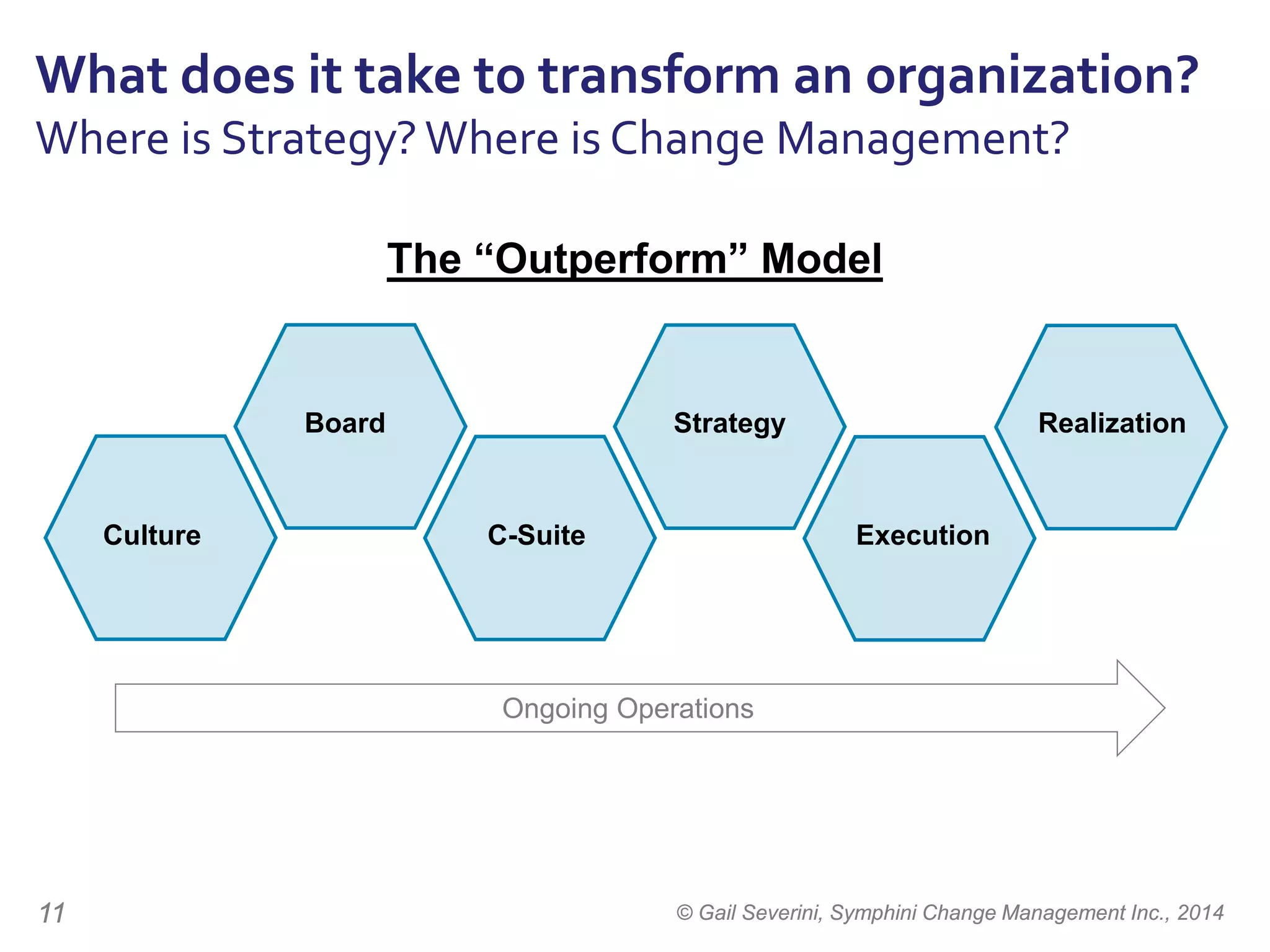
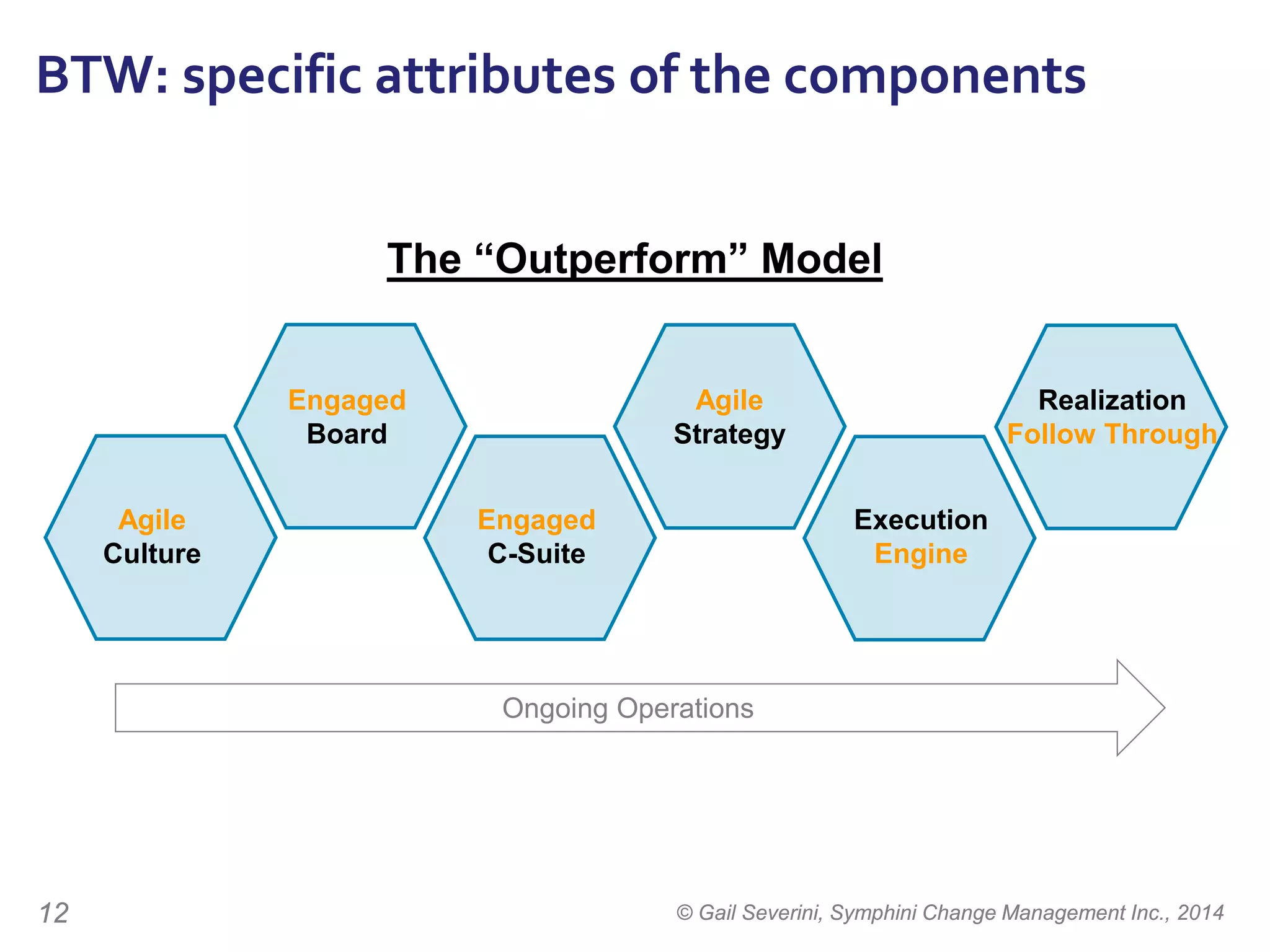
The document discusses the importance of change management in organizational transformation, outlining the strategic versus tactical characteristics of change management. It presents the 'outperform model' which emphasizes executing a change management plan and the integration of various disciplines like project management and stakeholder engagement. The text also highlights that successful change initiatives often encompass long-term organizational culture impacts and require effective leadership across multiple functions.




![OUTPERFORM
Working on any of these components
will improve results ...
The secret is … [and]
and, sub-optimization of any one of them
will hinder your ability
to outperform.
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ischangemanagementtacticalorstrategicv6-140607061638-phpapp02/75/Is-change-management-tactical-or-strategic-v6-13-2048.jpg)