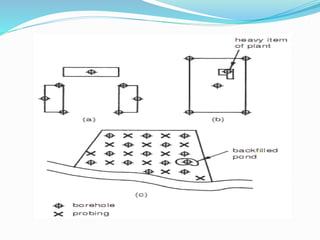
Site investigations are conducted to obtain subsurface information needed for designing structures and planning construction techniques. Soil exploration involves determining the soil and rock profile, geological features, groundwater levels, physical properties, and other relevant data. The depth and spacing of explorations depends on factors like the type and size of structure, load intensities, soil variability, and depth of influence. Careful planning is required to obtain necessary information at minimum cost. Execution involves drilling boreholes to depths of at least 1.5 times the footing width and spacing of 10-30 meters depending on soil conditions. Exploration reports document the findings following a standard format.