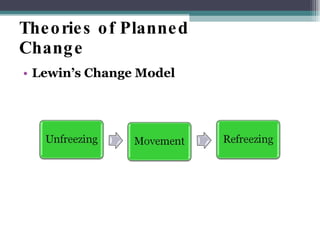
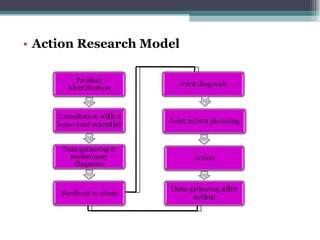
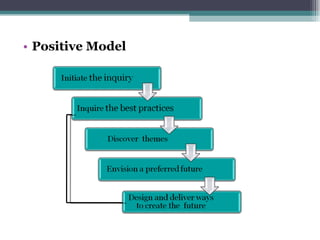
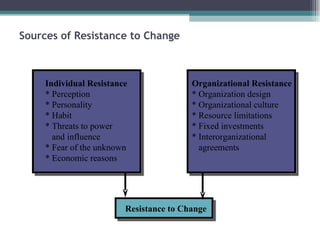
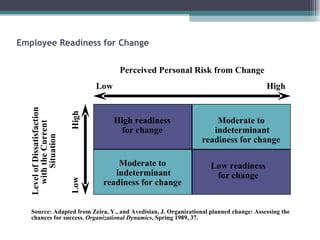
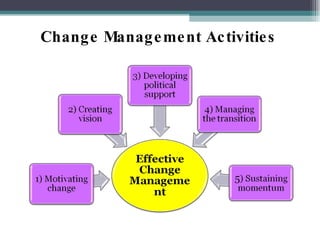
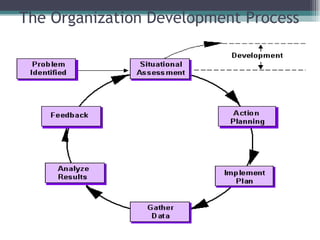
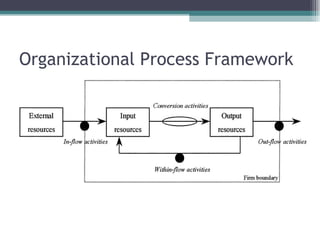
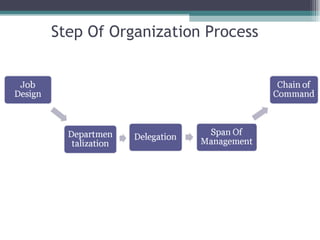
This document discusses organizational change and development. It defines change as the continuous adoption of corporate strategies and structures to changing external conditions. It also describes several theories of planned organizational change, such as Lewin's three-stage change model of unfreezing, movement, and refreezing. Resistance to change is discussed, including sources of resistance at the individual and organizational level. Strategies for managing change and minimizing resistance are also outlined.