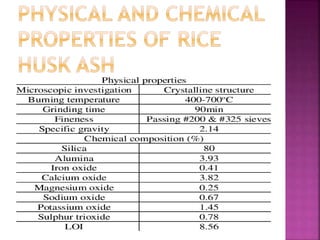
Rice husk is a significant agricultural residue that can be utilized as a supplementary cementing material to mitigate environmental pollution caused by its burning. The chemical composition and pozzolanic activity of rice husk ash (RHA) depend on various factors like incineration temperature and duration, with optimal conditions identified for achieving high reactivity. Despite its advantages in enhancing concrete properties, RHA has not been widely adopted in the construction industry, partly due to insufficient knowledge of its effects on concrete characteristics.