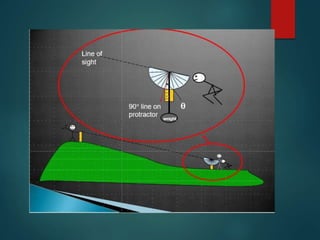
This document provides an overview of surveying instruments. It defines surveying as determining relative positions of objects on Earth's surface by measuring horizontal distances and preparing maps. Common instruments are then described, including chains of various types for measuring distance, tapes, clinometers for measuring angles of inclination, staff rods, ranging rods, compasses, optical squares, Abney levels, auto levels, theodolites, total stations, tripods, scales, and plane tables. Additional instruments mentioned include passometers, pedometers, odometers, perambulators, line rangers, cross staffs, alidades, sextants, French cross staffs, geodimeters, fathometers, ghat tracers, substense bars,