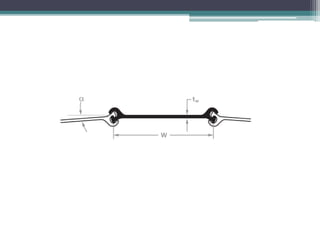
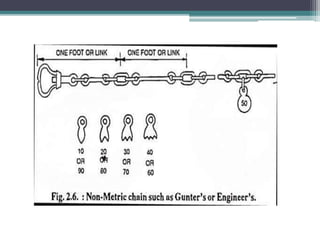
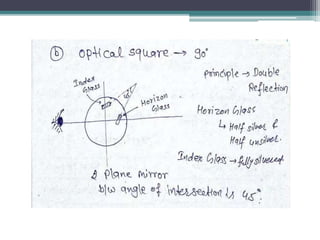
Chain surveying is a method of surveying that measures distances directly in the field without taking angular measurements, utilizing instruments like chains and tapes for various tasks such as determining area and boundaries. The document outlines the types and purposes of chains, including metric and non-metric chains, and details related surveying tools such as ranging rods, cross staffs, and plumb bobs. It emphasizes the practical applications of these tools in engineering and land measurement, showcasing the evolution and specifications of different chain types.